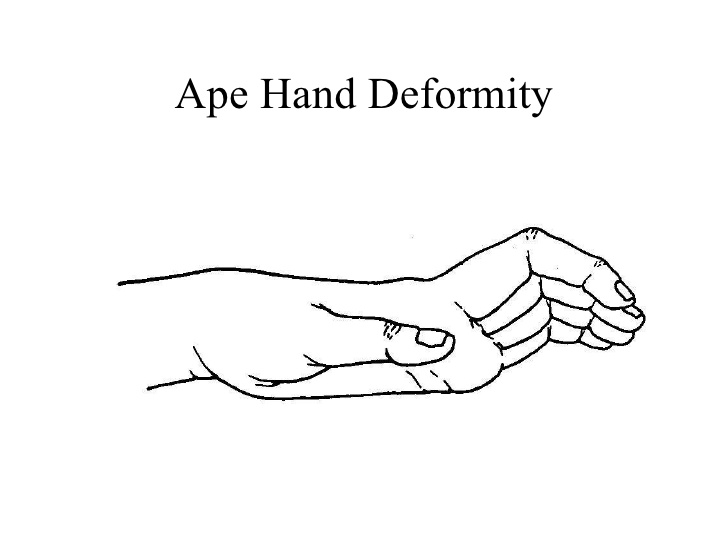
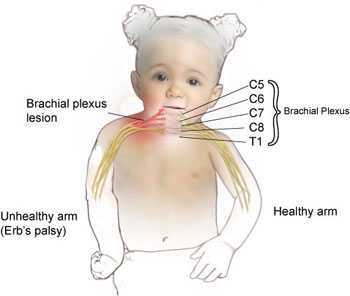
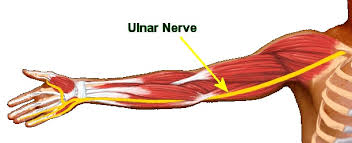
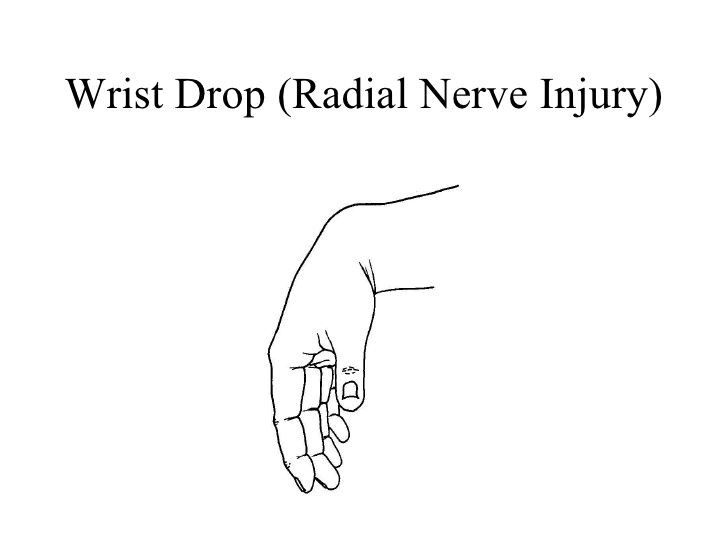
Athetoid cerebral palsy | Dyskinetic cerebral palsy
What is Athetoid/Dyskinetic cerebral palsy? What are the types of athetoid cerebral palsy? The various types of athetoid cerebral palsy include: What are the causes of athetoid cerebral palsy? Basal ganglia diseases Birth problems Jaundice Drug toxicity Cerebral palsy Stroke What are the symptoms of athetoid cerebral palsy? The most frequent symptoms that come with…