Polymyositis
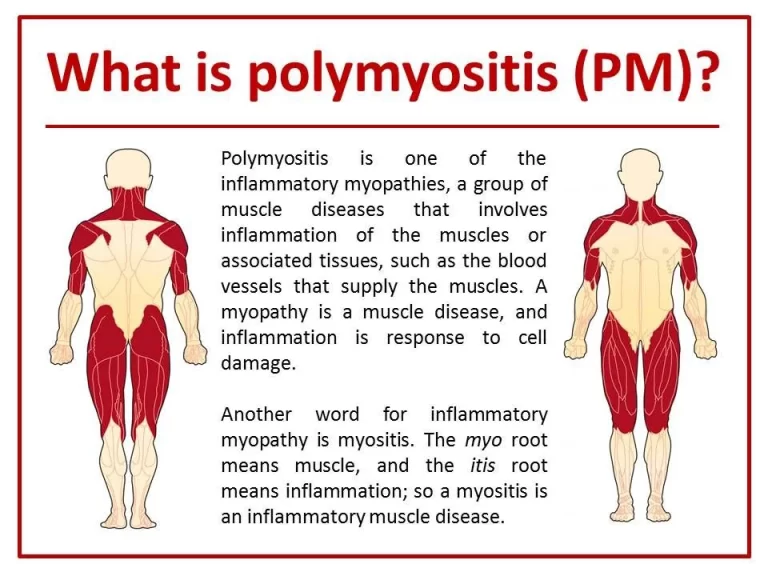
What is polymyositis? Polymyositis is an inflammatory muscle disease that causes muscle weakness. Myositis means inflammation of the muscle. Commonly, polymyositis affects the muscles that are closest to the trunk of the body. Eventually, people with polymyositis have trouble when rising from the sitting position, climbing stairs, lifting objects, or reaching overhead. In certain cases,…