IONTOPHORESIS USED IN PHYSIOTHERAPY
Table of Contents
DEFINATION :
Iontophoresis is a treatment technique, in which an electrical current is used in physical therapy. It is applied to the skin soaked in tap water allowing ionized or charged particles to pass the normal skin barrier.
The iontophoresis method is used as a non-invasive transdermal drug delivery treatment technique based on the transfer of charged molecules using low-intensity electric current.
this is the term used to describe the technique in which useful ions are driven through the patient’s skin into the tissues. the basic principle is to place the ion under an electrode with the same charge,e.g. a negative ion is applied under the cathode. this electrode would then be known as the ‘active electrode’ a constant current is then applied and the ion is electrically propelled into the patient.
- although constant current is seldom used today the exception would be in the treatment of hyperhidosis which is an extremely common condition and reacts well to this method of treatment
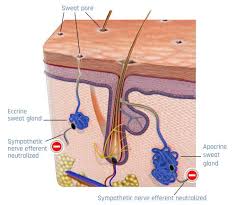
- the use of tap water for this treatment produces no side effect but the ions in it may not inhibit sweating sufficiently and therefore the use of an anticholinergic compound in distilled water is recommended. the introduction of glycopyrronium bromide under the anode electrode has been shown to have long-standing effects.
- the hands and feet may be affected and require treatment but no attempt should be made to treat hands and feet on the same day, and an interval of several days should elapse between treatments.
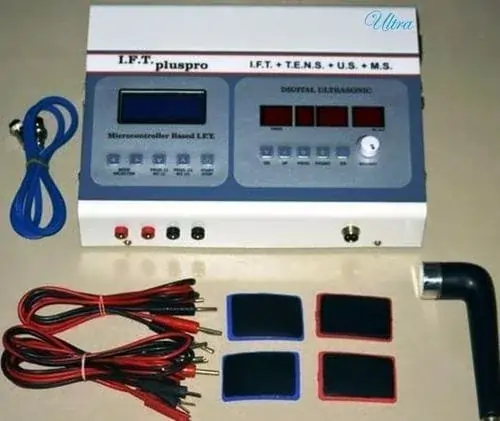
APPARATUS REQUIRED
1) a source of constant current of low voltage and low amperage
2) a shallow plastic tray for the anode
3) a foot or arm bath for the cathode
4) two large electrodes and leads
5) two large lint pads to cover the electrodes
6) solution of anticholinergic compound
7) distilled water
the machine should be tested prior to use. leads are attached to the terminals and held with free ends, not touching in a bowl of tap water. the control should be turned up and the needle of the miliampere meter watched to ensure that the regulation of the current is even.
METHOD OF TREATMENT
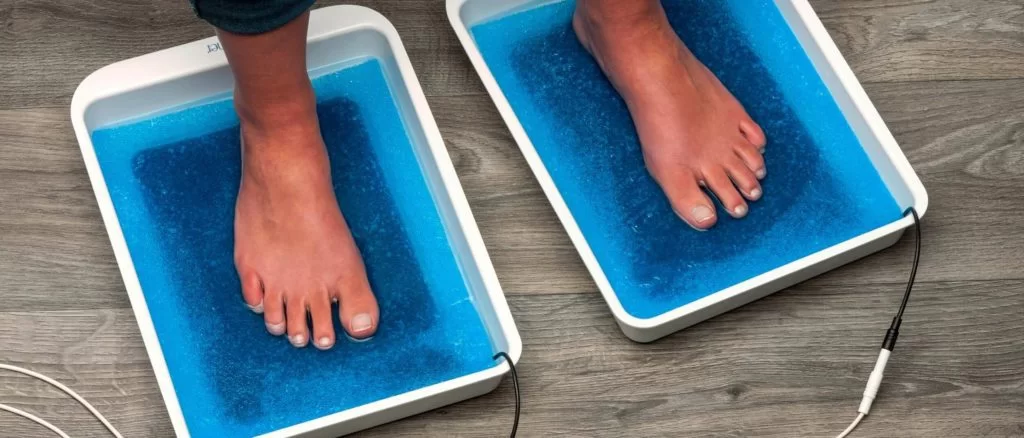
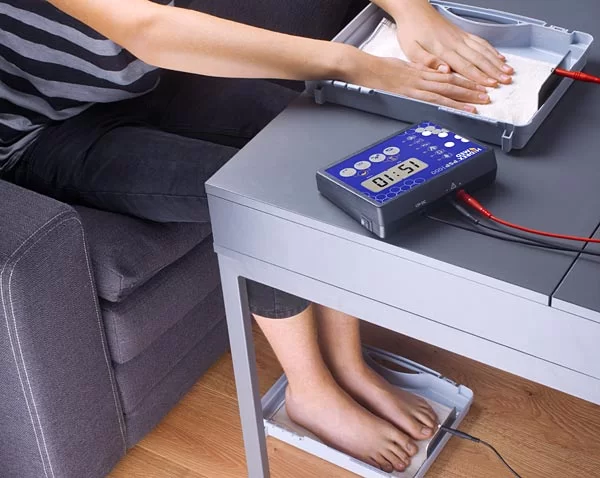
1) HANDS
the shallow plastic tray is placed on an arm bath table and the patient sits alonside. the active electrodes is placed in the plastic tray and covered with one of the lint pads. the pads should be at least eight layers thick so that they make good contact with the tissues and with the electrode and are effective to absorb any chemicals which might form during the treatment.
the tray also contains enough of a 0.05 percent solution of the anticholinergic compound, glycopyrronium bromide in distilled water to cover the palm well. the hand is placed in the tray and the electrode connected to the positive terminal of the treatment unit.
one of the patient’s feet is placed in a few cms of warm water in the foot bath on a lint pad covering the electrode which is connected to the negative terminal. the current is now switched on and slowly increased to the desired amount for the desired time.
the glycopyrronium becomes the positive ion when the salt is dissolvedter so, the patient is in distilled water so, the patient having completed the circuit, the positive ions will be repelled by the anode and attracted to the cathode.

2) FEET
for treatment of the feet, the arrangement should be reversed by placing the shallow tray with the anode on the floor and the arm bath with the cathode, for the arm to complete the circuit.
DOSAGE
the first treatment is based on the size of the patient and modified by skin tolerance. for an average adult 12 milliamps for 12 minutes, and half this amount for a child.
the need to repeat the treatment varies with each patient: some have relief for months after one treatment and few require a repeat in less than four to six weeks
PRECAUTION
1 skin abrasions
2 remove the patient’s rings.
3 warn the patient to remain still during treatment.
4 ensure the correct thickness of the pads
SIDE-EFFECT
anticholinergic compounds have an atropine-like action; patients may therefore experience
1 drying of the mouth and throat.
2 restricted general body sweating. the patient should be advised not to engage, for the rest of the day, in strenuous activities which require sweating for the maintenance of body temperature.
CONTRAINDICATION
- Pregnancy
- Epilepsy
- Seizures
- Cardiac Pacemakers
- Heart diseases
- Metal implant
- Recent Injuries, wounds, scars, or skin grafting.






3 Comments