Muscle Spasm: Physiotherapy Treatment
Table of Contents
What is a Muscle Spasm?
Muscle Spasm of skeletal muscles are most common and are often due to overuse and muscle fatigue, dehydration, and electrolyte abnormalities. The spasm occurs abruptly, is painful, and is usually short-lived. It may be relieved by gently stretching the muscle.
Muscle spasms can occur at any time to anyone. Whether you are old, young, sedentary or active, you may develop a muscle spasm. It can happen when you walk, sit, perform any exercise, or even sleep.
Some individuals are prone to muscle spasms and get them regularly with any physical exertion. However, those who are at greater risk for muscle spasms are infants, the elderly (over age 65), people who overexert during exercise, those who are ill, and endurance athletes.
spasms occur when a muscle involuntary and forcibly contracts and cannot relax. These are very common and can affect any muscle. Typically, they involve part or all of a muscle, or several muscles in a group. The most common sites for muscle spasms are the thighs, calves, foot arches, hands, arms, abdomen and sometimes along the ribcage. When occurring in the calves, especially, such cramps are known as “charley horses.”
Muscle spasms range in intensity from mild twitches to severe pain. The spastic muscle may feel harder than normal to the touch, and/or appear visibly distorted. It may show visible signs of twitching. Spasms may typically last from seconds to 15 minutes or longer, and may recur multiple times before going away.
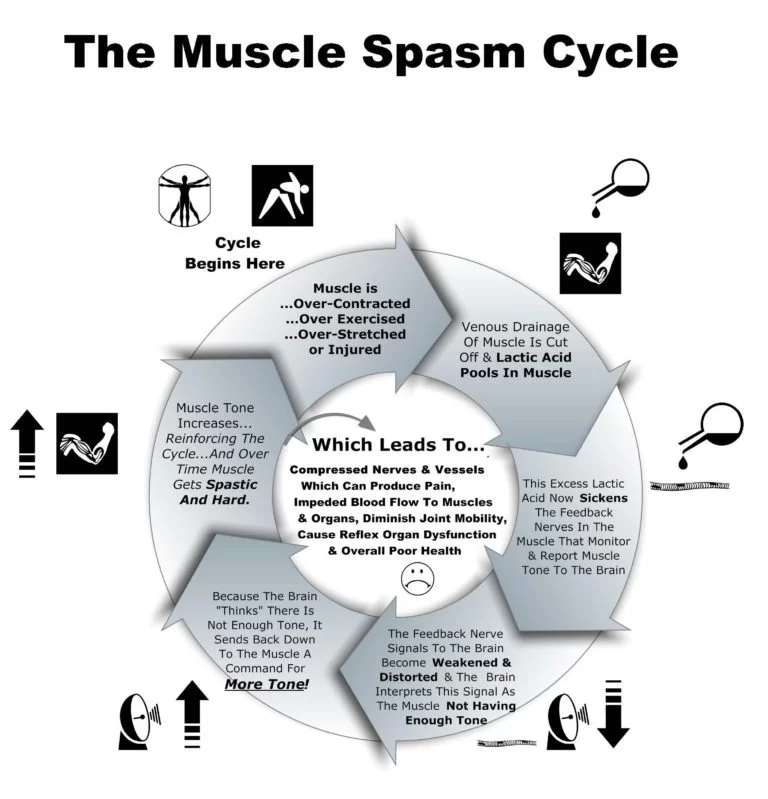
Muscle spasm of facts :
Spasms can affect many different types of muscles in the body, leading to many different symptoms.
Spasms of skeletal muscles are most common and are often due to overuse and muscle fatigue, dehydration, and electrolyte abnormalities. The spasm occurs abruptly, is painful, and is usually short-lived. It may be relieved by gently stretching the muscle.
If muscle spasms are especially painful, if they do not resolve or if they recur, medical care should be accessed to look for other possible underlying causes.
Smooth muscles that are within the walls of hollow organs (like the colon) can go into spasm, causing significant pain. Often this pain is colicky, meaning that it comes and goes. Examples include the pain associated with menstrual cramps, diarrhea, gallbladder pain, and passing a kidney stone.
A special form of muscle spasms are the dystonias where an abnormality perhaps exists with the chemicals that help transmit signals within the brain. Examples include torticollis and blepharospasm. Treatment may include medications to help restore the neurotransmitter levels to normal and Botox injections to paralyze the affected muscle and relieve the spasm.
What causes muscle spasm ?
The muscle itself is rarely the cause of this condition. There is usually an underlying cause for the muscle pain that is causing the muscle to contract at a low level. When this occurs, the muscle never has a chance to relax and becomes very painful.
This can be due to undue stress from prolonged sitting, poor posture, psychological stress, or any number of neck conditions such as instability or low level inflammatory processes. Occasionally patients who overuse their neck muscles while performing normal breathing can have these myofascial pain syndrome.
Deficiency of electrolytes (salts and minerals eg. potassium, magnesium and calcium in your body).
Overexercise – Too much high-intensity exercise may also cause muscle spasm.
What does muscle spasm feel like ?
Mostly muscle spasms are not painful, but some cases it can cause pain. It can feel as though the muscle is jumping or moving on its own, with this feeling typically lasting just a few seconds. Some people might even be able to see the muscle twitching.
Sometimes, it can feel as though the whole muscle has cramped up and cannot move. This effect most commonly happens in the legs, and it can be quite painful. The muscle may feel hard to the touch. While the muscle spasm sensation tends to pass within several minutes or so, the muscle may continue to hurt for some time afterward.
If a muscle spasm is part of a neurological health condition, the person will usually experience other related symptoms. These might include :
- Muscle pain in the leg, back, neck, or head
- weakness in the muscles
- skin numbness
- Involuntary movement of leg, Hands.
- a pins-and-needles sensation
- a tremor
- paralysis
- poor co-ordination
- slow movements
- double vision
- sleep problems
Risk factors :
Factors that might increase your risk of muscle cramps include :
- Age : Older you are, your muscle mass are low , so the remaining muscle can get over-stressed more easily, may increase the risk of muscle spasm.
- Dehydration : Athletes who become fatigued and dehydrated while participating in warm-weather sports frequently develop muscle cramps.
- Pregnancy : Muscle cramps also are common during pregnancy.
- Medical conditions : You might be at higher risk of muscle cramps if you have diabetes, or nerve, liver or thyroid disorders.
Muscle spasm Diagnosis :
Most people have experienced a skeletal muscle spasm due to overexertion, especially in a warm environment, and are able to self-diagnose. However, if the spasms are severe, last a long time, or keep recurring, it is reasonable to see a health-care professional for evaluation.
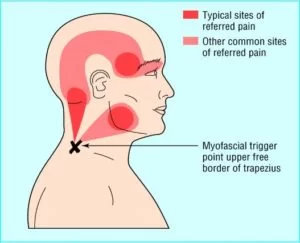
Medical Treatment :
Muscle spasms usually resolve on their own. It might take a few seconds or even several minutes for them to stop, but they do not often require treatment.
Drinking plenty of water can help relax dehydration-related muscle spasm. Rest, Ice pack also helps to relieve your muscle pain.
If you have a painful muscle spasm, they can try a few methods to help reduce the symptoms. The following tips recommend:
- stopping any activity that led to the cramp eg. running
- massaging the cramping muscle gently
- Relax passive movement.
- gradual stretching the cramping muscle
- using a heating pad to relax painful muscle spasm
- applying an ice pack to reduce muscle pain.
Physiotherapy treatment :

- Gently stretch and massage the spasmodic Hold it in a stretched position until the spasms stop, this will relieve muscle pain and give you feel relax.
- Apply cold to sore/tender muscles or heat to tense/tight muscles.
- Manual therapy interventions are found to be very beneficial in treatment of this condition. Techniques of joint mobilization, deep tissue mobilization and muscular retraining are proven to be significantly effective treatments.
- Specific exercises to improve blood flow through the muscles are beneficial. An individualized exercise program is developed for each patient’s specific problem often focusing on the deep neck muscles and the postural muscles of the shoulders and shoulder blades.
- Re-education of breathing patterns is also found to be helpful. Relaxation techniques and assistance in stress management are key components of the treatment when stress is noted to be a significant source of the symptoms.
- Education on proper techniques and postures for work, athletic and daily activity is an essential component of treatment.
If the calf muscle spasm, you can try putting their weight on the affected leg and bending their knee slightly. Doing this will stretch the muscle.
If the quadriceps muscle spasm that are located at the front of the thigh, you can try holding the foot of the affected leg behind them and gently pulling it backward to buttocks, keeping the knees together.
In cases where an underlying neurological condition is causing the muscle spasms, doctors may recommend an antispasmodic medicine.

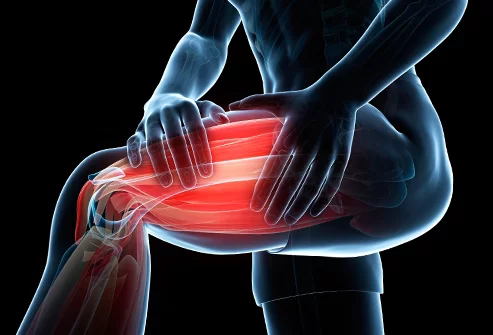


I AM 64 YRS OLD AND I WENT SWIMMING. AND THE WAVES WAS ROUGH BUT I KEPT GOING THE WAVES WERE HITTING ME HARD BUT AT THE TIME I FELT GREAT THAT NEXT MORNING THE PAIN ARRIVED