HAG-LUND ‘S SYNDROME
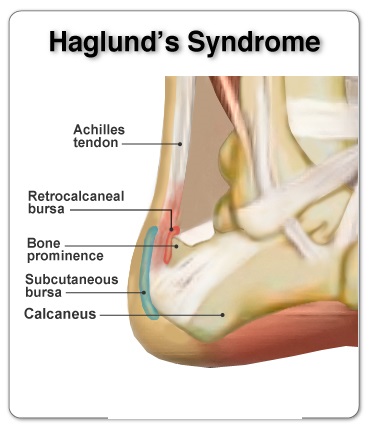
DEFINATION : Haglund’s syndrome is a constellation of soft tissue and bony abnormalities and represents one cause of retro-calcaneal pain consisting of inflammation of the regional soft tissues, e.g., retro-calcaneal bursitis, superficial tendo Achilles bursitis, and thickening and/or inflammation of the Achilles tendon, associate
Haglund’s syndrome is a cause of retrocalcaneal pain. The clinical diagnosis of Haglund’s syndrome is often confusing as the clinical picture may mimic other causes of hindfoot pain such as isolated retrocalcaneal bursitis or hindfoot involvement from more systemic arthropathies such as Reiter’s syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis. With the increasing frequency of employing sonography as a diagnostic tool in the evaluation of foot and ankle pathology, recognition of the sonographic appearance of Haglund’s complex is important. We report a case of Haglund’s syndrome diagnosed and treated with sonography.
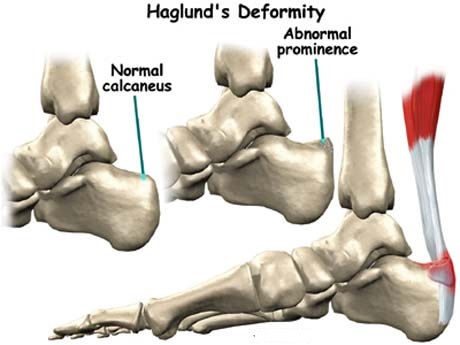
Table of Contents
Causes :
Haglund’s deformity occurs when there’s frequent pressure on the backs of your heels. It may be caused by wearing shoes that are too tight or stiff in the heel. Since it often develops in women who wear pump-style high heels, Haglund’s deformity is sometimes referred to as “pump bump.
The most common causes of Haglund’s Deformity are:
Footwear:- The most common cause of Haglund’s Deformity is footwear. Shoes with rigid backs, like pumps, ice skates, and high heels place excessive pressure on the back of the heel, hence the alternative name for this condition, pump bump. This can result in the formation of heel bone spurs, forming the characteristic lump.
Genetics:- People with high foot arches are more prone to this condition as it causes the calcaneus to tip backwards increasing the pressure around the Achilles region
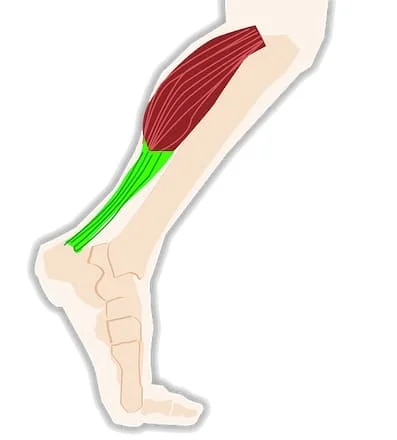
-Haglund’s deformity is a bony enlargement on the back of the heel that most often leads to painful bursitis, which is an inflammation of the burs(a fluid-filled sac between the tendon and bone). In Haglund’s
deformity, the soft tissue near the Achilles tendon becomes irritated when the bony enlargement rubs against shoes.
Haglund’s deformity is often called “pump bump” because the rigid backs of pump-style shoes can create pressure that aggravates the enlargement when walking. In fact, the deformity is most common in young women who wear pump
Symptoms :
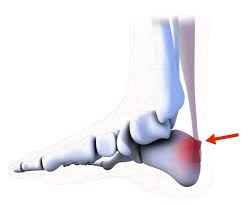
A person with heel pain.
Haglund’s deformity can cause heel pain.
Haglund’s deformity can cause symptoms that range from mild to severe and may include:
pain in the back of the heel when walking
a visible bump on the back of the heel
swelling or redness on the heel
calluses or blisters on the heel where the bump rubs against shoes
A doctor may be able to identify Haglund’s deformity by looking at the heel and discussing the symptoms.
Diagnostic tests :
such as an X-ray or MRI, may be used to evaluate the shape of the heel bone and to determine the severity of the condition. An X-ray or other tests can help a doctor decide which treatment options may be best.
-People with Handguns syndrome will have a bony bump at the back of the heel, and experience severe pain in the back of the foot, where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. The heel area may become red and swollen and may be warm and tender to the touch. People often have difficulty wearing shoes when the condition flares up.
Physiotherapy for Haglund’s deformity :
Handgun’s deformity is a bony bump that appears on the back of the heel bone. This bump forms where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. The condition often needs treatment if it causes pain or walking problems. Treatments for Haglund’s deformity may initially include shoe modifications and physical therapy
- stretching exercises
- Heel lifts for patients with short calf muscles.
- Heel pads to cushion the heel.
- Orthosis devices to help control the motion of the foot
Physiotherapists can play a big role in the conservative management of Hugland’s Deformity, especially with the management of the bursitis associated with this deformity.
Toe stretch
Sit in a chair, and extend your affected leg so that your heel is on the floor.
With your hand, reach down and pull your big toe up and back. Pull toward your ankle and away from the floor.
Hold the position for at least 15 to 30 seconds.
Repeat 2 to 4 times a session, several times a day.
pump and bump-
Handgun’s deformity is a bony enlargement on the back of the heel. The soft tissue near the Achilles tendon becomes irritated when the bony enlargement rubs against shoes. This often leads to painful bursitis, which is an inflammation of the bursa (a fluid-filled sac between the tendon and bone).
What is the bump on the side of my heel-
A pump bump is a bony growth at the back of the heel bone in men or women, towards the outer side of the foot. It can become irritated by footwear and in this case, may appear red or swollen. Sometimes an inflamed bursa (fluid filled sac) can overlie this bony bump and cause it to look larger and become more painful.
treatment for pump bump-
The treatment for Handgun’s deformity usually focuses on relieving pain and taking pressure off of your heel bone. Nonsurgical options include: wearing open-back shoes, such as clogs. taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSA IDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) or aspirin (Buffer in)
Review-
Haglund’s deformity is an abnormality of the posterior part of the calcaneus, where there is a bony enlargement at the attachment of the Achilles tendon. The adjoining soft tissues can get irritated when this bony lump rubs against rigid shoes. It often leads to retrocalcaneal bursitis, calcaneal tendon bursitis, and thickening and inflammation of the calcaneal tendon. This combination of pathology is known as Handguns syndrome. Inflammation of the different parts of soft tissue in the area can lead to an isolated condition; however, the treatment options are different in these conditions, and so they should be differentiated.—-Exercises for Prevention–
You can also use Achilles tendon exercises to help stop Haglund’s deformity from forming in the first place. Additional steps that will help you prevent the onset of Haglund’s include avoiding running uphill or on hard surfaces, wearing shoes that have arch supports or other supporting devices, wearing shoes that fit you properly and avoiding wearing pumps, high heels or other footwear with rigid backs. If you recover from the symptoms of Haglund’s, Achilles tendon exercises and these additional steps can also help you prevent symptom recurrence.
Professional Treatment for Haglund’s Deformity
The painful symptoms may bring you in to our office for treatment, but there are prevention methods that can help you avoid the condition. These start with your choices in footwear. Always limit the amount of time you spend wearing high-heeled shoes, like pumps and stilettos. You do not necessarily have to avoid them completely, but try to save your stylish footwear for special events.
In addition to limiting how often you wear high heels, another important preventative measure is to use a regular stretching regimen.
A definite risk with this condition includes skin being rubbed off when the pump bump gets too big and you continue wearing high-heeled shoes with stiff backs. Something you may wish to consider—particularly if you aren’t keen on the idea of ditching high heels altogether—is to choose footwear like pumps without heels.
WARNING!! This is a NO INJECTION ZONE. A steroid added to this area will weaken the tendon and increase the risk of tearing.
How do you treat Haglund’s deformity?
Last reviewed Wed 11 July 2018By Jennifer Berry Reviewed by William Morrison, MD
Causes Symptoms Treatment Prevention Takeaway
Haglund’s deformity is a bony bump that appears on the back of the heel bone. This bump forms where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. The condition often needs treatment if it causes pain or walking problems.
Treatments for Haglund’s deformity may initially include shoe modifications and physical therapy. If these do not relieve pain, a doctor may recommend surgery to remove the bony ridge or repair the Achilles tendon.
People also refer to the condition as Haglund’s syndrome or “pump bump.” The term “pump bump” followed doctors observing that women who wore high-heeled pump shoes had the condition.
Experts now know that Haglund’s deformity can happen to anyone, and pumps and other shoes are not necessarily exclusively to blame.
A person’s natural foot structure may sometimes make them more prone to Haglund’s deformity.
Doctors have linked some features to Haglund’s deformity, including:
A prominent heel bone that slopes outward, making the heel more likely to rub on the backs of shoes.
Feet that roll outward when walking, are known as supination.
Tight Achilles tendons, which may put pressure on the heel bone.
High arches, which can force the heel slightly backward during walking and rub the Achilles tendon.
Wearing certain types of shoes may cause Haglund’s deformity, or some shoes may aggravate the condition and bring on symptoms such as pain.
Shoes or boots with rigid backs can cause friction that aggravates a foot structure that is prone to Haglund’s deformity.
People with the foot types listed above may wish to avoid shoes with rigid backs and ensure their footwear fits properly.
The shoes most often linked to Haglund’s deformity symptoms include:
ice skates and roller skates
dress shoes, including men’s dress shoes, women’s dress shoes, and high-heeled pumps
steel-toed work boots
stiff winter boots or rain boots
What is abnormal gait?
Haglund’s deformity may cause walking difficulties or an abnormal gait.Mostly Lumping Gait Seen.
Haglund’s deformity treatments
Doctors will often try non-surgical treatments for Haglund’s deformity first.
Although none of these treatments can alter the bone or the foot structure, they may provide pain relief for some people and may improve quality of life.
Physiotherapy treatment
Changing the type of shoes worn, especially avoiding rigid-backed shoes and pumps.
Placing heel lifts in shoes to help bring the heel up and avoid friction.
Using heel pads inside the backs of shoes to help reduce irritation and friction on the heel.
Inserting footwear arch supports for people with high arches.
Taking anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, to ease pain from an inflamed bursa or Achilles tendon.
Using ice on the heel to help relieve inflammation and pain.
Doing stretching exercises to alleviate a tight Achilles tendon.
Avoiding exercises that aggravate the condition, especially running and running uphill.
Using a soft cast or walking boot to help keep the heel bone from rubbing on the bursa or Achilles tendon.
Trying physical therapy to bring relief.
Surgery may be needed when non-surgical treatments do not relieve symptoms. Surgery aims to remove the part of the heel bone that is sticking out. Surgery may also be used to repair the Achilles tendon if it is damaged.
Podiatrists and foot and ankle surgeons can perform different types of surgery to correct Haglund’s deformity. The type of procedure depends on how severe the Haglund’s deformity is, the person’s health history, and their lifestyle.
Endoscopic surgery is less invasive than traditional surgery. Because it uses smaller incisions than traditional surgery, the recovery is often shorter. According to 2018 research, it results in good to excellent outcomes in the short and medium-term.
Conventional surgery, however, also appears to have successful outcomes. One study found that the majority of those who had traditional surgery had relief of their pain at their one-year follow-up. But, the authors noted that doctors should tell people that the recovery from surgery can be several months.–



2 Comments