Soleus strain: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise
Table of Contents
What is soleus strain?
A soleus muscle strain occurs due to muscle fibers are damaged by the loads placed on them by jerky activity. The soleus muscle is injured while the knee is in flexion. Strains of the proximal medial musculotendinous junction are the most general type of soleus muscle injuries. It crosses only the ankle and is largely a term of type one slow-twitch muscle fibers.
Soleus injuries are relatively common in runners. This type of injury is known as an overuse injury, which is why endurance and long-distance runners are at higher risk. Injuries commonly occur as a result of fatigue or over training. They can also occur when the knee is flexed for a long time while running, such as during uphill running.
Anatomy of Soleus muscle
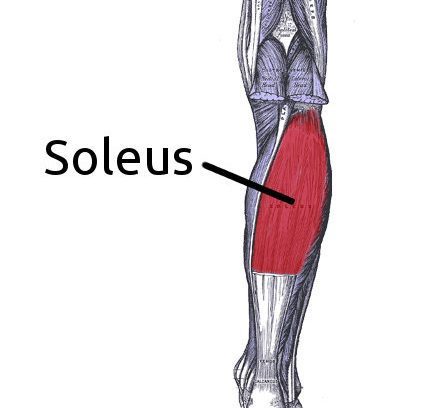
Soleus muscle is a flat, broad muscle of the calf of the leg lying just beneath the gastrocnemius muscle. It arises from the upper part of the tibia and fibula, the bones of the lower leg, and then attach to the gastrocnemius to attach via the Achilles tendon at the heel.
It is a large muscle located in the posterior leg. The soleus and gastrocnemius, along with the plantaris muscle, belong to the group of superficial posterior compartment calf muscles.
Origin:
Proximal half of back surface of tibia along soleal line.
proximal 1/3 of the posterior fibula.
Insertion:
Posterior heal via a calcaneal tendon.
Nerve supply:
Its supplied by the tibial nerve, L4, L5, S1, and S2. it has no sensory supply to the intramuscular aponeurosis.
Blood supply:
Its supplied by branches of the popliteal artery trunk, the posterior tibial artery, and the peroneal artery.
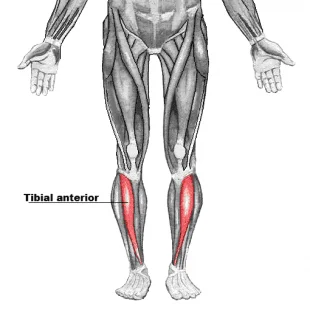
Antagonists of soleus: Tibialis anterior
What causes of soleus strain?
Soleus muscle strains generally occur when someone suddenly moves or overstretches their soleus after standing more time.Fast pivots, jumps or abrupt stops can cause strains. This injury is mainly common when toes get forced upward (toward body) and ankle pulls soleus muscles down too rapidly.
An acute soleus muscle strain is once muscle tears rapidly and unexpectedly. muscle tears will happen either from injuries or trauma. this will result to:
• Not warming up correctly before physical activity
• deficient flexibility
• deficient conditioning
• Overexertion and fatigue
• calf muscle Weakness
Acute soleus muscle strain:
Slip body, jump, run, throw something, raise something heavy, lift something while clumsy position.
Chronic soleus muscle strain:
Sports like row, tennis, golf, or baseball, poor posture, holding back or neck in an ungainly position for long periods of time, like after work at a desk.
Overuse:
Repeating a similar movement, whether or not at work or during an associate activity like taking part in sports — will cause overuse syndrome.
Don’t stretch or warm up prior to exercise: Stretching prior exercise step by step will increase how much stress you place on muscles.
A lack of flexibility: If you’re not much flexible, your calf muscles (and the fibers in them) are tighter, which build them additional susceptible to strains.
Other risk factors for soleus strain
Age: People over 40 may be more likely to obtain strains during physical activity.
Sex: Men are more likely to get calf muscle injuries.
Lack of conditioning: It’s important to warm up and stretch prior to physical activity and condition
muscles before he start of a sports season.
Muscle quality: individuals with tight or short calf muscles have a more risk of calf strains.
Grades of soleus strain
Grade 1: Grade 1 injury causes minimal muscle damage, although there may be sharp pain at the time of injury. May be able to continue an activity, without pain or with mild discomfort.
Average time to come back to sport:10-12 days
sign-pain on unilateral calf raise.
Grade 2: Grade 2 injuries cause moderate muscle damage, and people with this category of muscle injury may have difficulty walking. They will often experience a sharp pain that worsens when they flex or extend their foot.
Average time to come sport:16-21 damage days
sign-pain with active plantar flexion, pain and weakness with resisted plantar flexion, loss of flexion.
Grade 3: A grade 3 injury is a complete tear of the muscle, and it can cause significant bruising and swelling in the calf.Full recovery can take three to four months and, in some instances, surgery may even be needed.
Average time to come sport: 6 months once surgery
sign-inability to contract calf muscle may have the palpable defect, & Thomson’s test positive
What are the symptoms of soleus strain?
- Pain with active or resisted plantar flexion
- Pain during walking, running, jumping or hopping
- Tenderness on palpation of the injury site
- Muscle pain when flexing ankle or pointing toes.
- Problems bending knee.
- Snapping or popping sensation in calf.
- Sudden pain in the back of lower leg.
- Swelling in calf muscle.
- Bruising on calf muscle.
How is a soleus strain diagnosed?
It becomes too challenging to identify this muscle injury just from a physical examination.
So doctors typically use an MRI & ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis of the muscle injury.
Ultrasound = USG is less good at detecting this type of muscle injury.
The doctor also asks the patient about the symptoms & tries to know about the causes of the injury.
Assessment
Subjective assessment
history with associated symptoms
mechanism of injury:
Inciting trauma- side and magnitude of injury force
recurrent trauma-faulty postural related injuries
Objective assessment
Examine the foot and ankle in supine and standing position
Ankle Active range of motion
Ankle Passive range of motion
Resisted strength check the ankle and foot
Knee Active ROM and manual muscle testing
On objective assessment, there will be:
muscle Tenderness- to touch at the point of injury
Swelling
Bruising may appear within hours or days
Stretching of the muscle will reproduce pain
Pain on resisted plantar flexion.
Differential diagnosis of soleus strain
Medial leg bone stress syndrome
Plantar fasciopathy
Ankle Joint sprain
Medial leg bone stress syndrome
Leg injuries related to sports with same symptoms and treatment as a calf strain are mentioned below.
Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS)
Achilles tendinopathy
Popliteal Artery entrapment Syndrome (PAES)
What is the treatment of soleus strain?
RICE principal:
R- rest
I- ice for cooling
C- compression: tapping and splinting
E- elevation
Rest: Refused some activities that cause pain, swelling, or discomfort. don’t avoid all physical activity.
Ice: Ice is a tried-and-true tool for decrease pain and swelling. Apply an ice pack (covered with a light, absorbent towel to help prevent frostbite) for 15-20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours during the first 24 to 48 hours after injury.
Compression: This means wrapping the injured part to prevent swelling. Wrap the affected part with an elastic medical bandage. You should to be snug but not too tight.if it’s too tight, it’ll interrupt blood flow. If the skin under the wrap turns blue or feels cold,numb, or tingly, loosen the bandage. If these symptoms don’t disappear right away, seek instantly medical help.
Elevation: Elevate the leg on high of your heart’s extent, importantly at night time, that allows gravity to help reduce swelling.
Medical treatment
Pain reliving medicine mainly Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) — during the first 48 hours after a muscle strain. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and others can be helpful for pain relief during this period.
Physiotherapy Treatment and Exercise:
The goal of physiotherapy treatment are:
Relieve soleus muscle pain
Reduce muscle swelling
Increases soleus muscle strengths.
restore patient’s confidence
restore patients’ full functional activities
increase full mobility of the ligament and corresponding joint
Massage
- When in the soleus muscle pain presents to tender & trigger points in the physiotherapy treatment therapist is advised to massage the area of muscle pain.
- It is applied with the help of oil & powder for 5 to 10 minutes to the area of muscle pain.
- Effleurage massage is mostly help to relive muscle pain.
- It is applied in a circular motion. It is also applied with the help of a messenger.
Electrotherapy
physiotherapy rehabilitation can be begin after 48 hours of injury, For the first few days give electric modality give to reduce swelling and pain
Ultrasound
ultrasound has been used about tissue healing increases blood circulation and mobility & reduce swelling.
Cryotherapy
Inflammation and swelling can be decrease by applying cryotherapy in form of ice packs, and cold water baths to the affected part. Constant application of cold several times a day for 15-30 minutes at a time is suggest.
TENS or IFT
Trans cutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) or Interferential therapy(IFT) may be able to help decrease pain and muscle spasms.
Stretching of soleus muscle:
Stretching is helpful to you for releasing the muscle tightness & pain.
- Soleus Stretch (Flexibility).
- Standing Soleus Stretch.
- Soleus seated bent-knee stretch.
- Soleus bent knee standing wall stretch.
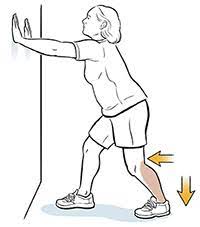
Soleus Stretch (Flexibility):
- You are standing facing a wall from 3 feet away.
- Then Take to one step toward the wall with the right foot.
- Place both palms on the wall.
- Bend both knee joints & lean forward.
- Must be Keep both heels on the floor.
- Hold for this position for 30 to 60 seconds. Then relax both legs.
- Repeat the exercise 3 times.
- Then Switch legs & repeat.
- Repeat this stretching 3 times a day.

Standing Soleus Stretch :
- You are in a Standing position for the stretch & take a half step forward.
- Must be Keep the weight evenly distributed on both feet & heels on the ground.
- Slowly bend the knee joint & sink toward the ground.
- In this position, You should feel a stretch in the back leg, just above the heel.
- Then Continue to sink slowly with the hip joint to deepen the stretch.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds & change sides.
- When you bend your knee joint, it is targeted to stretch the soleus & Achilles tendon rather than the gastrocnemius muscle.
Soleus seated bent-knee stretch :
- You are sitting on the floor bend one knee joint & point the toes up towards the ceiling.
- Hook a band & towel around the middle of the foot.
- Then Pull on the band & towel to feel the stretch.
- Hold this exercise for the desired time & repeat it on the other side.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Soleus bent knee standing wall strech :
- Place both hands against the wall & take one leg back with the knee joint straight.
- Bend both knees till you feel a stretch in the back leg.
- Hold this stretching for the desired time & then switch sides or repeat.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Exercise:
All exercise helps you release pain & weakness.
- Calf raises
- Standing heel calf raise
- Soleus bridge
- Squat with soleus raise
- Donkey calf raise
Calf raises :
- The patient is in a Standing position straight, then push through the balls of the feet & raise the heel till you are standing on the toes. Then lower to slowly back to the start.
- Do this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Calf raise variations :
- Weighted calf raise:
- It is a good idea to increase the difficulty of the calf raises with the weights with the exercise.
- The patient is Holding a dumbbell in each hand while doing the calf raises which is help to prepare the calf muscle to handle the put extra pressure during the exercise.
- Do this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Raised calf raise:
- You are in the Standing position on a step so that your heel is dropping lower than the rest of the foot at the bottom of the movement. Then provides a greater range of motion in the calf muscle during the exercise.
- You can hold the dumbbells to make this variation tougher, but it is difficult to must keep the balance when holding the dumbbells too heavy.
- Do this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Bent-knee calf raise:
- When Bending the knee joint slightly when doing any kind of calf raises which is mostly used for soleus muscle.
- During the bent knee position do the calf raise exercise.
- Do this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Seated calf raise:
- You are in a sitting position on a chair with the feet on a raised surface so that heels are hanging off the back.
- With the latter, you can rest dumbbells on the knee joint to add resistance to the movement.
- Seated calf raises are mostly good for working the soleus muscles & allow to you add significant weight to the exercise with less risk of losing the balance.
- Do this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Standing heel calf raise:
- This exercise starts with the standing position and then holding onto a stable surface for support.
- Then Slowly raise the heels off the ground as far as you can & lower them back to the floor
- You are Make sure to keep the balls of the feet on the ground & maintain the balance.
- Then Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Foam Roller Exercise:
- You are in a sitting position on the floor with your legs extended in front of you.
- Then place the roller under the calves.
- Use the hands for support then slowly roll from the knee joint down to the ankle & pausing on any tight or sore spots.
- Do this roll for 30 seconds to 1 minute & repeat 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Soleus bridge :
- The patient is lying supine on the floor & places the balls of the feet on an elevated surface like a foam roll & weight plate.
- Then Perform a hip extension & squeeze the glutes muscle at lockout = glute bridge position.
- While in the top position perform a calf raise & pause for a second.
- Then Reverse the movement & reset.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Squat with soleus raise :
- You are Holding a squat rack with both hands an upright torso & feet hip-width apart & toes pointed forward.
- You can also hook a band to a pole & sturdy object to wrap it around the waist so that you can lean back safely.
- It allows you to must keep the shins perpendicular to the floor when squatting down.
- Must be Keep the shoulder down & chest up perform a squat till the thighs are parallel with the ground.
- Then Perform a calf raise by the raising up onto the toes.
- Hold for 30 seconds & return to heel to the ground.
- Then Stand up from the squat & reset.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Donkey calf raise :

- You are Set up in the donkey calf raise machine by securing the hands hinge back at the hip joint & placing the balls of the feet at the far edge of the step.
- Bend the knee joint as much as tolerated.
- Then lower the heels as far as possible to the floor & hold for 30 seconds.
- Then lift the heels as far as possible & squeezing the calves at the top.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening exercise:
Strengthening exercise is help to you for release the muscle weakness & strengthen the muscle.
- Strengthening exercise for soleus muscle
- Single-Leg Calf Raises With Bent Knee On A Step
- Seated soleus raises with weight
Strengthening exercise for soleus muscle :
- You are standing with the feet are shoulder-width apart.
- Then Raise the heels to the count of 2 & lower them to the count of 4.
- Make sure to you are on the tips of your toes.
- Use a chair & wall for support if you need it.
- Do the 10 to 20 repetitions of 2 to 3 sets daily.
- To make this exercise harder, try doing this exercise on one leg.

Single-Leg Calf Raises With Bent Knee On A Step:
- You are standing on a step with the heels hanging off the edge.
- Hold the something for stability
- Then Stand on the leg you want to for exercise & bend the knee joint to as close the 90 degrees as you can.
- Next, raise onto the toes & slowly lower back down till you get a stretch in the calf muscle & repeat.
- If you are ready for this exercise more times then add weight to the hand.
- Then Choose a resistance that is high for strengthening & low for endurance.
- Perform this exercise for 6- 10 repetitions &repeat this exercise for 3-5 sets in total for strength.
- For endurance, you do this exercise for 15-25 repetitions & repeat for 3-5 sets.
- You need to rest at least 3 minutes between the sets for strength & no more than 30 seconds for endurance.
- You must be taken to aim the work either 2 to 3 times per session per week.
Seated soleus raises with weight:
- This exercise is performed in the 3 versions like as isometric, eccentric, and concentric.
- An isometric version of this exercise :
- This exercise involves holding this right foot tiptoe position for up to 30 seconds.
- Then the weight needs to be heavy enough to allow no more than 30 seconds.
- Once you feel stronger from this exercise & do this exercise over 30 seconds then you will add more weight.
- An eccentric version of this exercise :
- This exercise involves holding this right foot tiptoe position for 2 seconds.
- Then slowly lowering the heel back down over the edge of the step for 3 seconds.
- Repeat this movement by using the two feet to lift the weight, one foot to hold & lower, and so on.
- The weight needs to be heavy enough to allow no more than 12 repetitions.
- Once you feel stronger for this exercise & do the 12 repetitions & you add more weight.
- A concentric version of this exercise
- In exercise involves using just one foot to lift & lower the weight.
- Must be Keep the tempo slow & controlled & use enough the weight to allow no more than 12 repetitions.
- Once you feel stronger for this exercise & do the 12 repetitions & you add more weight.
Preventive measures:
- Do Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for your sports, fitness, or work exertion, as a part of an overall physical activities
- An exercise program can help to minimize your danger of muscle strains.
- Try to be in a shape to play your sport; don’t play your sport to get in shape.
- If you have a physically demanding occupation, regular exercise can help to help injuries.
- Follow a healthy diet and an exercise program to maintain a healthy weight. The overweight can put added pressure on the muscles, making muscle strains again probable to do.
- Walk at a moderate pace for 3 to 5 minutes before doing any sports or a different physical activity.
- Going this will warm up the muscles and prepare them for an increase in the intensity of the exercise.