Extensor carpi radialis longus tear
Table of Contents
What is a Extensor carpi radialis longus tear?
An Extensor carpi radialis longus tear refers to a partial or complete rupture of the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon, which is one of the forearm muscles responsible for wrist extension and stabilization. This type of injury usually occurs due to sudden trauma or repetitive overuse, particularly during activities that involve repetitive wrist extension or forceful gripping motions.
Anatomy of Extensor carpi radialis longus
The extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the muscles located in the forearm that is responsible for various movements of the wrist joint. Here are the key aspects of its anatomy:
Origin:
The extensor carpi radialis longus originates from the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus, which is a bony ridge located on the outer side of the lower end of the humerus bone (upper arm bone).
Course:
From its origin, the muscle goes down the forearm in a diagonal direction, passing through a groove between the brachioradialis muscle and the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.
Insertion:
- The extensor carpi radialis longus inserts onto the base of the second metacarpal bone, which is the bone located at the base of the index finger.
- It attaches to the dorsal (back) surface of the metacarpal bone.
Function:
- The primary function of the extensor carpi radialis longus is to extend and abduct the wrist joint.
- It is involved in movements such as wrist extension, which is the backward movement of the hand at the wrist joint, and radial deviation or abduction, which is the motion of the hand towards the radial side of the forearm.
Innervation:
- Innervation- By the radial nerve.
- The radial nerve provides the necessary nerve signals for the muscle to contract and control its actions.
- Understanding the anatomy of the extensor carpi radialis longus is important for diagnosing and treating injuries or conditions that may affect its function, such as tears, strains, or overuse injuries.
Causes of extensor carpi radialis longus tear
- The etiology, or causes, of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear, can vary, but they often involve sudden trauma or repetitive overuse. Here are some common factors that can contribute to the development of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear:
Trauma:
- A sudden and forceful impact or injury to the forearm or wrist can lead to a tear in the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon.
- This can occur during activities such as a fall onto an outstretched hand, direct impact to the forearm, or a sports-related injury.
Repetitive Overuse:
- Overuse of the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle can strain and weaken the tendon over time, increasing the risk of a tear.
- This is commonly seen in activities that involve repetitive wrist extensions and gripping motions, such as playing racquet sports, weightlifting, or occupations that require repetitive use of the wrist.
Age and Degeneration:
- Tendons naturally weaken and become less resilient with age, making them more susceptible to tears.
- Degenerative changes in the tendon, such as tendinopathy or tendinitis, can also weaken the tissue and make it more prone to tearing.
Improper Technique or Equipment:
- Using incorrect techniques during sports or exercise, or using equipment that is not properly fitted or suited for the activity, can increase the strain on the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon and potentially lead to a tear.
Previous Injuries or Conditions:
A history of previous injuries or conditions in the forearm or wrist, such as tendonitis, can weaken the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon and make it more prone to tearing.
- It’s important to note that each individual case may have unique contributing factors, and a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the specific cause of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear.
- They will consider factors such as the patient’s medical history, physical examination findings, and any relevant imaging studies to make an accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Extensor carpi radialis longus tear
Symptoms of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear may include:
Pain:
You may experience localized pain at the site of the tear, which can worsen with wrist movement or gripping.
Weakness:
The tear can weaken the affected muscle, leading to a loss of strength and difficulty in performing activities that involve wrist extension.
Swelling and bruising:
In some cases, there may be swelling and bruising around the area of the tear.
Limited range of motion:
The tear can restrict the normal range of motion of the wrist, making it difficult to fully extend or stabilize the joint.
- If you suspect that you have extensor carpi radialis longus tear, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
- They will likely perform a physical examination, evaluate your medical history, and may order imaging tests such as an MRI or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of extensor carpi radialis longus tear
The diagnosis of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and imaging studies. Here are the common methods used for diagnosing an extensor carpi radialis longus tear:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Your healthcare provider will begin by discussing your symptoms, including any pain, weakness, or limitations in wrist movement.
- They will also inquire about any previous injuries or activities that may have contributed to the tear.
- During the physical examination, they will assess the affected wrist for tenderness, swelling, bruising, and any visible deformities.
- They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the strength and range of motion of the wrist and assess the integrity of the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon.
Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound imaging can help visualize the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon and assess its integrity. It can also provide information about the location and extent of the tear.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
MRI scans can provide detailed images of the soft tissues, including tendons. It can help identify and evaluate tears or other abnormalities in the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon.
These imaging studies can be particularly useful in confirming the diagnosis, assessing the severity of the tear, and ruling out other potential causes of wrist pain or dysfunction.
- It’s essential to consult with a physician for an exact diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
- They will consider the findings from the medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies to determine the presence and extent of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear.
Treatment of extensor carpi radialis longus tear
The medical treatment of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear depends on the severity of the injury. Here are some common treatment approaches:
Conservative Treatment:
Rest and modification
Resting the affected wrist and immobilizing it with a splint or brace can help protect the torn tendon and promote healing.
Ice and Elevation:
Applying ice packs to the affected area and elevating the hand above the heart level can help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Pain Management:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be given to decrease pain and reduce inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections:
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and provide short-term pain relief. However, their use should be cautious as they can weaken tendons and may not be suitable for all individuals.
Surgical Intervention:
- Severe tears or tears that do not respond to conservative treatment may require surgical intervention.
- The surgical procedure typically involves repairing or reattaching the torn extensor carpi radialis longus tendon using sutures.
- Physical therapy is often prescribed following surgery to regain strength and functionality.
- It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or a sports medicine physician, who can evaluate the specific characteristics of the tear and provide personalized treatment recommendations based on your individual circumstances.
- They will consider factors such as the extent of the tear, your overall health, and your goals for recovery to determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Physiotherapy treatment of extensor carpi radialis muscle tear
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of an extensor carpi radialis longus tear. A physiotherapist can design a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and stage of recovery. Here are some common physiotherapy treatments for an extensor carpi radialis longus tear:
Range of Motion Exercises:
Initially, the focus will be on gentle range of motion exercises to maintain mobility in the wrist joint and prevent stiffness. This may involve simple movements such as wrist flexion, extension, and rotation.
Reverse wrist curls

- To start, sit on a flat bench and lean forward.
- Take the weight with your hands or you can do it by only your body weight (mainly palms down) and place your hands either on a bench or on your knees.
- Use your wrists only during the wrist movement, rotate the weight upwards, and exhale during the movement.
- If you want, repeat this movement 10 times.
- Lower the weight slowly until you feel comfortable and breathe during the movement.
Strengthening Exercises:
As the healing progresses, specific exercises will be prescribed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon. This may include resistance exercises using dumbbells, resistance bands, or hand weights to target wrist extensors and other forearm muscles.
Extensor Carpi radialis longus muscle strengthening exercise
Strengthening the wrist extensions
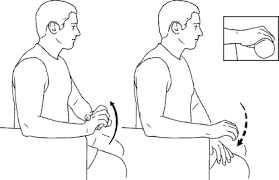
- To strengthen the wrist muscles, the wrist extension exercise can be done with an exercise band.
- It is useful for the rehabilitation of wrist, elbow, and forearm injuries.
- Place your hands on a bench or table, palm down, and hold the exercise band.
- Gently pull your wrist back to create tension on the strap.
- Repeat 3 times and return to the starting position.
- This can also be done with a dumbbell instead of a resistance band.
Stretching Exercises:
Stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, restore the length of the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon, and prevent scar tissue formation. The physiotherapist will guide you through stretches that target the wrist extensors and other relevant muscles.
Wrist extensor stretching
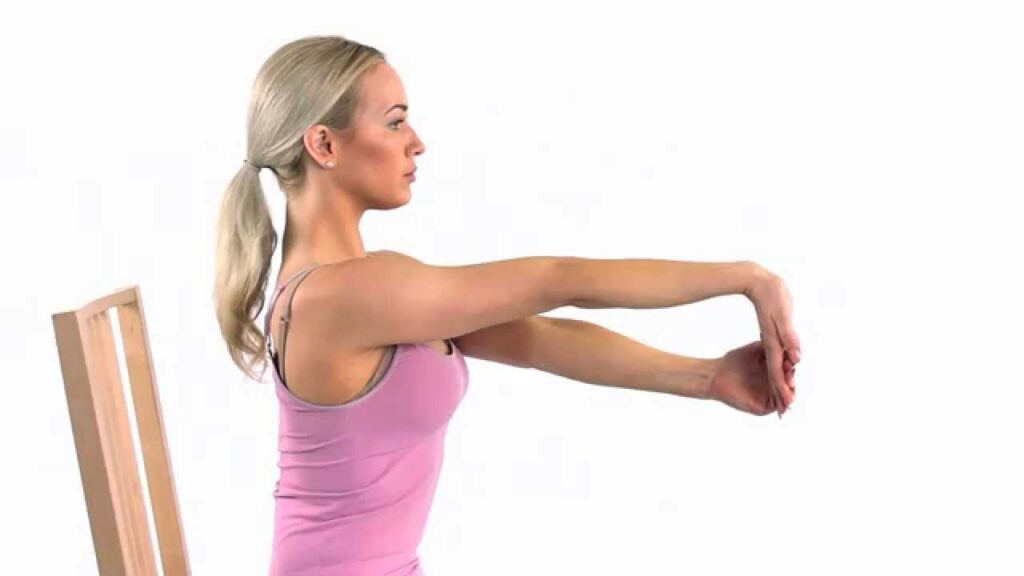

- This is a great exercise to prevent wrist extensor injuries.
- It is also recommended for standard treatment of tennis elbow and lateral epicondylitis.
- To perform the stretch, straighten one arm and lightly squeeze the opposite arm, bending the wrist down so that the fingers point to the ground.
- Hold the stretch for 10 seconds. Instead of the opposite hand, a person can use a wall to apply pressure. In this case, both hands can be extended at the same time.
- This exercise should be done every day if you do long hours of continuous activity that involves the muscles.
Proprioception and Balance Training:
Proprioception exercises aim to enhance joint position sense and control. Balance training exercises can help improve stability and coordination, which are important for functional activities. These exercises may involve various balance boards, stability balls, or specific balance-focused activities.
Manual Therapy:
Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization, massage, and joint mobilizations, can help alleviate pain, reduce muscle tension, and promote tissue healing.
Modalities
Therapeutic modalities, including ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or heat/cold therapy, may be utilized to reduce pain, and inflammation, and promote tissue healing. The specific modality chosen will depend on your individual needs and the stage of recovery.
Functional Training:
- The physiotherapist will gradually incorporate functional exercises and activities that mimic your daily tasks or specific sports requirements.
- This will help you regain strength, endurance, and coordination in the wrist and forearm.
- Throughout the rehabilitation process, the physiotherapist will closely monitor your progress, modify the treatment plan as necessary, and provide guidance on activity modifications and gradual return to functional or sports activities.
- Remember, it is essential to follow the guidance of your physiotherapist and adhere to the prescribed exercises and treatment plan to optimize your recovery and prevent re-injury.
FAQs
The ECRl is an extensor muscle of the wrist and may trigger elbow pain when affected by trigger points or tension. Tennis elbow pain is a common symptom experienced when this muscle contains trigger points, which can be a byproduct of excessive muscle tension.
This condition can cause pain and burning in the elbow and hand. This may lead to inflammation in the tendons and muscles that control arm movement. It may be cured with a mixture of rest, physical therapy, NSAID pain relievers, and in some cases, surgery.
In some cases, extensor tendon injuries can be treated without surgery. This can be done using a rigid support called a splint, which is worn around the arm.
Some tendon tears can heal without surgery. However, complete tears require surgery, especially if the patient wants to resume activities. Tendon repair surgery is also necessary when conservative therapy fails
Tendons have the ability to heal on their own, like all forms of connective tissue, but a variety of elements are crucial for tissue regeneration and repair. Similar to muscles, tendons typically have insufficient blood flow, which is a highly important component of mending and the healing process.