Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion And Extension
Table of Contents
What Is Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion and Extension?
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) is the joint at the end of the finger or toe, near the nail. DIP flexion means to flex a finger or toe, bringing the tip of the finger to the palm or sole of the foot.
The extension is a reverse movement in which the finger or toe straightens and returns to its natural position. These movements are important for activities involving the fingers and toes, such as grasping, grasping, and pointing.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
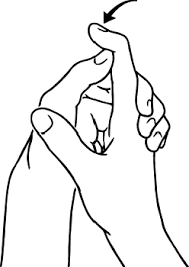
What Is Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion?
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) is one of the joints located inside the palms and toes. Specifically, it’s miles the joint that connects the center phalanx (the second bone from the bottom of the finger or toe) to the distal phalanx (the bone on the tip of the finger or toe).
Distal interphalangeal joint flexion refers to the bending or motion that takes place on the DIP joint, resulting in a lower withinside attitude between the center phalanx and the distal phalanx. In easy terms, it’s miles the movement of bringing the end of the finger or toe in the direction of the palm or sole, respectively.
This flexion motion is vital for diverse sports concerning the palms and toes, including gripping objects, typing on a keyboard, gambling musical instruments, and strolling or running. It lets in for accelerated dexterity and manipulation of the digits, permitting particular actions and manipulation.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexores Muscles
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) flexion inside the arms is mostly managed with the aid of using the subsequent muscles:
- Flexor digitorum profundus: This muscle originates from the ulna and interosseous membrane inside the forearm. It travels down the forearm and passes through the carpal tunnel earlier than placing it into the distal phalanx of the finger. It flexes the DIP joint and is accountable for bending the fingertip.
- Lumbricals: These small muscle masses originate from the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus inside the palm of the hand. They break up into slips, with every slip placed on both aspects of the extensor hood mechanism (the shape that enables coordinated finger movements). The lubricants help in flexion on the DIP joint while the arms are extended.
- Interossei muscle: There are 4 dorsal interossei muscle masses and 3 palmar interossei muscles positioned among the metacarpal bones inside the hand. These muscle masses make a contribution to DIP joint flexion not directly with the aid of using presenting balance and managing the finger movements.
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis: This muscle is observed inside the palm of the hand, and it assists in flexing the DIP joint of the little finger.
These muscle mass paintings collectively provide flexion on the DIP joint and are vital for numerous sports that contain gripping, grasping, and first-class motor management of the arms.
Range Of Motion Of Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
The variety of movement (ROM) of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint refers back to the flexion (bending) and extension (straightening) that can arise on the joint. The DIP joint is placed on the distal give-up of the finger or toe, mainly among the second one and phalanges.
In a wholesome individual, the common variety of movement for DIP joint flexion is usually around zero to ninety degrees. In this manner, the finger or toe may be flexed or bent downwards in the direction of the palm or sole, respectively, till it reaches a proper attitude with the center phalanx.
It’s vital to notice that the variety of movement can range amongst people because of elements together with joint health, injury, or anatomical differences. Additionally, positive situations or injuries, together with arthritis or trauma, might also additionally limit the ordinary variety of movement of the DIP joint. Consulting with a healthcare professional, together with an orthopedic expert or bodily therapist, can offer greater particular facts concerning an individual’s variety of movement and any obstacles they will have.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion Test
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) flexion take a look at is a bodily exam maneuver used to evaluate the variety of movement and integrity of the DIP joint inside the hands. It is commonly accomplished with the aid of a healthcare professional, including a medical doctor or therapist. Here are the stairs worried inside take a look at:
- Patient position: The affected person is normally seated comfortably, with the hand resting on a flat floor or held with the aid of the examiner.
- Joint positioning: The examiner stabilizes the hand and positions the finger to be examined in a barely prolonged position (straightened).
- Test movement: The examiner applies mild stress or resistance to the fingertip even as educating the affected person to flex (bend) the DIP joint. The affected person is requested to actively flex the joint towards the resistance provided.
- Observation: The examiner observes and assesses the variety of movements completed with the aid of using the affected person’s finger all through DIP joint flexion. They search for any limitations, aches, or abnormalities inside the movement.
- Comparative testing: The take a look at is commonly accomplished on every finger in my view for comparison. The examiner may also examine the DIP joint flexion of a couple of hands to assess the complete hand.
The DIP joint flexion takes a look at facilitating discovering any restrictions, joint stiffness, or aches related to the DIP joint. It may be beneficial in diagnosing situations including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, tendon injuries, or joint deformities. The effects of the take look-at, together with different medical findings, can manually similarly assess and remedy planning. It is crucial to observe that this take a look at ought to be accomplished with the aid of a skilled healthcare professional.
Exercise For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
There are diverse physical games that could assist in enhancing distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) flexion inside the hands. These physical games intend to boost the power and energy of the muscle groups and tendons that manipulate DIP joint movement. Here are some physical games you may try:
1. Passive DIP Joint Flexion:
- Place your hands on a flat floor together along with your palm down.
- Use your different hand to softly push the fingertip downwards, flexing the DIP joint.
- Hold the stretch for some seconds after which release.
- Repeat the exercise for every finger, focusing on the DIP joint.
2. Active DIP Joint Flexion:
- Start together with your hands comfortable and hands extended.
- Slowly and actively flex the DIP joint of 1 finger, bringing the fingertip closer to the palm.
- Hold the flexed role for some seconds.
- Repeat the exercise for every finger, focusing on the DIP joint.
3. Rubber Band Resistance:
- Place a rubber band across the fingertips of your hand.
- Extend your hands after which actively flex the DIP joint towards the resistance of the rubber band.
- Hold the flexed role for some seconds earlier than slowly returning to the beginning role.
- Repeat the exercise for every finger, focusing on the DIP joint.
4. Hand Grips or Squeezes:
- Hold a gentle ball or strain the ball inside the palm of your hand.
- Squeeze the ball with the usage of your hands, specializing in flexing the DIP joint.
- Hold the squeeze for some seconds after which release.
- Repeat the exercise for every finger, focusing on the DIP joint.
It’s crucial to begin those physical games with mild actions and progressively boom the depth as tolerated. If you revel in aches or pain throughout any exercise, you need to forestall and seek advice from a healthcare expert for guidance. Additionally, acting in those physical games frequently and constantly can assist in enhancing DIP joint flexion over time.
Special Test For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
There aren’t any precise unique checks which are extensively identified or usually used especially for assessing distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) flexion. However, there are some scientific maneuvers that may be beneficial in comparing the general characteristics and variety of movement of the fingers, such as DIP joint flexion. These checks are part of a complete evaluation of the hand and finger characteristics. Here are multiple such checks:
1. Finger Range of Motion (ROM) Assessment:
- The examiner instructs the affected person to actively flex and increase every finger, such as the DIP joint, to the greatest extent.
- The examiner observes and measures the variety of movements finished on the DIP joint.
- Any obstacles or regulations in DIP joint flexion may be mentioned for the duration of this evaluation.
2. Grip and Pinch Strength Testing:
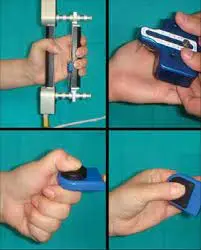
- Grip energy and pinch energy checking out offer an oblique evaluation of the characteristics and energy of the finger flexor muscles, such as the ones answerable for DIP joint flexion.
- Various dynamometers or pinch meters may be used to degree the energy of grip and pinch in kilograms or pounds.
- A lower grip or pinch energy might also additionally imply a weak point or disorder of the finger flexors, such as the ones worried about DIP joint flexion.
It’s critical to notice that those checks compare universal finger characteristics and energy, in place of especially focusing on the DIP joint flexion. If there are precise issues approximately DIP joint flexion, a complete exam via way of means of a healthcare professional, which includes a hand therapist or orthopedic specialist, might be suitable. They can carry out a radical evaluation, such as assessing the precise joint and muscle characteristics, and suggest suitable diagnostic checks or remedies primarily based on the findings.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
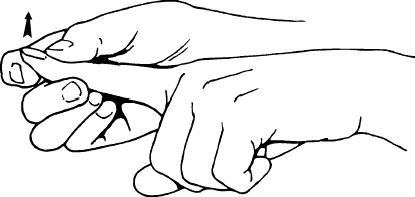
What Is Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension?
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) extension refers back to the straightening or motion that takes place on the DIP joint. Resulting in an inside attitude among the center phalanx and the distal phalanx. In easy terms, it’s the motion of straightening the finger or toe, extending the end far from the palm or sole.
When the DIP joint is prolonged, it lets in the finger or toe to be located in an immediate or prolonged function. This is the other motion to flexion, in which the DIP joint is bent. DIP joint extension is essential for numerous activities, which include liberating objects, accomplishing items, and attaining a practical and prolonged function of the hands or toes.
The muscle groups chargeable for DIP joint extension are in the main the extensor digitorum communes (inside the hands) and the extensor digitorum brevis (inside the toes). These muscle groups originate from the forearm or leg and make bigger right all the way down to the hands or toes, in which they connect to the extensor hood mechanism and assist in manipulating the extension of the DIP joint.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extensors Muscles
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) extension inside the hands is mainly managed through the subsequent muscle tissue:
- Extensor digitorum communis: This muscle originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the posterior floor of the ulna. It extends down the forearm and divides into 4 tendons that tour via the extensor hood mechanism. These tendons insert into the bottom of the center phalanx and make a contribution to DIP joint extension.
- Extensor indicis proprius: This muscle is an extension of the extensor digitorum communis and is liable for extending the index finger. It has a separate tendon that inserts into the index finger’s distal phalanx, bearing in mind DIP joint extension.
- Lumbricals: While mainly liable for DIP joint flexion, the lumbrical muscle tissue additionally makes a contribution to DIP joint extension whilst the hands are actively prolonged towards resistance.
In the toes, the DIP joint extension is managed through the extensor digitorum brevis muscle, which is a small muscle placed at the pinnacle of the foot. It extends from the calcaneus (heel bone) and divides into 4 tendons, every of which extends into the respective toe. The tendons insert into the bottom of the center phalanx, facilitating DIP joint extension inside the toes.
These muscle tissue paintings collectively provide extension on the DIP joint and are vital for sports which include greedy objects, freeing items, and accomplishing a straightened function of the hands or toes.
Range Of Motion Of Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
The regular variety of movement for distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) extension inside the hands is usually around zero to 70 degrees. This way the hands may be prolonged or straightened from a function in which the DIP joint is bent or flexed (around zero degrees) to a function in which the DIP joint is completely prolonged (around 70 degrees).
However, it’s vital to be aware that there may be a few herbal versions inside the variety of movement among people or even among exclusive hands inside the identical individual. Additionally, elements along with age, joint health, preceding injuries, and positive clinical situations can have an effect on the variety of movements of the DIP joint.
A healthcare professional, along with a hand therapist or orthopedic specialist, can carry out an in-depth evaluation of the DIP joint extension and degree of the variety of movement with the use of a goniometer, which is a specialized device for measuring joint angles. This assessment allows for deciding of whether there are any limitations, restrictions, or abnormalities in DIP joint extension and the publication of a suitable remedy or rehabilitation plan if necessary.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension Test
To test distal interphalangeal joint extension (DIP), do the following.
- Positioning: Make sure the person being tested is comfortable and sitting. Their arms or legs should be accessible for examination.
- Stabilization: Hold the person’s arm or leg firmly to prevent unnecessary movement during the test. 3. Test: Gently grasp the tip of your finger or toe and slowly extend it, trying to fully extend it. Observe the person’s movement and any obstruction or discomfort.
- Comparison: Compare the tested finger or toe with others on the same hand or foot. Look for significant differences in tightness, pain, or swelling.
- Feedback: Ask the person if they feel any pain, discomfort, or limitations during the test. This information can provide valuable information about the health of these joints.
Keep in mind that unless you are a trained medical professional, it is best to have this test performed by a qualified healthcare provider to ensure accurate evaluation and correct interpretation of the results.
Exercise For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
Here’s an exercise to help stretch the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP):
1. Finger extension:
- In a relaxed position, begin sitting or standing.
- The fingers of your outstretched hand should be facing you.
- Start with one finger at a time. With the other hand, gently press down on the tip of the finger, encouraging the DIP joint to flex.
- Release the pressure and extend the bent finger as far as possible in the DIP joint. For a few seconds, maintain this stretched posture.
- Repeat the process with each finger of both hands.
- Does this stretch several times a day, gradually improving the range of motion of the DIP joints?
- Remember, it’s important not to push your joints beyond their comfort level. If you experience pain or discomfort during exercise, stop and contact a health professional. If you have existing joint conditions or medical problems, it’s a good idea to seek advice from your doctor or physical therapist before starting any new exercises.
Here is a simple exercise to improve distal interphalangeal joint extension (DIP):
2. Finger Tapping Exercise:
- Start off in a relaxed stance, either sitting or standing.
- Place your hand on a table or any flat surface, palm down.
- Lift one finger at a time, starting with the thumb. Gently tap the table with the tip of your finger while holding the other fingers.
- After touching each finger, release it back to the table.
- Repeat the tapping motion with each finger through the thumb, index, middle, ring, and pinky fingers.
- Do this exercise for a few minutes each day, gradually increasing the speed and intensity as your DIP joint flexibility improves.
This exercise helps engage and stretch the DIP joints, which promotes better stretching and flexibility.
Special Test For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
One specific test to assess distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint extension is called the “Mallet Finger Test” or “Baseball Finger Test.” This test is used to detect extensor tendon injuries or DIP joint avulsion fractures. This can be done as follows.
1. Club Finger Test:
- Get them comfortable by asking them to sit or stand.
- Hold their hand, palm down, on a flat surface.
- Ask them to hold all their fingers straight while you hold the other fingers down.
- Gently and slowly try to extend the distal finger (tip) of the affected finger. See if they can extend their finger all the way by themselves.
- If they are unable to actively extend the DIP joint and the fingertip remains flexed, this may indicate a club finger injury.
If the fingertip does not straighten on its own during this test, it may indicate tendon damage or an avulsion fracture of the DIP joint. If you suspect an injury based on this test, it is important to contact your healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Summary
Distal interphalangeal joint flexion refers to the bending or motion that takes place on the DIP joint. Resulting in a lower withinside attitude between the center phalanx and the distal phalanx. Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexores Muscles are Flexor digitorum profundus, Lumbricals, Interossei muscle and Flexor digiti minimi brevis. Exercise For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion is Passive DIP Joint Flexion, Active DIP Joint Flexion, Rubber Band Resistance, and Hand Grips or Squeezes. Special Test For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion is Finger Range of Motion (ROM) Assessment and Grip and Pinch Strength Testing.
The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) extension refers back to the straightening or motion that takes place on the DIP joint. Resulting in an inside attitude among the center phalanx and the distal phalanx. Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extensors Muscles are Extensor digitorum communis, Extensor indicis proprius and Lumbricals. Exercise For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension is Finger Extension and Finger Tapping Exercise. The special Test For Distal Interphalangeal Joint Extension is Club Finger Test.
FAQs
Extension of the interphalangeal joint of the thumb is carried out by the extensor tendon (pollicis longus). The proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of fingers 2-5 are expanded by the extensor muscles, lumbar vertebrae, and dorsal interossei.
Two extensors and one flexor of the forearm insert directly into the bases of the distal fingers, making these actions possible. These include flexor digitorum flexors, flexor pollicis longus, and extensor tendon support.
The DIP joint of the finger is located at the tip of the finger just before the beginning of the nail. Common problems with this joint include Mallet Finger, Jersey Finger, arthritis, mucoid cysts, and fractures. The PIP joint is the first joint in the finger and is located between the first two bones of the finger.