Quadriceps muscle Tightness and Pain
Quadriceps muscle Pain are due to muscles tightness are most cause of pain in Front Part of Thigh. This can leads to difficulty in performing day to Day activity like Walking, Cross leg sitting, running and stair climbing.
Sometimes the Quadriceps pain can occur after trauma or an injury. Other times, it may starts for no proper reason.
- While increased activity on your feet may lead to tight quads, so can inactivity.
- Sitting for hours reduces the amount of time you spend lengthening and shortening these muscles.
- With increased sitting, the quads become static and more resistant to lengthening or stretching
- When the quads get really tight, they pull on the hip bone, which in turn tips the whole pelvis downward, or forward, into a position technically called anterior tilt of the pelvis.
- stretch the muscle and relive the tightness
Table of Contents
Where is quadriceps located ?
Quadriceps muscles anatomy :
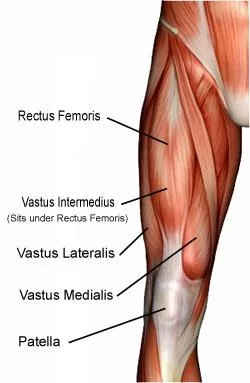
- It is located in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
- The four 4 sub-components are:
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus lateralis
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus intermedius
Origin:
- The muscles that form the quadriceps femoris unite proximal to the knee and attach to the patella via the quadriceps tendon.
- In turn, the patella is attached to the tibia by the patella ligament.
Vastus Lateralis :
- Proximal attachment: Originates from the greater trochanter and the lateral lip of linea Aspera.
- Actions: Extends the knee joint and stabilizes the patella.
Vastus Intermedius :
- Proximal attachment: Anterior and lateral surfaces of the femoral shaft.
- Actions: Extends the knee joint and stabilises the patella.
Vastus Medialis :
- Proximal attachment: The intertrochanteric line and medial lip of the linea aspera.
- Actions: Extends the knee joint and stabilizes the patella, particularly due to its horizontal fibers at the distal end.
Rectus Femoris :
- Attachments: Originates from the ilium, just superior to the acetabulum. It runs straight down the leg (the Latin for straight is rectus), and attaches to the patella by the quadriceps femoris tendon.
- Actions: The only muscle of the quadriceps to cross both the hip and knee joints.
- It flexes the thigh at the hip joint, and extends at the knee joint.
- Innervation of these muscles is by the femoral nerve. (L2, L3, L4)
Artery :
- The lateral femoral circumflex artery.
Action :
- The quadricep muscles all work to extend (straighten) the knee.
- The rectus femoris also flexes the hip,.
- The vastus medialis adducts the thigh and also extends and externally rotates the thigh and stabilizes the kneecap
- The quadriceps are primarily active in kicking, jumping, cycling and running. eg sports like basketball that requires jumps.
- In everyday life, they help you get up from a chair, walk, climb stairs and squat.
- They are used in walking and running at the onset of a stride and get used significantly when going downhill.
Which causes are common in Quadriceps muscle tightness?
- While increased activity on your feet may lead to tight quads
- overuse the muscle
- Any hip or knee pathology
- After Injury or Trauma
- Sedentary Lifestyle eg. office workers
Which Symptoms are common in Quadriceps muscle tightness?
- Sudden pain in the front part of the thigh.
- Pain, swelling, or bruising
- Knee Pain especially when resistance is applied to the muscles
- Quadriceps Muscle fatigue
- Difficulty in walking, jumping, Stair Climbing
Which Special test for Quadriceps muscle tightness are used?
Ely’s test :
Purpose :
- Ely’s test or Duncan-Ely test is used to assess Quadriceps femoris spasticity or tightness.
Technique :
- The patient lies prone in a relaxed state.
- The therapist is standing next to the patient, at the side of the leg that will be tested.
- One hand should be on the lower back, the other holding the leg at the heel.
- Passively flex the knee in a rapid fashion.
- The heel should touch the buttocks.
- Test both sides for comparison.
- The test is positive when the heel cannot touch the buttocks, the hip of the tested side rises up from the table, the patient feels pain or tingling in the back or legs
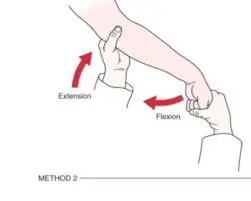
Kendall test :
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatment for Tight Quadriceps Muscles is mainly Stretching and Strengthening exercise with Pain relieving Modalities in Painful area eg. Hot Pack, Cold Pack, TENS, IFT (Interferential Therapy), SWD (Short Wave Diathermy)
Quadriceps muscle pain treatment :
- Quadriceps muscle pain treatment is anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants (NSAIDs). These medications are the most commonly used.
- Massages of Quadriceps Muscles – Various massage techniques are used to ease pain and relax muscles.
Exercise for quadriceps muscle :
Quadriceps Muscle exercise divided mainly into two types :
- Quadriceps Muscle stretching Exercise
- Quadriceps Muscle strengthening Exercise
Quadriceps muscle stretching :
The Lying Quad Stretch :
- The best quad stretches are those that address not just the quadriceps, but all aspects of your leg, from the hip to the thigh, to the foot.
- The lying quad stretch is great for people who suffer from knee pain, as well as those who prefer reclining to standing up.
- Lie in a face-down position, propping your head on your left hand.
- Alternatively, you can lie on your side to perform this stretch.
- After a couple of seconds, pull your right foot toward your butt and bend your left knee to stabilize yourself.
- Hold onto your ankle and maintain the position for 30 seconds before returning to the starting position.
- Switch sides, pulling your left foot toward your back and bending your right knee.
The Simple Quad Stretch :
- This simple stretch exercise is great for fixing your muscles, anytime, anywhere.
- Stand on your left leg, one knee touching the other. You can hold a chair or the wall to keep you steady if needed.
- Grab your right foot, using your right hand, and pull it towards your butt. Be sure to push your chest up and hips forward. Try not to worry about pushing your foot too close to your backside; your focus should be on feeling the stretch in your quad muscle and pushing your hips forward to get a good hip flexor stretch.
- Hold the position for 20 to 30 seconds, then repeat, switching from your left leg to your right.
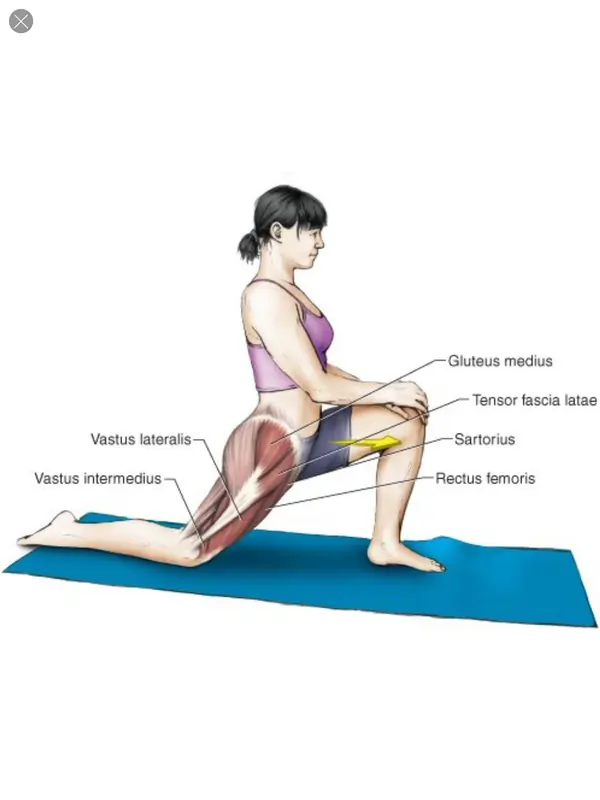
The Kneeling Quad Stretch :

- A slightly different form of quad stretch, this position will help to loosen the muscles just above the knee joint, increasing mobility and preventing knee pain.
- Start the stretch in a high lunge position, with your left foot forward.
- Carefully drop your right knee to the floor and take a moment to find your balance.
- Once you’re ready, reach back with your right arm, and grab your ankle, or toes, depending on what’s easiest.
- Hold the position for 30 seconds, keeping your body steady. Push a little further to get a hip flexor stretch as well.
- Gradually come back into the starting position and switch from your left foot to your right.
Lying Pigeon Progression :
- Some of the best quad stretches originate from yoga.
- This particular pose is an excellent way to stretch not only your quads but your quadratus lumborum (back) as well. It’s also a great hip flexor stretch and can help you progress to the pigeon and pigeon twist stretches.
- Place a mat on the floor and lie face down.
- Secure a resistance band around your left foot, with the excess band in a reachable area.
- If you don’t have a resistance band handy, you can use a towel instead.
- Grab the band with your left hand. While keeping your right leg extended, bend your left knee, keeping your toes pointed toward the ceiling.
- Use the resistance band to pull forward until you feel the stretch. Hold for twenty seconds then pull further.
- Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side.
- pigeon_alternative
The Frog Pose :
- If you’re looking to stretch out the gluteus maximus and the thighs, then this could be a great stretching pose for you. It will also help to stretch your arms, chest, and shoulder blades.
- Begin by lying on your stomach, propping your torso up on your elbows.
- Bend both of your knees and reach back to hold onto your feet. You should already feel the stretching at this point. If you lack the mobility to do this now, use a towel to fill the gap.
- Adjust your fingers to point the same way as your toes, then carefully lift up your elbows to point to the ceiling.
- Push your chest up as high as you can.
- Stop the pose completely if you feel any pain in your hip or knee.
- Stay here for five breaths, then relax.
Quadriceps muscle strengthening exercises :
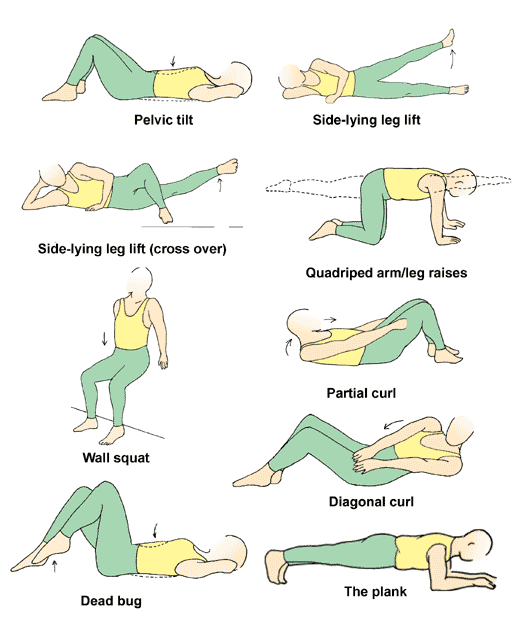
Quadriceps muscle isometric Exercise :

Flexibility exercise :



3 Comments