Patellar Tendinopathy:
Patellar Tendinopathy is sometimes known as ‘jumper’s knee’ because this injury mostly happens during sports activities involving jumping, like basketball, netball & volleyball.
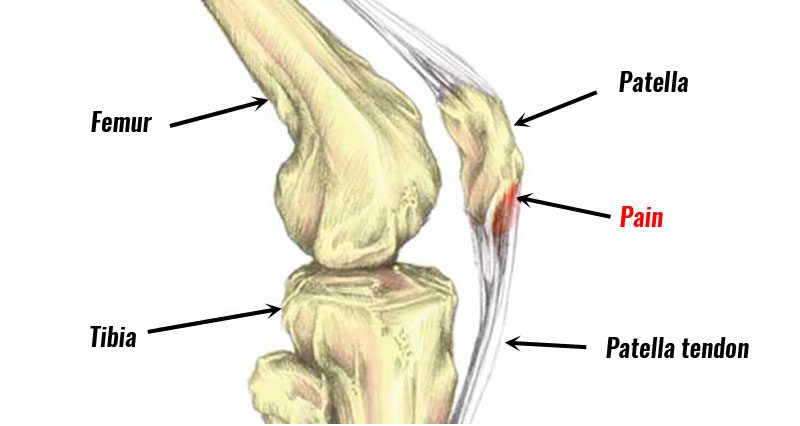
This condition is a source of anterior knee joint pain which is characterized by pain localized at the inferior pole of the patella bone.
This Pain is aggravated by loading & increased with the demand on the knee joint extensor musculature & release of energy in the patellar tendon.
This condition primarily occurs in relatively young (15-30 years old) athletes mostly men, who participate in sports activities like volleyball, basketball, Tennis, and football & athletic jump events which require repetitive loading of the patellar tendon.
risk factor of this condition is gender, weight, and body mass index.
Table of Contents
What is the clinically relevant anatomy of Patellar Tendinopathy?
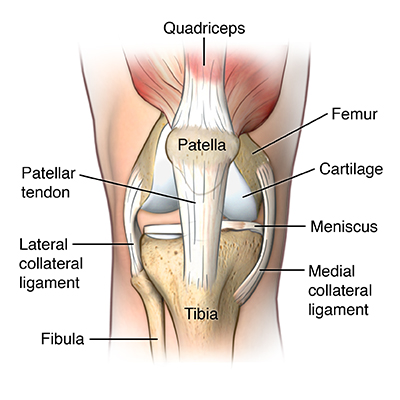
- Quadriceps muscles are connected to the inferior pole of the patella bone by the common quadriceps tendon through the patella, sesamoid bone.
- Then patellar ligament connects the bottom of the patella bone at the tibial tuberosity.
- The force is generated from the quadriceps muscles & acts through the patella bone as a pulley so that produces movement knee to extend.
- A healthy quadriceps tendon is composed mostly of parallel collagen fibers which are closely packed together.
- Other components of this tendon matrix are elastin (2%), inorganic components (0.2%) & proteoglycans (1–5%).
- All this collagen in tendons is held together with proteoglycan components Decorin & Aggrecan, which bind to the collagen fibrils at the specific locations.
- Tenocytes are a tendon which is specific fibroblast type cells that produce the collagen molecules, which cluster together & perform to collagen fibrils.
- These fibril bundles which is organized to form fibers that are elongated tenocytes with closely packed fibers between them.
- All cells communicate with each other through gap junctions & this signaling gives the ability to detect & respond to mechanical load.
- Blood vessels run parallel to collagen fibers of the tendon with some branching of transverse anastomoses.
What are the causes of patellar tendinopathy?
- This condition occurs due to an overuse injury, which is develop after repeated stress on your patellar tendon.
- It occurs when you are performing to jump a lot during the volleyball & basketball spots.
- When occur strain the patellar tendon so that jumping activities are damaged & gradually wear down your tendon.
- Does this strain occur due to overtraining
- Playing on hard surfaces
- Poor technique
What are the symptoms of patellar tendinopathy?
- You feel pain just below your kneecap.
- This pain probably starts with a gradual increase in pain, rather than occur to an injury suddenly causes.
- You feel this pain after exercise which is reduced after your warm-up.
- You are observing swelling & redness in the pain area.
What is the pathological process for Patellar Tendinopathy?
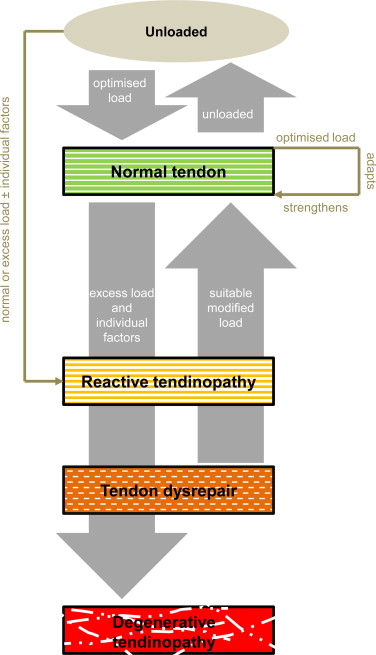
The pathological process of this condition includes 3 stages :
- Reactive tendinopathy
- Tendon disrepair
- Degenerative tendinopathy
This load is considered to be the primary stimulus which is the drive to tendon health forward & back along the continuum.
Reactive tendinopathy:
- It is a non-inflammatory proliferative response in the cell & matrix which occurs with acute tensile & compressive overload. in this stage increase in tenocyte proliferation & protein production.
- It produces a short-term adaptation & thickness in the tendon which is give to the net results of reducing stress by increasing cross-sectional area & allow for adaptation for compression.
- It is a different response from the normal tendon response to load, which generally occurs through tendon stiffening.
- Clinically these reactive tendinopathies occur with unaccustomed physical activity.
- Less commonly occur after a direct blow like falling directly onto the patellar tendon.
Tendon disrepair:
- The continued attempt at tendon healing is following the reactive stage but with a greater matrix breakdown.
- It is an increase in the number of cells present in the matrix, which is given to increase protein production.
- These increased proteoglycans give result in the separation & disorganization of collagen.
- It is also an increase in vascularity & neuronal growth.
- Clinically, this pathology stage is seen in chronically overloaded tendons & which appear across a spectrum of ages & loading environments.
Degenerative tendinopathy:
- There are some areas of cell death due to apoptosis, trauma & tenocyte exhaustion.
- There are some large areas of the matrix which are disordered & filled with matrix breakdown products, vessels & little collagen.
- It is little capacity for the reversibility of pathological changes at this stage.
- This pathological stage is primarily seen in the older person.
What is the clinical Presentation of the Patellar Tendinopathy?
It is one of the many potential diagnoses of this condition is presenting with anterior knee joint pain.
- You feel pain at the inferior pole of the patella bone.
- Load-related pain which is increases with the demand on the knee joint extensors which is notably in activities in the store or release the energy in the patellar tendon.
- You feel pain with the prolonged sitting, squatting & stairs activities, but these all symptoms are also felt you in the patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- You feel pain is rarely experienced in a resting state.
- Pain occurs instantly with loading & usually ceases immediately when the load is removed.
- This pain is improved with repeated loading.
- An important feature of this condition is dose-dependent pain which increases as the magnitude & rate of application of the load on the tendon increases.
- Practical application this an examination of pain which is increase when progressing from a shallow to a deeper squat position & from a smaller to a greater hop height.
- some aggravating activities are predominantly loading activities, like walking downstairs when performing a decline squat activities.
What are diagnostic Procedures for Patellar Tendinopathy?
- When you perform energy-storage activities it helps you assess clinically by observing jumping & hopping activities.
- Stiff-knee vertical jump-landing strategy is sometimes used by individuals with a history of this condition.
- A complete lower extremity examination is necessary to identify relevant deficits at the hip, knee & ankle/foot regions.
- This condition must be examined something & give to some common symptoms of this condition include :
- Reduced strength
- Atrophy
- Reduced ankle dorsiflexion
- Quadriceps and hamstring inflexibility
- Mal-aligned foot posture
- Swelling around the knee joint
- This all patellar tendon imaging is not confirmed patellar tendon pain in every situation so the doctor is advised to ultrasound imaging which is present in asymptomatic individuals.
What is the treatment of the Patellar Tendinopathy?
RICE principle:

When you feel muscle pain in the knee joint due to this syndrome doctor is advised to RICE principle as home treatment or primary treatment.
- R – rest = When you feel muscle pain doctor is advised to your rest for sometimes form of activity release to muscle pain, this means doing a total rest or even using the crutches & another mobility aid.
- I- ice = You are applied to ice on the area of the pain for the 20 minutes, release to swellings & muscle pain but always applied to the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice to prevent ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C – Compression = to the prevent form the additional swelling you are lightly wrapping the knee joint with the elastic bandage
- & also leaving to hole in the area of the kneecap or patella & but make sure the bandage is not to fits tight & not produce the additional pain.
- E – Elevation =if possible, rest with the knee joint raised higher than the heart by applying to pillow under the leg which helps you release swelling.
Medical treatment:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- This drug is used in the treatment of tendinopathy which remains controversial both in the acute & chronic stages.
- NSAIDs also help in impede soft tissue healing.
- The doctor is also advised of glycosaminoglycan polysulfate (GAGPS).
- You can also apply pain-relieving gel & spray like volini gel & spray on the area of muscle pain release to muscle pain & swellings.
Corticosteroid injections:
- These injections are used to decrease pain but also decrease cell proliferation & protein production which is used in the reactive tendinopathies.
- Repeated peritendinous corticosteroid injection is reduced to tendon diameter at 7 & 21 days after injection in tendons.
What is physiotherapy treatment for Patellar Tendinopathy?
When this syndrome pain is not relieved after the home treatment & pain medication then the doctor has advised physiotherapy treatment to release syndrome pain.
Physiotherapy treatment is help you relieve pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the muscle.
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy treatment & exercise therapy.
Massage:
- When the trigger & tender points are present in the syndrome pain area physiotherapist is advised to massage therapy release to these tender points.
- Massage is applied after 2 – 3 days of following the RICE principle when you are not feeling to release the syndrome pain.
- Massage is applied with the help of the oil & applied for 5 -10 minutes.
- Massage is applied 3 times per day at home.
Electrotherapy treatment:
After the RICE principle, pain medication & massage if the syndrome muscle pain is not relieved then used Electrotherapy treatment for releasing this syndrome pain.
To relive the swellings, spams & pain physiotherapist is advised to you electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the treatment therapist is used to many machines.
- When the trigger & tender points are present therapists are advised & to apply US = ultrasound therapy for the release of syndrome pain.
- This treatment is applied with the help of gel & applies for 5 to 10 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you release pain & swelling.
- Reduce to pain physiotherapist is applied to SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Interferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on the area of pain.
- SWD = Short wave diathermy is hot therapy for release to spams on the area of muscle pain.
- IFT = Interferential Therapy & TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of muscle pain.
- This therapy is applied for 10 minutes to the area of muscle pain.
Exercise therapy for this syndrome pain :
After following the RICE principle for the 2- 3 days at home & primary treatment & the help of pain medication, you feel released from the pain.
When you feel too comfortable & release from your muscle pain then the physiotherapist is advised to you exercise therapy reduce to muscle weakness & tightness.
The exercise therapy for muscle pain includes stretching & strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to relieve muscle tightness as well as strengthening exercise is help you relieve muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
After the follow of electrotherapy for 2-3 days for release to muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to stretch for release to muscle tightness.
This stretching is applied when your pain is released & when you feel comfortable.
- Quadriceps stretch
- Standing calf stretch
- Standing hamstring stretch
- Kneeling hip flexor stretch

- The starting position of this stretching is the standing position.
- You are standing with the left hand resting gently on something on a sturdy surface, such as to piece of the furniture.
- Try to pull the right foot toward the buttocks or grasp to the top of the right foot with the help of the right hand.
- Then point to the right knee joint toward the floor & you feel a stretch into the front of the leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & perform the 3 sessions per day.
Standing calf stretch:
- You are facing a wall & put your hands against the wall at about eye level.
- Must keep one leg back with the heel on the floor & the other leg forward.
- Try to turn your back foot slightly inward as you slowly lean into the wall till you feel a stretch in the back of your calf muscle. Hold this stretching position for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing hamstring stretch:

- You are standing upright with the spine in a neutral position.
- Place your leg in front of the body with the foot flexed.
- The heel pushed into the ground & the toe pointing toward the ceiling.
- Then slightly bend the left knee joint.
- Try to gently lean forward & place the hands on the straight leg.
- Must keep a neutral spine.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Kneeling hip flexor stretch:
- You are in a kneeling position on one knee joint, with your other leg in front of you at a 90-degree angle.
- Try to lean forward, bending your front knee joint slightly till a stretch is felt from the hip to the knee joint on the knee-down leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Switch legs & repeat this exercise.
- Perform in 2 sets.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow of Electrotherapy & massage for 2 -3 days to release this pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to you do strengthening exercises for muscle weakness.
This strengthening exercise is always advised when you feel to release pain & when you feel comfortable.
This all strengthening exercise helps to you muscle weakness & pain.
- Straight leg raise
- Drop Squats
- Single-Leg Knee Bends
- Wall Slide
- Step-up

Straight leg raise:
- You are lying on your back means in a supine position with your legs are straight out in front of you.
- Try to bend the knee joint on your unaffected side & place the foot flat on the floor.
- First, tighten the thigh muscle of the affected leg & lift the leg about 8 inches off the floor.
- Must keep the thigh muscle tight throughout all exercise.
- Then slowly lower your leg back down to the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Drop Squats:

- Start this exercise with a standing position with feet hip-width apart.
- Try to slowly lower your glute muscles toward the ground while keeping your feet & knee joints stable.
- You are lowered as far as you can go without pain in your knee joint, slowly lift back up to in starting position.
- Repeat this exercise in 2 to 3 sets, with 10 repetitions.
Single-Leg Knee Bends:
- You are standing on your injured leg, with your other leg bent slightly behind you.
- Then lifted off the ground.
- Try to drag your leg back till only your toes touch the ground, then lift the leg just a bit higher.
- Then squat down on your affected leg till you feel slight pain in your knee joint.
- Slowly put your weight onto your good leg & stand up.
- Repeat 2 to 3 sets, with 10 repetitions each.

Wall Slide:
- Start this exercise by standing with your heels about 6 inches away from a wall & your feet about a foot apart.
- Your back & buttock is pressed against the wall.
- Try to slowly slide your hip joint down the wall till your knee joint is bent at roughly a 45-degree angle.
- Hold this exercise position for about 5 seconds & slowly return to starting position.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Step-up:

- You are standing with the foot of your affected leg on a support such as a small step & block of wood at 3 to 5 inches high.
- Must keep your unaffected foot flat on the floor.
- Try to shift your weight onto your affected leg for support & straighten your knee joint as the unaffected leg comes off the floor. then lower your leg back to the floor slowly.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
What is the Surgical Treatment for this Patellar Tendinopathy?
After the medical treatment & physiotherapy treatment pain is not relieved then the doctor is advised surgical treatment.
Most people with this condition do not need surgery. But it is advised when your symptoms don’t improve with other treatments after 3 to 6 months.
This surgery aims to repair your tendon & it is usually done by an arthroscopy procedure, it is a type of keyhole surgery.
this takes about 6 to 9 months to recover from surgery.