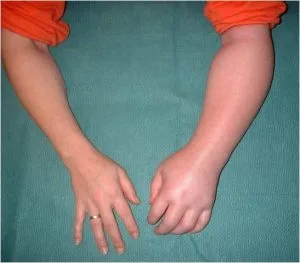
SPASTICITY IN LEG
Table of Contents
What is Spasticity in legs?
- Spasticity in leg may be as mild as the feeling of tightness of muscles of leg or may be so severe as to produce painful, uncontrollable spasms of extremities, usually of the legs.
- Spasticity may also produce feelings of pain or tightness in and around joints, and can cause low back pain.
Causes of Spasticity in Leg :
- Spasticity in leg mostly occurs in central nervous system (CNS) disorders.
- Spasticity is generally caused by damage or disruption to the area of the brain and spinal cord that are responsible for controlling muscle and stretch reflexes.
- These disruptions can be due to an imbalance in the inhibitory and excitatory signals sent to the muscles, causing them to lock in place.
- Spasticity can be harmful to growing children as it can affect muscles and joints.
- People with brain injury, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis can have varying degrees of spasticity.
Symptoms of Spasticity in leg :
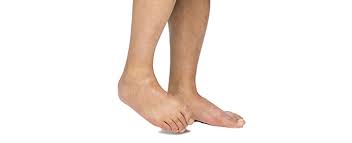
Spasticity in the Leg mainly seen in flexor group of Muscles. eg. Calf and Hamstring muscle spasticity are most common.
- Increased muscle tone of leg
- CTEV Deformity. (Congenital Telipus Equino Varus) also called clubfoot
- Overactive reflexes
- Muscle stiffness, causing movements to be less precise and making certain tasks difficult to perform.
- Muscle spasms, causing uncontrollable and often painful muscle contractions.
- Involuntary crossing of the legs.
- clonus – rapid muscle contractions
- exaggerated deep tendon reflexes
- fixed joints
- Muscle and joint deformities.
- Muscle fatigue.
- Inhibition of longitudinal muscle growth.
- Pain or discomfort
- Less ability to function
- Problems with care and hygiene
- Abnormal posture
- Contractures (permanent contraction of the muscle and tendon due to severe lasting stiffness and spasms)
- Bone and joint deformities
- scissoring – involuntary leg crossing
Trigger spasticity in leg :
- Spasticity is generally caused by damage or disruption to the area of the brain and spinal cord that are responsible for controlling muscle and stretch reflexes.
- These disruptions can be due to an imbalance in the inhibitory and excitatory signals sent to the muscles, causing them to lock in place.
Spasticity in legs look like :
- Spasticity symptoms include continuous muscle stiffness, spasms and involuntary contractions, which can be painful.
- A person with spasticity may find it difficult to walk or perform certain tasks.
- Spasticity in children can result in growth problems, painful and deformed joints and disability.
Muscle spasticity feel like:
- Symptoms of spasticity can vary from being mild stiffness or tightening of muscles to painful and uncontrollable spasms.
- Pain or tightness in joints is also common in spasticity.
Complications of Spasticity :
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Chronic constipation
- Fever or other systemic illnesses
- Pressure sores
- Frozen joints
Test for leg spasticity:
- For Good Measure. One quick and easy way to measure spasticity is the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS).
- The MAS measures resistance during passive soft-tissue stretching.
| Scale | Description |
| 0 | No increase in tone |
| 1 | Slight increase in tone , catch / release at end ROM |
| +1 | Slight increase in tone , catch / release and resistance through at ROM ( 1/2 ROM ) |
| 2 | More marked increase in tone through ROM , but affected part move easily |
| 3 | Considerable increase in tone , passive movt. difficult |
| 4 | Affected part in rigid flexion & extension |
Treatment of Spasticity in Leg :
Spasticity in Leg can be reduced by Oral Medicines Prescribed mainly by your doctor or Physician and Physiotherapy Treatment mainly exercise and Ice Pack Helps.
Medical Treatment :
If the spasticity is sever (Grade 2 to 3 ) in the leg then systemic medication is used. This commonly prescribed Medicines are :
- Dantrolene (Dantrium)
- Baclofen (Lioresal and others)
- Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
- Diazepam (Vallium)
- Benzodiazepines
- Gabapentin
- Pregabalin
- Canabinoids
If the spasticity is locallised then local medication is used.
This medicines are :
- Boutulinum Toxin (Botox)
- Regional Nerve Block
- Intrathecal medications can also be used. These include:
- Baclofen
- Phenol
Physiotherapy Treatment for Spasticity in Leg :
- Physiotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for spasticity, and is designed to reduce muscle tone, maintain or improve range of motion and mobility, increase strength and co-ordination, and overall improve mobility and comfort.
- Standing. Standing frame. Treadmill training (body-weight supported if needed) Tilt table.
- Active exercises.
- Passive movements.
- Functional electrical stimulation.
- 24 hour positioning management.
- Splinting and the use of orthotics.
- Long Muscle Stretching Exercise.
Spasticity can be reduced by:
- Performing stretching exercises daily.
- Prolonged stretching can make muscles longer, helping to decrease spasticity and prevent contracture.
- Splinting, casting, and bracing. These methods are used to maintain range of motion and flexibility.
Exercise Helps Reduce spasticity :
- Spasticity is increased resistance felt on a passive stretch of a muscle caused by damage to part of the central nervous system (the brain or spinal cord) that controls voluntary movements.
- Spasticity is also accompanied by muscle weakness and sensory loss as well as pain and soft tissue contractures.
To Break spasticity :
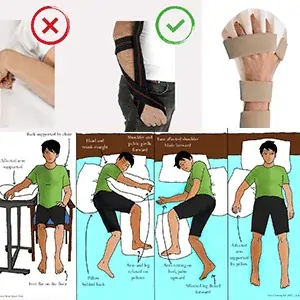
- Exercises. Physiotherapy and occupational therapists can teach you stretching, positioning and exercise activities that may help maintain range of motion and prevent shortening or tightening of the muscles (contracture).
- Positioning, prolonged muscle stretching, splinting, and motor-level stimulation were indicated as modalities most commonly used by clinicians to manage spasticity.
- The most commonly indicated treatments for spasticity, in descending order, were positioning, prolonged muscle stretching, splinting, motor-level stimulation, other treatment modalities, vibration, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), traction, and prolonged icing.
Following Exercises for spasticity :
Weight-bearing Exercise
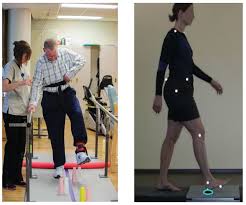
- Any weight bearing of the upper extremity either at the wall, table, or floor helps sends signals to the brain that reminds it the arm is still there.
- Strengthening can improve spasticity in two ways.
- By strengthening the antagonist (opposing) muscle, it can help inhibit the reaction of the spastic muscle.
- If you are able to get your arm or leg (where the spasticity is) in a straightened position, performing weight-bearing exercises is an excellent treatment for spasticity.
Stretching Exercise :

- Flexibility exercise mainly stretching the muscle and tendon to its full length and moving the joint through its full range.
- These activities decrease muscle tightness and prevent loss of full range of motion which may occur with decreased activity, weakness, or spasticity. Hold stretches for 30–40 seconds, as tolerated.
Icing reduce spasticity :
- Efferent and afferent neurotransmission is reduced through prolonged use of ice, which is effective for the reduction of spasticity.
- In order to achieve this, the muscle spindles need to be cooled requiring that ice is applied until there is no longer an excessive reflex response to stretching.
Heat help spasticity
- Sometimes heat or ice can be used to temporarily relax a spastic muscle. Warm baths or swimming pools can also help to relax a spastic muscle.
- Medications Sometimes the effects of spasticity can be improved by medication.
Massage help with spasticity:
- Massage therapy helps relax spastic muscles by manually lengthening the shortened muscle fibers.
- By reducing muscle tone, massage therapy helps improve range of motion, motor control, and flexibility.
Massage good for leg cramps :
- If you have a cramp, these actions may provide relief: Stretch and massage.
- Stretch the cramped muscle and gently rub it to help it relax.
- For a calf cramp, put your weight on your cramped leg and bend your knee slightly.
Walking help in spasticity :
- When the researchers looked at the results of the walking tests they found that the PF spasticity did not have an effect on walking performance.
The following tips will help you find quick relief:
- Get up and walk around.
- Distract yourself with a game or activity.
- Apply hot or cold packs to your legs.
- Try calf stretches, yoga poses, knee bends, or a simple ankle or foot rotation.
- Relax your muscles with massage or a hot bath.
Yoga help spasticity:
- Eisenberg says yoga has the potential to lessen several physical symptoms of MS and may contribute to improved strength, flexibility, posture, balance, focus, circulation, digestion, elimination, and pelvic floor health and to decreased tension, fatigue, and spasticity.
Can spasticity be permanent?
- Spasticity can range from mild to severe, and in many cases can interfere with normal daily activity, including walking, movement, and speech.
- Over time, untreated spasticity can lead to permanent contracting and shrinking of muscles, which may lock joints into a single position.
- But continue physiotherapy exercise and Proper Medical treatment helps to reduce spasticity.
Splint / Orthosis to Reduce Spasticity in leg :
Spasticity in Leg also reduced with the help of Splint and Orthosis, For Spasticity in Calf Muscles, then AFO (Ankle Foot Orthosis) are highly recommended by your doctor’s. Derotation with AFO splint also prescribed if leg is externally rotated.