Wrist Bursitis
Table of Contents
What is Wrist Bursitis?
Wrist bursitis is a condition in which the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles, become inflamed and painful. The bursae in the wrist are located near the joints and can become inflamed due to repetitive motion, injury, or infection.
Symptoms of wrist bursitis can include pain, swelling, warmth, and redness around the affected area. Treatment options for wrist bursitis may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE therapy), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy, and in some cases, aspiration or surgical removal of the inflamed bursa.
If you suspect you have wrist bursitis, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional who can properly diagnose and treat the condition.
- Wrist bursitis is a rash of a bursa, which is a little sack of liquid that permits oil the action of tendons over bone. There are two bursas in a wrist, and repetitious trauma or friction can push them to become inflamed. Treatment concerns rest and decreasing inflammation. It is a discouraging condition that occurs when a bursa in the wrist becomes bloated and inflamed.
- A bursa is a small sac that perspires a lubricating liquid called synovial fluid which reduces friction between tissues, serves as a cushion between the muscles, tendons, and bones, and helps oil the joints to move freely.
- There are more than 150 Bursae in Human Body. There are two bursae in the wrist, both of which can produce bursitis:
- Radial bursa
- Ulnar bursa
Causes & anatomy
- Bursas are all over the body, in locations where wimpy tissues may scratch against each other or the underlying bone. Wrist bursitis involves people who manage to place a lot of weight on their hands, for example, Cyclists.
- There are two bursas in the wrist; Radial Bursa and Ulnar Bursa.
- The Ulna Bursa protects the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus muscles, more centrally on the palm side of the wrist.
- The causes of bursitis are either a sudden concussion or redundant stress/overuse. In the latter, the bursa becomes inflamed and puffy due to repetitious conflict.
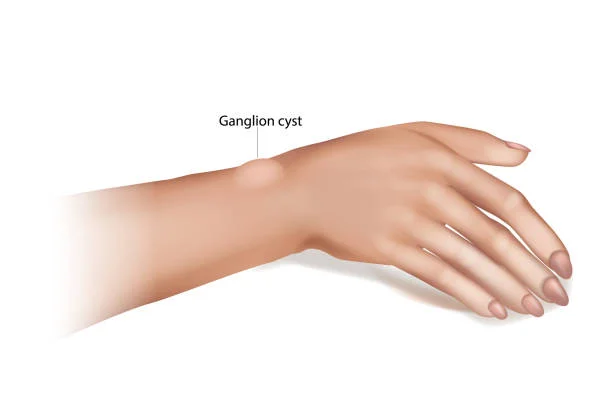
Symptoms of Wrist Bursitis
Symptoms of wrist bursitis contain:
- Pain on weight-bearing
- A small node or swelling on the lid of the wrist
- Tenderness stuffing in
- May heat to the touch
- Achy, rigid wrist
- Quick shooting pain or pain that gets worse when you push your wrist or press on it
- Limited range of motion
- Wrist pain, especially when opening (bending backward)
Treatment of Wrist Bursitis
Treatments for wrist bursitis can contain:
- Using ice, resting your wrist, and avoiding movements
- Physiotherapy
- Medicines, including:
- Topical medications such as lotions, sprays, gels, or patches
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), either specified, or over-the-counter, such as Advil, Motrin, or Aleve
- Antibiotics (if your wrist bursitis is induced by an infection)
- Draining a distended bursa of excess fluid with a needle and needle which can then be tested at a lab to determine if the bursa is infected
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation (only if the cause is not due to infection)
- Surgery
- Surgical reduction of the bursa is very rare. If surgery is required after other less invasive therapies have not helped, physiotherapy is an important part of the restoration.
Physiotherapy for Wrist Bursitis
- Physiotherapy is a drug-free and non-surgical therapy that concentrates on reducing discomfort and swelling, regaining strength, increasing joint mobility and process, and preventing reproduction.
- At pt Health, you’ll receive a thorough assessment that addresses the basis of your issue.
- Depending on your separate needs, physiotherapy for wrist bursitis can include: As with most types of damages, early diagnosis and proper therapy for wrist bursitis give you a better option of healing at a quicker rate. After an exhaustive evaluation, treatments will largely depend on the severity of your situation, but may include any of the following hand therapy options:
- Heat and cold treatment following the PRICE protocol
- Stretching, strengthening, and range of motion movements
- Activity changes and functional retraining
- Patient Education
- Assistive gadgets such as bracing or splinting
- Cross-disciplinary pain-relieving therapies such as:
- Therapeutic ultrasound
- Hand treatment
- Acupuncture
- Interferential current therapy (IFT)
- Analysis of a range of movement
- Occupational therapy
- Education regarding appropriate activities to allow for recovery to occur
- Rest and apply cold treatment if it is acute or painful. Use a reduction bandage to help decrease swelling.
- A doctor may define anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen. Ultrasound treatment may be used to help relieve pain and inflammation. In more extreme cases the bursa can be aspirated, where a needle is inserted to stink out the liquid, although it is likely the bursa will bear. Bursitis usually breaks down after a week or so if it is gone to heal.
FAQs
How do you dine bursitis of the wrist?
Most cases of wrist bursitis can be relieved with conventional treatment, such as rest, ice or cold remedy, an anti-inflammatory drug, and a drop bandage to help reduce bumps, and surgery is not usually required.
What are the 3 signs of bursitis?
Pain.
Localized tenderness.
Limited motion.
Swelling and redness if the inflamed bursa is near the cover of the skin.Can bursitis be cured?
Bursitis generally gets nicely on its own. Conservative measures, such as rest, ice, and taking a pain reliever, can relieve pain. If conservative measures don’t work, you might need Medication.
At what age does bursitis begin?
Bursitis is typical in adults, especially after age 40. It’s usually pushed by recited pressure on an area or by using a joint too much.
How long does it take for bursitis to recover in the wrist?
Bursitis is when a joint evolves painful and swollen. It can usually be feasted at home and should go away in a periodic week.