Anterior Drawer Test Of The Shoulder
Purpose
- The objective of the anterior drawer test of the shoulder is to examine instability in the anterior shoulder.
- We have been able to reliably diagnose anterior subluxations even in patients who may have a negative apprehension test because it can also be used on aching shoulders where the apprehension test is difficult to interpret.
Technique of the Anterior Drawer Test Of The Shoulder
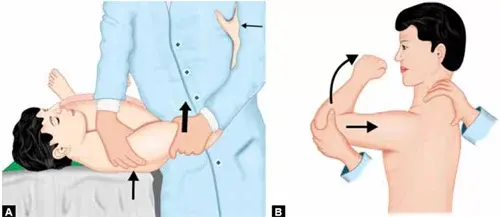
- The patient lying down.
- Holding the patient’s arm or placing one hand on the axilla while the therapist uses one hand helps to relax the affected shoulder.
- The patient’s shoulder should be abducted between 80 and 120 degrees, with forward flexion of up to 20 degrees and a lateral rotation of up to 30 degrees.
- Push the spine of the scapula with the index and middle finger to stabilize the patient’s scapula with the opposite hand of the therapist. Using the therapist’s thump to apply counterpressure to the patient’s coracoid process.
- uses the hand that is holding the patient’s arm or the hand that is placed on the axilla to move the humerus forward (anteriorly).
- A positive test indicates anterior instability by comparing the amount of accessible anterior translation to the normal side.
| Grade | Diagnosis |
| grade 0 | Minimal displacement |
| grade 1 | The humeral head touches the glenoid rim |
| grade 2 | The humeral head may be dislocated, however spontaneously resolved |
| grade 3 | A humeral head may not be spontaneously decreased. |
FAQs
If the tibia, or shinbone, has greater development, or then again assuming that the tendon is free contrasted and the other knee, the foremost cabinet test is viewed as sure.
An in-depth medical history, a radiological examination, and the following three specific tests are all used to diagnose anterior shoulder instability: fear, relocation, and surprise (release) test. Traumatic anterior glenohumeral instability is strongly predicted by these tests, which are highly specific.
In the event that the tibia pulls forward or in reverse more than typical, the test is viewed as sure. While excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury to the posterior cruciate ligament, excessive anterior displacement of the tibia suggests injury to the anterior cruciate ligament.
Purpose: to check the ankle for ligamentous laxity or instability. The Anterior Talofibular Ligament’s strength is the primary focus of this test.
The anterior drawer sign is less sensitive than the Lachman test. When the knee is only in a flexion range of 20-30 degrees, it may be difficult for the patient to contract his hamstrings, preventing the tibia from sliding forward.