Muscle Spasm In Arm
Table of Contents
Definition of muscle spasm-
- An Arm muscle spasm is an unexpected, involuntary movement in one or more muscles.
- An individual can also call it a charley horse or a muscle cramp or twitch.
- Muscle spasms (muscle cramps) are painful contractions and tightening of particular muscles.
- They’re common, involuntary, and unpredictable.
Arm Muscles Movement-
- Prior to learning about the different muscles, it’s necessary to understand the four major types of movement they’re involved in:
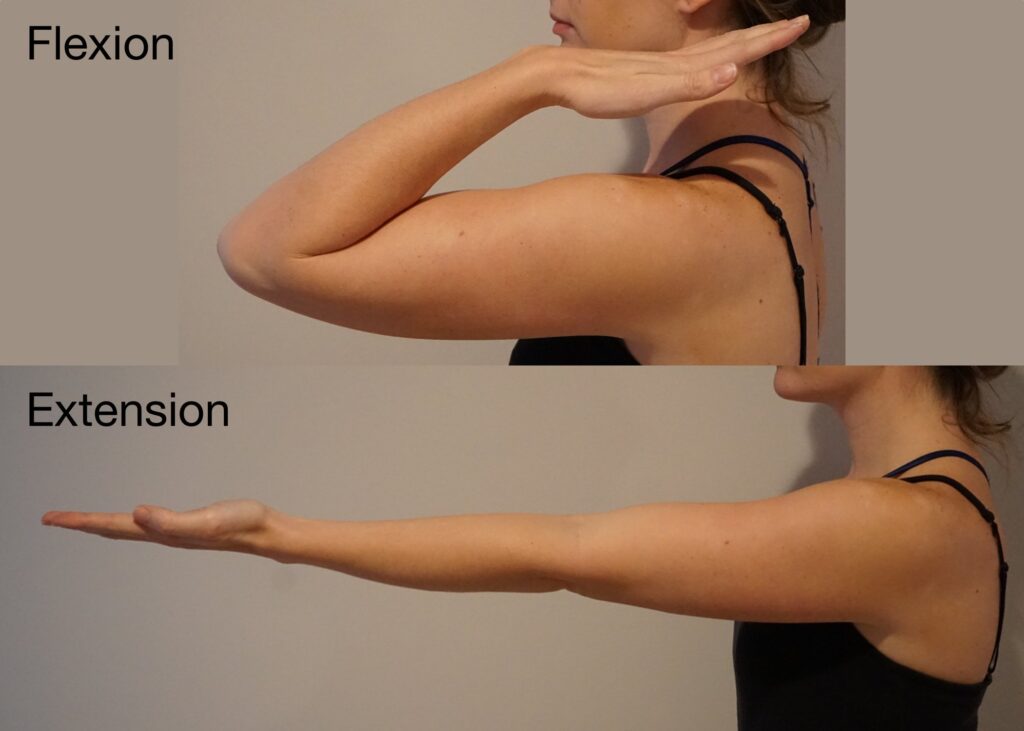
Flexion-

- This movement escorts two body parts closer together, like the forearm and upper arm.
Extension-
- This movement increases the space between two body parts. Such as straightening the elbow.
Abduction-

- This mention moving a body part away from the center of the body, such as lifting the arm out and away from the body.
Adduction-
- This mention moving a body part toward the center of the body, such as bringing the arm back in so it rests along the torso.
Causes of muscle spasm in Arm-
Causes of muscle spasm-
- Muscle pain, fatigue, and overuse of the arm are the most usual causes of muscle spasms.
- Other causes include stress or anxiety, which may lead to muscle twitches in the face.
- Trapped nerves may result in spasms in the back.
- An individual who have certain health conditions, like nerve disorders or thyroid-related problems, also tend to experience a greater-than-average frequency of muscle spasms.
- Muscle spasms are not generally anything to dwell on, but in some cases, they may be a sign of an underlying neurological health condition.
- Neurological health conditions influence the brain, which is responsible for making the muscles move.
- Not enough stretching.
- Muscle fatigue.
- Exercising in the heat.
- Dehydration.
- Consumption of electrolytes (salts and minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium in the body).
- Involuntary nerve discharges.
- Restriction in the blood supply.
- Stress.
- Too much high-intensity exercise.
Other causes of Arm muscle spasms-
- Unknowing exercise activities may also cause muscle spasms to occur.
- Abdominal muscle spasms may happen when an individual decides to begin working their abdominal muscles by doing sit-ups and repeating too many too swiftly.
- The writer’s cramps of the hand and fingers are correspondingly caused by extended use of the small muscles in the hand and the overused muscles cramp.
- An individual will routinely rest and stretch their fingers either to prevent or treat this situation.
- It is habitually thought that dehydration and depletion of electrolytes will lead to muscle spasms and cramping.
- Muscle cells need enough water, glucose, sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium to permit the proteins within them to develop an organized contraction.
- An abnormal supply of these elements may cause the muscle to become irritable and develop spasms.
Symptoms of Muscle Spasm In Arm-
- Not all muscle spasms are painful, but some can cause Arm muscle pain.
- It can feel as though the muscle is jumping or moving on its own, with this feeling consistently lasting just a few seconds.
- Some individuals might even be allowed to see the muscle twitching.
- Sometimes, it may feel as though the whole muscle has cramped up and may not move.
- This effect most habitually happens in the arm, and it may be quite painful.
- The muscle can feel hard to the touch.
- If a muscle spasm is part of a neurological health condition, an individual will generally experience some other symptoms.
- These might include:
- pain in the back, neck, or head
- weakness in the Arm muscles
- Skin numbness & tingling sensation in the arm
- A pins-and-needles sensation
- A tremor
- Pain that’s often worsened by holding the hand in one place for long periods, like when cooking, grooming, or working at a Computer
- Arm Muscle tightness and spasms
- Decreased ability to move the hand
- Headache
Diagnosis of Arm muscle spasm-
- Unless an individual may not move at all because of an injury, the doctor probably will test the patient’s range of motion, check how the nerves are working, and press on the back to zero in on the problem area.
- An individual might have blood and urine tests to find out other diseases, like an infection or a kidney stone.
- A doctor typically finds the diagnosis of the muscle spasm after considering the patient’s full history of symptoms and physical examination.
- The doctor may want to know about the onset of the pain, how long the muscle spasms last, and how frequently they happen.
- Other needful information may include which muscle or muscles are affected, whether the spasms happen consistently in the same muscles or affect various muscles, and the circumstances surrounding the spasms.
- Prevail a full personal and medical history (for example occupation, hobbies, history of genetic disorders) may help the doctor to rule out underlying factors that move to the muscle spasms inpatient.
Other tests-
Blood tests-
- If the patient’s medical history and physical examination are not enough to diagnose muscle spasms, the doctor may suggest blood tests to check the individual’s levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
A creatine phosphokinase –
- CPK blood test may be used to recognize muscle breakdown. CPK is released as a result of muscle damage, which may happen if muscle spasms are prolonged.
MRI-
- If there is a disturbance for arteriosclerosis, imaging tests, like; ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can be ordered to assess the blood vessels for narrowing.
CT SCAN-
- computed tomography angiography encompasses injecting dye into an artery near the groin or wrist, which may also be used to assess blood flow in the arteries.
EMG-
- Electromyography, which tests the muscle’s response to electric stimulation, may be ordered to find out any disorders of the nervous system, like; MS and ALS, that might potentially cause muscle spasms.
Treatment of Muscle Spasm In Arm-
- It includes first aid, heat, and cold therapy, medical intervention, exercise therapy, massage, and stretching.
First aid-
- In the middle of a back spasm, gently make her way to the nearest comfortable chair or sofa.
- Here, you can try the following techniques to overcome the pain:
- Gently massage the spasm with her hand or using the massage gun.
- This may give temporary relief to spasms. As a patient massage, the area, make sure that they should be mindful of their breathing.
- Take slow inhales and exhales to overcome stress-induced pain.
- Diaphragmatic breathing may help the patient to become calm down.
- Apply simultaneously heat and ice in 15–20 minute intervals.
- Muffle ice packs in a towel to avoid ice burns, and give your skin a break after icing.
- This requires the patient to stand up from the couch and get to the floor, so only proceed if you feel comfortable with these movements.
- Regular stretching helps people with chronic back pain, but for an acute back spasm, this may cause Trusted Source additional swelling to the affected area.
- The best treatment for the acute muscle spasm is to take for some time rest, take it easy, and call your doctor if the pain gets worse.
Medical treatment for Muscle Spasm In Arm-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)-
- such as Ibuprofen, will not give instant relief, but it can help slow the spasm within 30–60 minutes.
Muscle relaxants-
- A doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants when a patient has severe spasms that are visible and prominent. People should only take muscle relaxants for up to 72 hours.
Water and electrolytes-
- Dehydration can cause muscle spasms, or make existing spasms severe. Continue drinking water, or review switching to an electrolyte drink.
Exercise for Muscle Spasm In Arm-
1-Elbow Flexion-
- Stand with the arm at your side.
- Actively bend the elbow up as far as possible, then grasp the forearm or wrist with the other hand and gently add overpressure.
- Hold this bent position of the elbow for five to 10 seconds, and then release the stretch by straightening the elbow.
- Repeat the exercise 10 times.
2-Straighten It Out: Elbow Extension–
- Sit in a comfortable chair with the elbow resting on a table. You may want to rest the upper arm on a pillow or folded towel for relaxation.
- Straighten the elbow out all the way, and then apply pressure to the forearm or wrist to add overpressure to the stretch.
- Straighten the elbow out as far as an individual can with overpressure, and hold the movement for five to 10 seconds.
- Release the stretch and allow the elbow to bend a bit.
- Repeat the exercise for 10 repetitions.
- A person can also add a little bit of stretch to the elbow extension by holding onto a 2- to 3-pound weight.
3-Turn It Over: Forearm Supination–
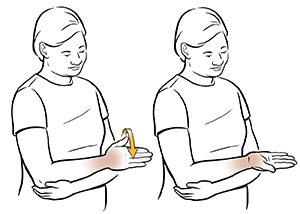
- The ability to turn the wrist over so the hand faces up is known as supination, and this motion occurs at both the elbow and at the wrist joint.
- To improve the ability to supinate the hand, perform the forearm supination ROM exercise.
How to perform this exercise-
- Stand or sit with the arm at the side and then allow the elbow to bend about 90 degrees.
- Keep the elbow by your side and turn the wrist and hand over so the palm faces up.
- To add overpressure to the stretch, use the opposite hand and reach underneath the forearm of the supinated arm.
- Seize the wrist and gently add overpressure by turning the hand further into supination.
- When a stretch is felt, hold this position for five to 10 seconds.
- Repeat this elbow supination ROM for 10 repetitions.
4- Forearm and Elbow Pronation–

- Forearm pronation refers to the ability to turn the hand over so the palm faces the floor.
- This motion is extremely important in performing tasks like pouring a cup of coffee or playing the piano.
How to perform this exercise-
- Stand or sit with the elbow bent 90 degrees and tucked in at your side.
- Turn the hand and wrist over as far as possible, then reach the other hand over the top of the forearm.
- Grab the wrist, and turn the arm further into a pronated position.
- Hold this position with overpressure for five to 10 seconds, and then liberate the stretch.
- Repeat this pronation exercise stretch 10 times.
Massage Techniques for Muscle Spasm In Arm-
Arm Massage–
- An arm massage pivot mainly on the muscles that make up the upper and lower regions of the arm.
- There is a range of various muscles that make up the arm. Muscles that constitute the arm encompass; the biceps, triceps, brachialis, brachioradialis, coracobrachialis, and the extensor carpi radialis brevis.
- An arm massage mainly focuses to decrease tension and pain using a variety of various techniques.
- Highly trained massage therapists at the physio center use an arm massage to help treat pain, stress, and muscle tightness.
Deep strokes –
- This technique is used during an arm massage.
- Deep strokes are where firm pressure is situated along the arm using flattened hands and fingers.
- The deep strokes goal is to get deep into the muscle tissues to relieve muscle tightness and tension.
- Deep strokes help to improve the temperature of muscles by creating friction between the hands and the skin.
- Deep strokes help to decrease restriction as muscle temperature increases.
- Decreasing restriction increases muscle elasticity and flexibility, therefore, relieving tightness and tension.
Frictions-
- These techniques are common techniques used during an arm massage.
- Frictions are carried out using fingertips or thumbs.
- Fingertips or thumbs are used to apply pressure through muscle fibers.
- Frictions are a technique that improves muscle temperature to help break down collagen fibers that are built up in muscles.
- Collagen fibers cause pain due to being restrictive.
- When the temperature is higher, collagen fibers loosen and increase in elasticity.
- An increase in elasticity decreases restriction and pain.
Kneading-
- This technique is also used during an arm massage.
- Kneading is carried out on areas containing soft tissues.
- This massage technique uses pulling and squeezing actions to reduce tightness and improve cellular exchange.
- As muscles are pulled and squeezed during an arm massage, muscles loosen because of being stretched.
- Stretched muscles allow them to relax therefore decreasing the tightness.
- Cellular exchange is improved using kneading. Increasing cellular exchange removes metabolic wastes and replaces them with oxygen and nutrients more efficiently.
- Cellular exchange reduces muscular fatigue and aches as waste products are removed.
- Due to an increase in oxygen and nutrients, muscles are able to become stronger and also become healthier.
Stretching –
UPPER ARM PAIN STRETCHES–
- The below given upper arm pain stretches are the exercises a person should perform to alleviate pain, strengthen muscles, and reduce inflammation:
SHOULDER STRETCHING-
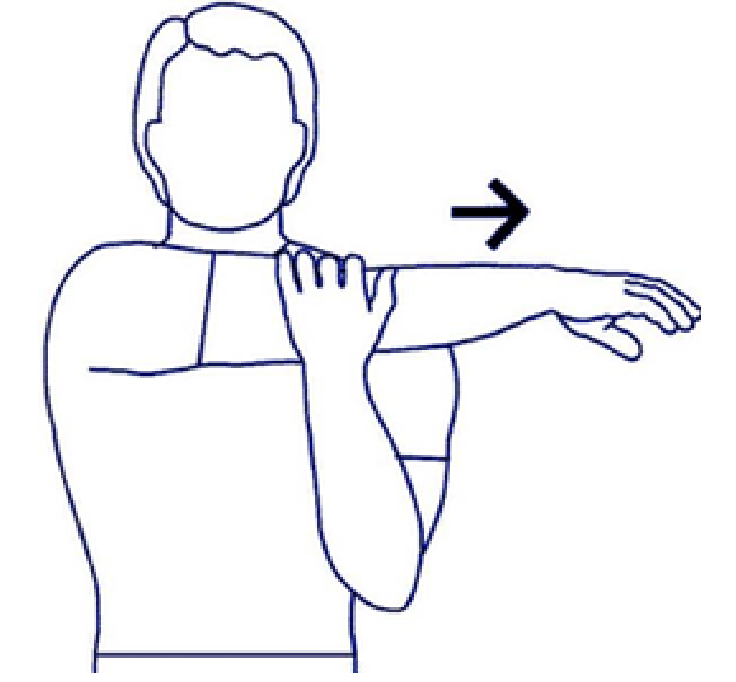
- In a sitting or standing position, cup the elbow with the opposite hand.
- Lift the elbow and pull it over the chest without rotating the body.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds, feeling the tension in the shoulder.
- Remove hold and relax, then repeat with the other arm.
- Do it for the next ten repetitions, each arm.
TRICEPS STRETCHING-

- In a sitting or standing position, lift one arm up above the head and bend it so a person reaches towards their back, behind the head.
- With the opposite hand, kindly push back against the bent elbow.
- Hold this stretch for 30 seconds, feeling the stretch in the triceps.
- Remove hold and relax, then repeat this stretch with the opposite arm.
- Do it for the next for 5-10 repetitions, each arm.
NECK STRETCHING-
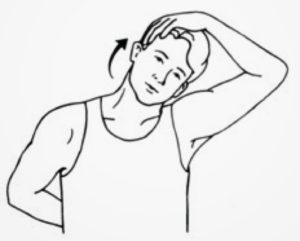
- In a sitting or a standing position, put the back up nice and straight, facing forward.
- Tilt the head to one side, as if the person were going to put their ear on the shoulder, but don’t move their shoulder.
- Keep it relaxed.
- Hold this stretch for 30 seconds, feeling the tension in the side of the neck.
- Take out hold and relax, then repeat on the opposite side.
- Continue this for ten repetitions, on each side.
Wrist and lower arm stretches-
Wrist rotations-
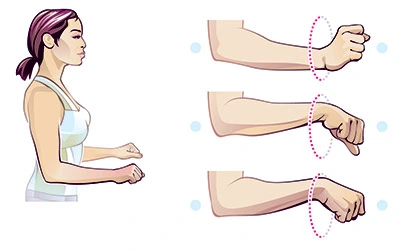
How to perform this stretch-
- Stretch the arm out in front of you. Slowly, point the fingers down until the person feels a stretch.
- Use the opposite hand to gently pull the raised hand toward the body.
- Hold this movement for 3–5 seconds.
- Point the fingers toward the ceiling until a person feels a stretch.
- Use the opposite hand to gently pull the raised hand toward the body.
- Hold this position for 3–5 seconds.
- Repeat this three times.
Prayer position-

How to perform this stretch-
- Sit with both palms together and both elbows on the table in a prayer position.
- Lower the sides of the hands toward the table until the person feels a stretch.
- Keep both palms together.
- Hold this position for 5–7 seconds.
- Relax and Repeat this three times.
Hooked stretch –
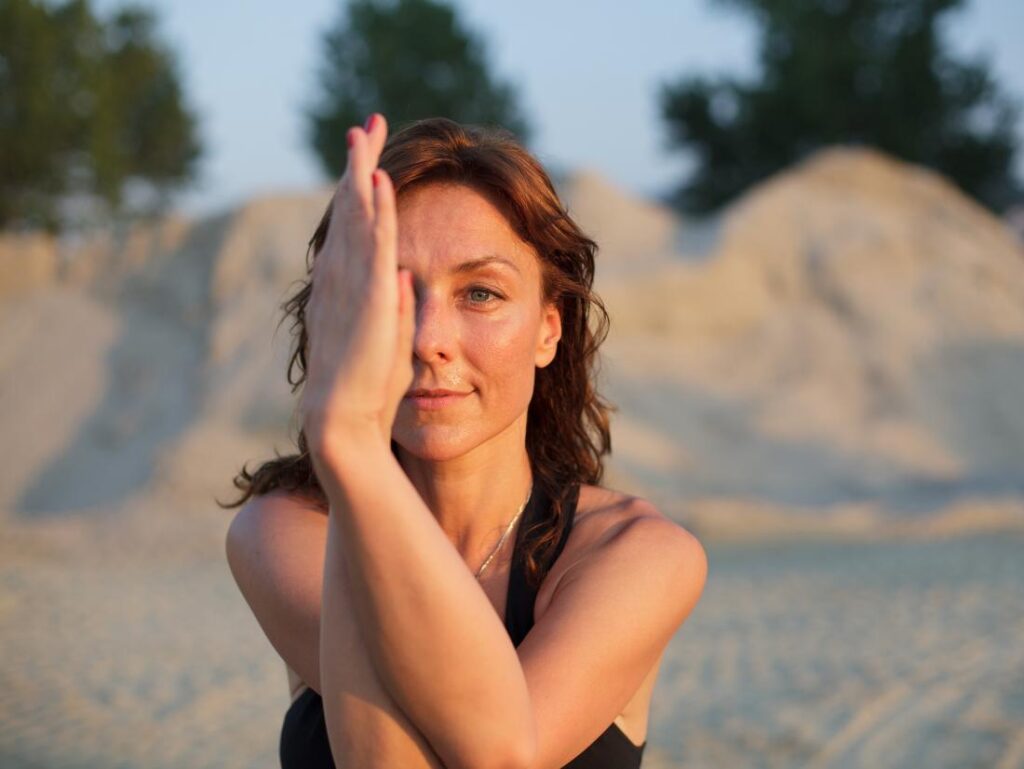

How to perform this stretch-
- Clasp one elbow under the other and pull both arms towards the center of the torso.
- The person should feel a stretch in their shoulders.
- Muffle one arm around the other so that the palms are touching.
- Hold this stretch for 25 seconds.
- Change arms and repeat it on the other side.
Sponge-squeeze-

How to perform this stretch-
- Compress a sponge or stress ball, making a fist. Hold the position for 10 seconds.
- Relax and repeat this 10 times.
Windshield wiper wrist movement-

How to perform this stretch-
- Start with the hand face down on a table.
- Gently, point the hand to one side as far as it may go without moving the wrist.
- Hold it there for 3–5 seconds.
- Do this exercise on the other side.
- Repeat this movement three times on each side.
Ergonomic advise-
Modify desk setup- Sit-stand desk –
- Periodic position changes may reduce the negative effects of sitting for long periods of time (Such as arm pain & stiffness).
Change the monitor’s height –
- The computer screen should be at eye level to help the person maintain a proper upright posture.
- Make use of a monitor stand, a small box, a stack of books, or reams of paper
Change the seat depth, seat height, backrest position, and armrest position-
Try new tools –
- Carry out some new tools that can modify the hand position:
- Ergonomic keyboard, vertical mouse, pen mouse.
Heat and/or ice-
- Heat and cold therapy applications can be helpful in decreasing arm pain.
Posture-
- Slouching puts muscles in the person’s neck, back, & shoulders at a mechanical disadvantage.
- This forces the muscles of the elbows, wrists, and hands to work harder which may lead to arm pain.
- The process of put the right posture takes time & persistence.
FAQ
Muscle twitching typically isn’t an emergency, but a serious medical condition can be causing it. Make an appointment with the doctor if a person feels twitching, and may it becomes a chronic or persistent issue.
A pinched nerve may also cause muscle spasms, especially in the arm or leg. An individual might feel a repetitive “flutter” when the arm or leg wasn’t moving. It is also possible to experience a muscle spasm that experienced like a twitch.
When nerve cells are injured, it changes the way they collaborate with each other and with the brain. Twitches and spasms can be warning signs that this common condition is affecting the nerves that control the muscles.
Pulled muscles are sometimes mistaken for pinched nerves, but may be ruled out based on the nature of the pain. A pulled muscle exhibits dull achy pain in a centralized location, Moreover, pinched nerve pain is sharp and radiates to other parts of the affected area.
Carpopedalspasms are frequent and involuntary muscle contractions in the hands and feet with associated pain. Hypocalcemia and low calcium levels can cause carpopedal spasms as a warning sign. It happens due to nerves and muscles hyperexcitability from decreased extracellular ionized calcium.