Cervical Medullary Syndrome
Table of Contents
What is Cervical Medullary Syndrome?
Cervical Medullary Syndrome (CMS) is a neurological condition that occurs as a result of damage or injury to the spinal cord at the level of the upper cervical (neck) region and the lower part of the brainstem.
Symptoms of this syndrome are headaches, dizziness, & brain fog have been unrelenting. Started after a slow-speed rear-end motor vehicle accident & has been developed. Physical therapy, drugs, & rest have failed to provide relief. Referrals to experts including neurologists, orthopedic surgeons, & neurosurgeons have been draining & demoralizing. Many Doctors are not able to provide any relief & suggest psychological counseling.
This syndrome is a clinical disorder that appears as a result of damage to the lower part of the brain. Treatment for CMS involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition, which may involve medication, surgery, or rehabilitation therapy. Depending on the severity of the condition, patients may need long-term care and support to manage their symptoms and maintain their quality of life.
What exactly is Cervical Medullary Syndrome?
This syndrome is a clinical situation that arises as a result of inflammation, deformation, or constriction of the lower part of the brain. Signs and symptoms can be comprehensive with fluctuating severity based on the extent of the underlying damage. For instance, mild disturbance of the brainstem may lead to mild, intermittent signs.
Important Neck Anatomy
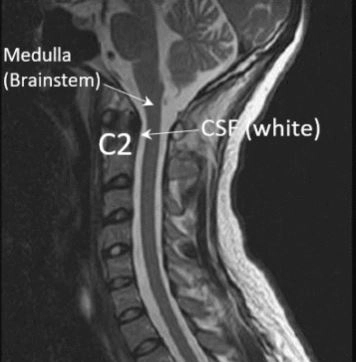
The brain is included in a defensive boney shell named the skull. There are several different regions of the brain. The lower part of the brain is known as the medulla. It links the cerebellum to the spinal cord & is tubular. The brainstem is accountable for crucial functions of life like breathing, heart rate, & blood pressure.
The medulla is covered & encircled by cerebral spinal fluid, and this is illustrated in the sagittal MRI of the brain & neck shown below. This is a side-view illustration of the anatomy. The medulla is dark in color and situated at the base of the skull. It links directly with the spinal cord which is dark in color. The bones of the cervical spine accumulate one upon another. In difference, the CSF ( Cerebral Spinal Fluid ) is white & which provides an important coating of protection.
7 vertebrae make up the cervical spine, and they sit in front of the spinal fluid & spinal cord. The 2nd highest bone is the C2 bone & is determined in white.
Causes of Cervical Medullary Syndrome
The upper cervical spine & brain are complicated with multiple systems. These structures reside within the skull & defensive confines of the cervical spine. Neither develops to adapt to inflammation, injury, & disease. Rather the delicate tissues of the brain & spinal cord are uncomfortable or compressed.
The four major conditions can Cause Cervical Medullary Syndrome:
- Chiari Malformation
- Craniocervical Instability
- Atlantoaxial Instability
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis
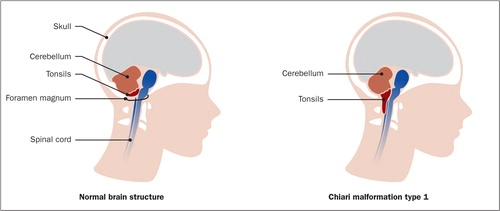
Chiari Malformation
Chiari Malformation is a medical situation where a portion of the brain protrudes via a normal opening at the base of the skull.
Craniocervical Instability
CCI (Craniocervical instability) is a medical disorder where the strong ligaments that maintain your head onto the upper neck are loose or damaged.
Atlantoaxial Instability
The C1 bone is frequently directed to as the atlas. The C2 bone is also known as the axis. The C1 & C2 bones stack upon one another constructing a joint. The joint is known as the atlantoaxial joint. Trauma & ligament fluctuation are the most common reasons for Atlantoaxial instability.
Cervical Spinal Stenosis
Stenosis just means narrowing. Cervical spinal stenosis is a condition where there is a narrowing of the spinal canal which can lead to irritation or damage to the spinal cord & nerves resulting in discomfort, numbness, pain & dysfunction.
Symptoms of Cervical Medullary Syndrome
Symptoms of cervical medullary syndrome will differ depending on the severity of the damage. Common symptoms include:
- Headache
- Neck pain
- Numbness & weakness in the upper and lower limb
- Dysautonomia
- POTS [ postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome ]
- Breathing problem
- Visual disorders
- Swallowing problem
- Dizziness
Brain Fog
Brain fog is the hallmark sign and symptom of Craniocervical fluctuation. It is indicated by slow thinking, problems in concentrating, confusion, insufficiency in focusing, forgetfulness, or haziness in thinking. The severity of signs and symptoms differs from patient to patient.
Some patients explain it as a generalized haziness in thinking as if cotton were stuck in the head. In addition to mental impairments, multiple patients also report generalized cognitive fatigue in completing complex tasks impossible.
Cervicalgia or Neck Pain
Neck pain is also called Cervicalgia, which is a common, undesirable pain. It is a medical word used to define neck pain. It is especially common & affects around two third of the population at some point in life. Cervicalgia is the 4th major reason for disability. Risk factors contain damage, previous history of neck & musculoskeletal pain, jobs that need a lot of desk work, low social support, job insecurity, physical weakness, & poor computer station structure.
Chronic Fatigue
Later that day or the next morning, moving across the room appeared almost impossible & took herculean power. 24×7 simple tasks are almost impossible due to a shortage of strength & energy. This is chronic tiredness, & it is one of the typical symptoms associated with craniocervical fluctuation. Severity can differ & in severe cases, patients are limited to their beds. Aggravating & alleviating factors oftentimes can not be determined.
Chronic Headaches
It’s an everyday issue, maybe once a week, maybe even less often, but one thing is for convinced when a chronic headache rushes in, it can be an absolute pain in the neck. To address chronic headaches, have to first decide if the pain is led by a problem in the neck. Some neck issues that can lead to headaches: Weak neck muscles; The head, on moderate, weighs about ten pounds, so when the neck muscles are inadequate, it can make the head feel a bit like a bowling ball that the neck can’t perfectly balance. There are numerous muscles that, along with the cervical spine, work together to assist and support the neck and movement.
Muscle pain after cervical fusion surgery
Cervical fusion is a significant surgery that affects the joining of one or more of the spinal bones jointly using screws, bolts, & plates. The hardware is placed in the anterior (front) or the posterior (back) of the cervical spine. The disc between the spinal bones is usually times removed & returned with a bone graft or a spacer. The neck of formed of 7 boney building partnerships that are numbered from 1 to 7. The letter C is associated with the numerals to designate the cervical spine. The bones in the neck region are C1 via C7. Sandwiched between neck bones are necessary to shock absorbers named discs.
Neck Pain & Dizziness
The body’s balancing system is compromised of 3 different systems that work closely together to support the body in balance: the eyes, inner ear, & upper cervical spine. The upper cervical spine involves & processes information about the space part, and it communicates this information to the eyes & inner ears through nerves. There is an enduring highway of electrical signals between the cervical spine, inner ear, & eyes that maintain us upright, create us conscious of position & allow us to walk, move & run.
How does Craniocervical instability (CCI) lead to Cervical Medually Syndrome?
In normal circumstances, the C2 bone works inside the C1 bone as shown above. This encourages the C2 to rotate near the C1 bone which is the place where arises half of the neck rotation.
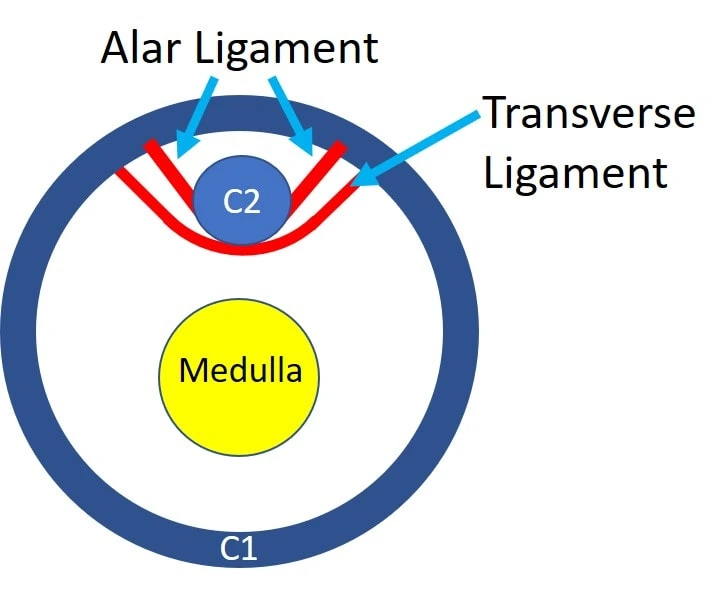
Two strong ligaments maintain the C2 bone which means the axis to the C1 bone which means atlas. They are two ligaments which are shown below, and the ligaments are Transverse &Alar ligaments. The picture is a cross-section outlook from the top down. As if an angel were glancing down upon you. Both ligaments are red and snuggly fit the top of the C2 bone into place, and behind the C2 bone is the cerebral spinal fluid along with the brainstem. The cerebral spinal fluid is white whereas the brainstem is yellow. The Alar & Transverse ligaments snuggly maintain the C2 bone stopping it from striking or damaging the medulla.
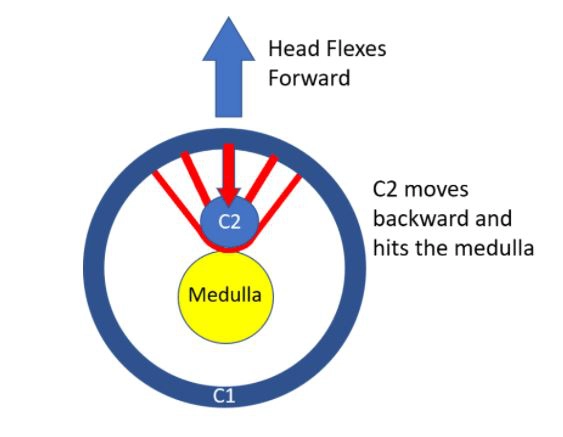
This is a situation where there is damage or injury of the alar &or transverse ligaments. This is shown down. Because both ligaments are easygoing the C2 bone is no longer maintained snuggly into position. Rather it drives backward & contacts the medulla when a patient flexes their head & neck. The protective cerebral spinal fluid is replaced and is no longer able to act as a buffer. The medulla is very, very susceptible tissue that is efficiently irritated or compressed by the C2 bone. This provides rise to symptoms of cervical medullary syndrome.
Treatment of Cervical Medullary Syndrome
The first treatment is usually physiotherapy and specific upper cervical chiropractic. It directly the malposition of C1 on C2, which tend to rotate on each other when there are loose or shattered ligaments. When this procedure doesn’t help, then recommended a surgical fusion of the upper neck bones is. This surgery uses screws & sometimes plates or rods to make sure that the upper neck bones accomplish the move.
This procedure is a high-risk procedure. In addition, it can also lead to Adjacent Segment Disease (ASD), which means that the spinal levels above & below can get worn out and harmed, demanding the requirement for more fusions.
An alternative is trying to tighten the ligaments via very specific x-ray-guided injections. In the back of the neck ligament tightening injection can be attempted, but the ligaments concerned here that cause Cervical Medullary Syndrome can’t be called and treated using that procedure. The procedure only functions at the Centeno-Schultz Clinic in Broomfield & Lone Tree, Colorado.
Cervical Fusion
Cervical Fusion is usually suggested when chronic neck pain issues worsen over time. Cervical fusion is a significant surgery that affects the joining of one or more of the spinal bones together using screws, bolts, & plates. The hardware may be established in the front which means anterior or the back means posterior of the cervical spine. The disc between the spinal bones is usually removed & replaced with a bone graft or a spacer. The neck is formed of 7 boney building blocks that are numbered from 1 to 7. The letter C is associated with the numbers to establish the cervical spine.
Occipital Cervical Fusion
An Occipital cervical fusion also known as Occipitocervical fusion is a main surgery. It is a challenging procedure due to the complex anatomy of the upper neck, it is not a normal operation. The technique involves rods, plates, and screws that are positioned into the cervical spine & occiput. A plate attached by screws is placed at the base of the occiput. Screws are also inducted into one or more cervical bones. The reason for occipital cervical surgery is to have a boney fusion between the skull & neck and to relieve pain.
PICL Procedure
CCI stands for cranial cervical instability which means that the ligaments that maintain the head on are too loose. To help with this situation, a new procedure known as PICL stands for percutaneous implantation of the CCJ Ligaments. In the PICL procedure for patients who have CCI, there are excesses of questions.
FAQ
The most noticeable symptoms before surgery contained headache [ 100% ], fatigue [ 100% ], dizziness [ 100%], muscle pain, vertigo, arm weakness, neck pain, balance problems, memory issues, night awakenings, numbness & weakness of the arms & legs, and gait difficulties.
It is the part of the brainstem that is most influenced by upper cervical instability. It includes the functional centers that control autonomic nervous system action that regulates respiration, heart rate, & digestive functions.
This syndrome can form when the vertebrae discovered in the neck and cervical spine are moved, collapsed, or misaligned. Generally, the upper cervical vertebrae & occiput [ sometimes directed to as C0 ] are the most commonly injured regions & may not show up on diagnostic tests such as an MRI.
The cause of this syndrome is either a deficiency genetic mutation or the development of diseases later in life or an injury about the neck: the cervical region, that damages the spinal nerves crossing via the cervical region resulting in ventral subluxation.
Treatment relies on the cause of the compression but generally involves surgery. Methods may involve depleting blood from the brain, removing a tumor or abscess, or removing a quarter of the skull to reduce intracranial pressure.
The cervical spine vertebrae C1-C7 & the occipitocervical area, where the cervical spine meets the base of the skull need precise treatment because wounds & conditions that affect that location can be life-threatening or harshly debilitating.