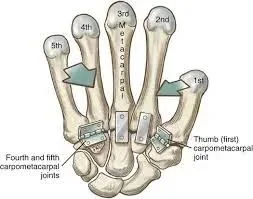
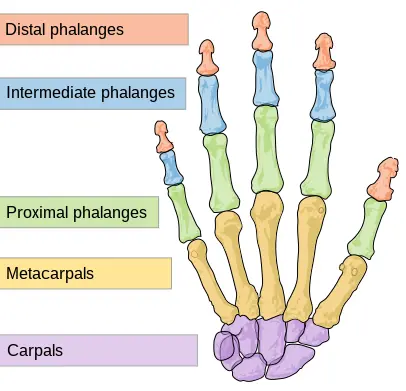
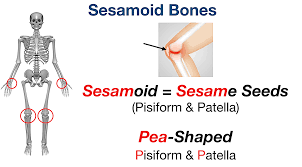
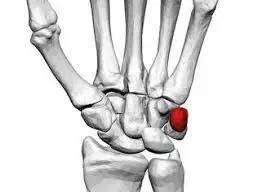
Bone
Introduction The Bone tissue has both stabilizing and motor activity. In terms of supplying the body’s physical structure bones allow muscles, tendons, and ligaments to connect to them, facilitating movement. Bone is a fibrous substance that contributes to metabolism, aids in motion, improves structure, and protects crucial organs. There are 206 bones in the skeleton of an adult…