Chondroplasty of knee
Table of Contents
What is chondroplasty of the knee?
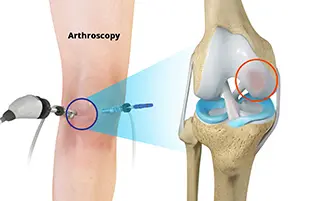
Chondroplasty of the knee is a minimally invasive surgical procedure. This surgery is used to repair the damaged knee cartilage. Using arthroscopic technology, a surgeon removes damaged tissue from the joint and helps address any future problems. Removal of damaged tissue allows healthy cartilage to heal in its place.
Because it’s a minimally invasive procedure, a chondroplasty requires fewer small incisions than other conventional surgery. Instead of large incisions, the surgeon can access the knee through tiny and small openings in the side of the knee. Since there are no large incisions, you can recover quickly after your procedure.
What is the knee joint?
The knee is the most important joint in the body and it consists of the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia) and fibula. It plays an extremely important role in supporting nearly the entire body weight and does this with the help of surrounding muscles, ligaments, and cartilage.
Muscles:
Many muscles around the knee joint help in providing stability and allow mobility. The main muscles surrounding the knee:
- The Quadriceps muscle (front of thigh)
- Hamstrings (back of thigh)
- Calf (back of the lower leg).
Ligaments:
Ligaments hold bones together, so they help in stabilizing the knee.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL): prevents excessive forward movement of the tibia on the femur(thigh bone). Other vital ligaments in the knee are:
- The Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
- The Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
- The Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL).
Cartilage:
There are two main types of Menisci:
- Disc-shaped fibrous cartilage: Situated between the femur and tibia. They provide stability, act as shock absorbers, and lubrication, and allow equal weight distribution.
- Articular Cartilage: This covers the end of the bones and allows them to move smoothly against each other with less friction. It also helps in spreading the load applied all over the joint.
Articular Cartilage damage
It can be caused by :
- Trauma
- Degenerative changes (OA Knee)
- Inflammatory disorders (RA)
- The damage leads to pain, swelling, locking, giving way, and grinding sensation (crepitus) • Articular cartilage does not have its blood supply therefore the limited capacity to heal again.
Why is a Chondroplasty Procedure Performed?
Chondroplasty may help in addressing symptoms from intense knee trauma, osteoarthritis(OA), and other degenerative conditions.
As the increases in age, the cartilage between knee joints can become damaged. Not like skin or bones, cartilage can not heal effectively or faster on its own because it does not get enough or a nourishing supply of blood to the joint. Having damaged cartilage makes simple and easy tasks like walking, painful and irritating burdens.
Chondroplasty allows some people to stop feeling leg pain and restore function in their legs. Surgery helps promote the regeneration of articular cartilage and restore knee function. This procedure helps reduce pain in the knee joints and improve leg function.
During chondroplasty, a surgeon can also use the opportunity to smooth rough arthritic joint surfaces. Your surgeon will also address any other knee abnormalities during the procedure. Attending to possible difficult spots will help make sure the treatment provides lasting results. The surgeon may also examine the cartilage in the joint and address any irregular growth during the procedure.
How to prepare the patient for chondroplasty surgery?
Properly preparing for surgery can help to improve recovery time and ensure the best results. Before your surgery, make sure the patient discusses both her prescription and OTC medications with your doctor. Patients have an open dialogue with their doctor about all of the current medications will help them advise you about which drugs to avoid in the lead-up to their surgery.
Patients should not have anything to eat or drink at least 12 hours before the surgery to avoid any infection or risks,
Indications for Chondroplasty:
- Chondroplasty may be recommended
- Mild to moderate cartilage wear
- A cartilage injury in the Knee joint, rather than widespread or irreparable cartilage damage.
- Typically, damaged cartilage does not heal on its own as it does not have a proper blood supply in the joint. Medical intervention is necessary to correct the condition of the knee. Chondroplasty prepares the joint for remaining cartilage restorative procedures.
Procedure:
Chondroplasty surgery is a minimally invasive surgical treatment for damaged joint cartilage. It is generally performed by a minimally invasive procedure known as arthroscopy.
During the procedure, the surgeon:
- Makes small incisions around the knee
- Insertion of an arthroscope (a surgical narrow tube with a camera) which provides an enlarged view of the inside of the joint on a monitor
- Pumps fluid into the knee joint which expands the knee to improve visualization in joint
- Using special tools to remove damaged cartilage or loose fragments
- The surgeon trims the damaged cartilage and smoothens the remaining surface of joint
- Drains out the fluid which is added from outside once the repair is complete
- A doctor will close the incisions with stitches to complete the procedure
- Recovery from Chondroplasty
- Though you may need crutches or other assistive aids after chondroplasty, you can usually return to normal activities within 3-4 weeks.
The whole procedure takes 1 hour.
Benefits of Chondroplasty:
Potential benefits of chondroplasty include:
- Reduced knee pain
- Improved joint function and mobility
- Slows cartilage degeneration in joint
- Fast recovery or immediate relief from pain
- Repair or treatment of other abnormalities in the cartilage can also be performed during arthroscopy
Risks Associated with Chondroplasty:
Chondroplasty is a minimally invasive surgery that involves small incisions in your skin. There is nothing that is safe for surgery. Every surgery has its own risk based on the area treated. Some of these risks include:
- Increased risk of bleeding in the knee
- Higher potential for infection in the knee joint
- Chronic stiffness in the knee
- Damage to areas that are not affected by osteoarthritis
- Blood clotting
- Bleeding in the knee joints
In addition, anesthesia can cause allergic reactions in some people. Severe complications from this surgery are uncommon. The doctor will make the patient know all possible risks of surgery
Post-operative Physiotherapy treatment
Rehab Knee Chondroplasty
Acute Phase I (0-2 weeks) Goals:
- Alleviate acute pain and swelling
- Increase ROM
- Increase hip, hamstring, and quadriceps strength
- Promote normal ambulation
- Maintain cardiovascular conditioning
Plan:
- ROM as tolerated (Active assisted)
- Heel/wall slides for ROM
- Aquatic therapy
- Hamstring and gastroc stretching
- Kinesiotaping as necessary
- Bicycle as tolerated
- Patellar mobilization
- Hamstring and quadriceps co-contraction
- 4-Quad (hip flexion, abduction, adduction, extension)
- Modalities for pain and edema control- IFT, Ultrasound, Cold therapy
Sub-Acute Phase I: (2-4 weeks)Goals:
- Decrease swelling
- Increase ROM
- Increase the strength of the hip/knee
- Improve general conditioning
- Independent ambulation w/o assistive device
Plan:
- Continue Phase I exercises
- For reducing swelling use Ultrasound and cryotherapy
- N-K for hamstrings only
- ROM knee flex/ext as tolerated
- Stairmaster, treadmill, Elliptical (Pain-free)
- Universal Equipment Progressive Resistive Exercises – leg press ¼ – ½
- Proprioceptive and balance training
- Calf raises
- Aquatic therapy
- Avoid knee extension exercises
Phase III: (4-6 weeks)Goals:
- ROM (pain-free) 0-90 degree
- Increase functional strength
Plan:
- Continue Phase II exercises
- Increase closed-chain activities
- Increase proprioception activity
At 6-8 weeks
- Protected Gait pattern with crutches
- Increase exercise range up to 120 degrees
- Straight leg raise without brace if able to maintain full extension
- Start stationary bike with low resistance
8-12 weeks
- Full range of motion
- Normalized gait without crutches
- Progress to full and pain-free movements
- Mini squats 0-45 degree
- Leg press 0-60 degree
- Closed chain terminal knee extension
- Toe raises
- Balance activities
- Hamstring curls
- Increase to moderate bike resistance

Summary:
Knee arthroscopy is a valuable diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for the treatment of various knee problems. Chondroplasty is a basic treatment option for treating damaged articular cartilage found on diagnostic arthroscopy. Key points include removing rough, damaged, and unstable cartilage with the shaver and curettes to establish a stable lesion without exposing subchondral bone. Cartilage damage is the most common reason for knee arthroscopy.
Chondropalsty is an effective treatment of the knee condition. In the early stages after the operation patient will experience pain and swelling of the knee. A doctor will advise on the application of ice packs, elevation, and the use of simple analgesia to relieve pain will be given on an individual basis by the surgeon. Before leaving the hospital you will be seen by the physiotherapist to discuss various exercises and how to use crutches for walking again. Dressings should not be wet until they are removed.
Rehabilitation plays a massive role in any orthopedic operation. After surgery, physiotherapy helps the patient to regain the pain less walk with various modalities and exercises. The emphasis of the program would depend on the injury and surgical procedure performed. All these factors will also influence the length of recovery, which may vary from weeks to months.
FAQ:
How effective is chondroplasty?
The non-functional joint is removed and pain is relieved. Total knee replacement is considered a relatively routine surgery with results from surgery indicating 85% of patients are happy with the procedure, approximately 10% do not see a significant improvement, and 5% of patients report worsening symptoms.
Can you walk after knee chondroplasty?
Patients do not harm putting full weight on their knees immediately. They are encouraged to try to walk as smoothly as possible. The patient must not do any strenuous activity such as running and jumping until I clear you for this. They may experience some discomfort as they walk.
How long does it take to heal from chondroplasty?
Recovery from Chondroplasty
Though the patient may need crutches or other assistive devices after chondroplasty, you can usually return to normal activities within 3-4 weeks.Can you climb stairs after arthroscopic knee surgery?
Immediately after surgery, you will learn to climb stairs safely using crutches or assistance. As recovery continues and the patient work on flexion and extension of the new knee, the patient will be able to climb stairs without crutches. With the help of physical therapy and building up the quadriceps muscles, stair climbing will be easy.
What can you not do after arthroscopic knee surgery?
Rest on the day of surgery. Although patients may feel normal, their reflexes and mental ability may be impaired. The patient may feel dizzy, lightheaded, or sleepy for 24-36 hours or longer. Patients do not consume alcohol, drive, operate machinery, or make important personal or business decisions for 24 hours.