Wilson’s test
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Wilson’s Test is a diagnostic test for osteochondritis dissecans of the knee. Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the knee is an idiopathic, focal, subchondral bone abnormality that can cause instability or detachment of bone and the overlying articular cartilage, resulting in osteoarthritis.
Data presented at the SoFCOT Symposium (2005) showed that the median age at diagnosis was 16.5 years.
Technique
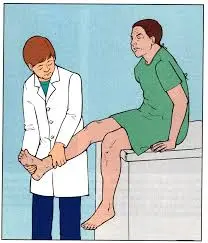
The test must be performed as follows:
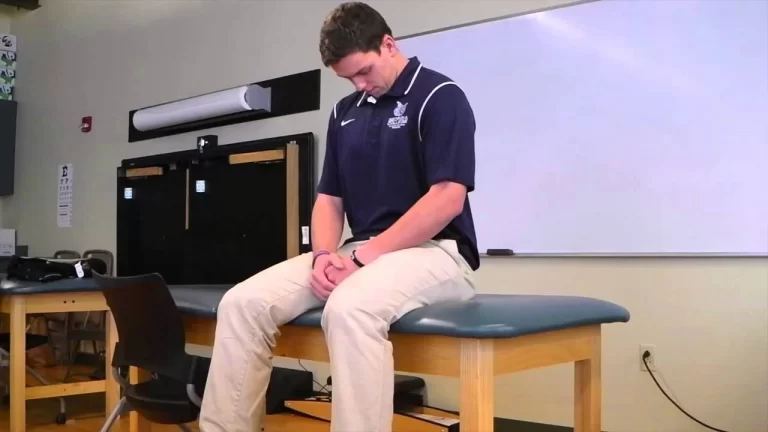
- Request that the patient sits on a table, his legs dangling over the side.
- Bend the patient’s knee so that it is 90° flexed.
Grasp the patient’s foot and rotate the tibia inside.
Instruct the patient to stretch his or her leg until discomfort is felt.
The test is positive when the patient reports discomfort in the knee around 30° from full extension and when the pain is relieved by turning the foot back (external rotation of the tibia) to its usual position.
What is Wilson’s test?
Wilson’s test is used to detect the presence of osteochondritis dissecans in the medial femoral condyle of the knee.
Internal rotation in the Wilson test
Internal rotation causes the tibial impingement on the osteochondral dissection lesion of the medial femoral epicondyle of the knee, causing pain.
External rotation in the Wilson test
External rotation moves the prominence away from the lesion, which relieves pain.
Important points in the Wilson test
The upper cartilage is destroyed by osteochondritis dissecans, an aseptic necrosis that affects the subchondral bone of the articular surfaces.
This developed part of the articular cartilage and the underlying bone can separate, creating an intra-articular loose body. Osteochondritis dissecans should always be considered in young people with knee pain and joint effusion.
Key studies
To date, there have been no studies on the validity and reliability of this test.
Clinical background
Make sure the patient extends the leg gradually during the test, rather than pushing it out quickly.
FAQ
What is Wilson’s knee test?
A good test for OCD is the Wilson test, where the knee is bent 90 degrees and the tibia internally rotated, then the knee is extended. Usually, pain can be seen at about 70 degrees of flexion around the medial femoral joint.
What is Wilson’s test?
The Wilson test is a test used to detect osteochondritis of the knee.
How is osteochondritis dissecans diagnosed?
To diagnose osteochondritis dissecans, the doctor performs a physical examination and assesses the stability of the joint. Your doctor may order tests, including the following: X-rays that show the bone, locate the lesion, and reveal its size. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound.
Reference
Wilson’s test. (n.d.). Physiotherapy. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Wilson’s_Test
O. (2022, May 25). Wilson’s test | OrthoFixar 2023. OrthoFixar. https://orthofixar.com/special-test/wilson-test/
Zaremski, J.L., Herman, D.C. Kaj Vincent, K.R. (2015, January 1). Clinical use of the Wilson test for osteochondral lesions of the knee. Current Sports Medicine Reports; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. https://doi.org/10.1249/jsr.0000000000000203
Verma, R. (2023, July 3). Wilson Test (last 2023) – Physical Examination. Physical examination. https://physio-study.com/wilson-test/
Wilson’s test – wiki doc. (n.d.). https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Wilson’s_test
Examination of the knee. (2022, September 14). Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knee_examination


![Test for tight retinacular [ collateral ] ligaments](https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Test-for-tight-retinacular-_-collateral-_-ligaments.webp)