MANUAI THERAPY: HANDS-ON TECHNIQUES
Table of Contents
DEFINITION
- Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a physical treatment primarily used by physical therapists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, chiropractors, massage therapists, athletic trainers, osteopaths, and osteopathic physicians to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability; it most commonly includes kneading and manipulation of muscles, joint mobilization, and joint manipulation.
- “ORTHOPEDIC MENUAL PHYSICAL THERAPIST is any “hands-on” treatment provided by the physical therapist. Treatment may include moving joints in specific directions and at different speeds to regain movement (joint mobilization and manipulation), muscle stretching, passive movements of the affected body part, or having the patient move the body part against the therapist’s resistance to improve muscle activation and timing. Selected specific soft tissue techniques may also be used to improve the mobility and function of tissue and muscles.”
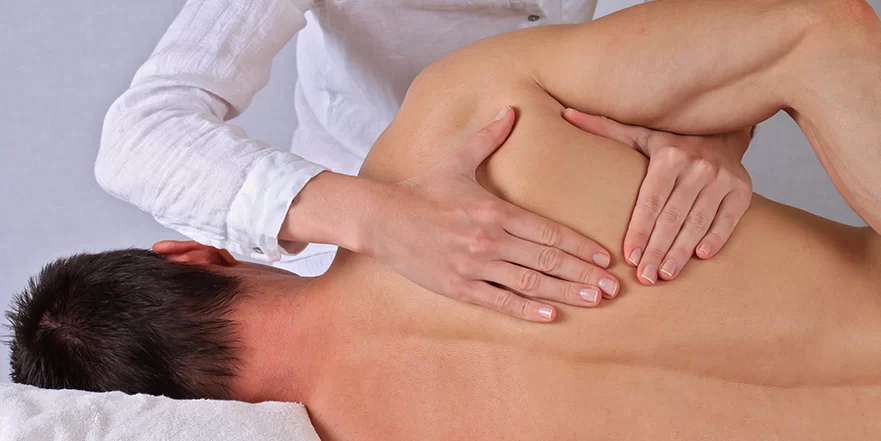
ABOUT ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL THERAPY :
- Orthopedic manual therapy physical therapy is the assessment and treatment of neurological, cardio-respiratory, and orthopedic problems through hands-on interventions. The objective of manual therapy is treating the neuro–orthopedic part of any disorder, thereby focusing on the disease or condition itself.
- For instance, after cardiovascular surgery, a patient may experience decreased movement of his ribcage, which may interfere with his usual breathing pattern. The treatment can include hands-on work that includes mobilization of the nerves, soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, and mobilization of spinal segments and joints.
- According to clinical recommendations, manual therapy can also include manipulation which enhances joint movement beyond its range of motion with the use of high velocity, low amplitude force. Manual therapy treatment is achieved through specific exercises as well as through the use of electro-therapy equipment like short-wave diathermy and ultra-sound.
TERMINOLOGY :
- There are two types of terminology used in manual therapy :1. Manipulation
2. Mobilization1. MANIPULATION :
- A passive, high velocity, low amplitude thrust is applied to a joint complex within its anatomical limit with the intent to restore optimal motion and function, and/ or to reduce pain.
2. MOBILIZATION :
- A manual therapy technique comprising a continuum of skilled passive movements to the joint complex that is applied at varying speeds and amplitudes, which may include a small-amplitude/high-velocity therapeutic movement (manipulation) with the intent to restore optimal motion, function, and/ or to reduce pain.
METHOD OF MANUAL THERAPY
> TECHNIQUES:
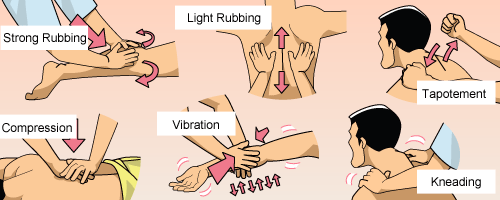
- Myofascial Therapy targets the muscle and fascial systems and promotes flexibility and mobility of the body’s connective tissues. It is said to mobilize adhesions and reduce the severity/sensitivity of scarring. A critical analysis finds that the relevance of fascia to therapy is doubtful.
- Massage may be used as part of a treatment. Proponents claim this may reduce inflammation. Science writer Paul Ingraham notes that there is no evidence to support the claim.
- Friction massage is said to increase the mobilization of adhesions between fascial layers, muscles, compartments, and other soft tissues. They are thought to create an inflammatory response and instigate focus on injured areas. A 2012 systematic review found that no additional benefit was incurred from the inclusion of deep tissue friction massage in a therapeutic regime, although the conclusions were limited by the small sample sizes in available randomized clinical trials.
- Trigger Point Release techniques claim to address Myofascial Trigger points, though the explanation of how this works is controversial, and reviews in 2008 and 2009 call into question whether trigger points are a valid diagnosis at all given the small amounts of poor quality evidence available.
- Soft Tissue Technique is firm, direct pressure to relax hypertonic muscles and stretch tight fascial structures. A 2015 review concluded that the Technique is ineffective for lower back pain, and the quality of research testing its effectiveness is poor.
> STRETCHING
- Medical evidence has shown stretching has no meaningful benefit in preventing muscle soreness.
- Apart from before running, stretching does not appear to reduce the risk of injury during exercise.
- Some evidence shows that pre-exercise stretching may increase the range of movement.
- The Mayo Clinic advises against bouncing and holding for thirty seconds. They suggest warming up before stretching or stretching post-exercise.
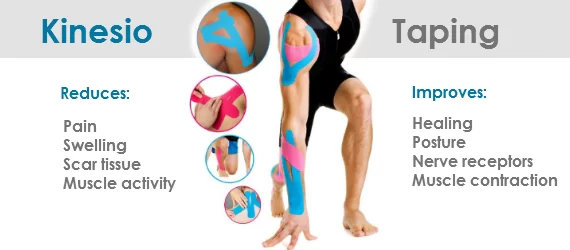
> TAPING TECHNIQUE :
- Manual therapy practitioners often use therapeutic taping to relieve pressure on injured soft tissue, alter muscle firing patterns or prevent re-injury. Some techniques are designed to enhance lymphatic fluid exchange. After a soft tissue injury to muscles or tendons from sports activities, over-exertion or repetitive strain injury swelling may impede blood flood to the area and slow healing. Elastic taping methods may relieve pressure from swollen tissue and enhance circulation to the injured area.
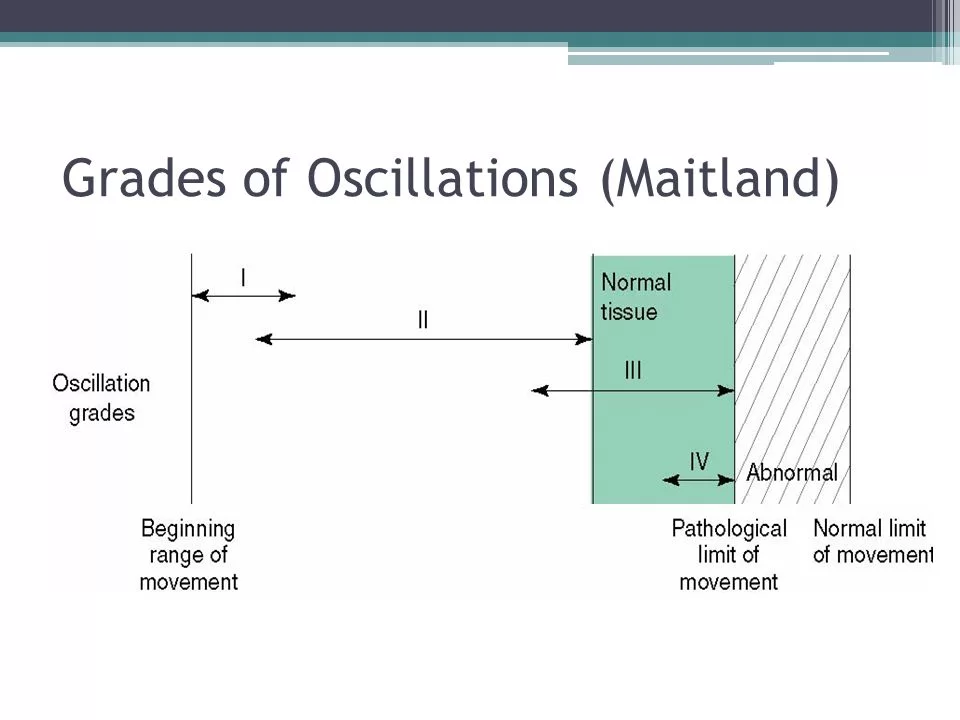
GRADES OF MOBILIZATION TECHNIQUE:
Maitland Joint Mobilization Grading Scale:
> Grade I – Small amplitude rhythmic oscillating mobilization in the early range of movement
> Grade II – Large amplitude rhythmic oscillating mobilization in the midrange of movement
> Grade III – Large amplitude rhythmic oscillating mobilization to point of limitation in range of movement
> Grade IV – Small amplitude rhythmic oscillating mobilization at end-range of movement
> Grade V (Thrust Manipulation) – Small amplitude, quick thrust at the end range of movement
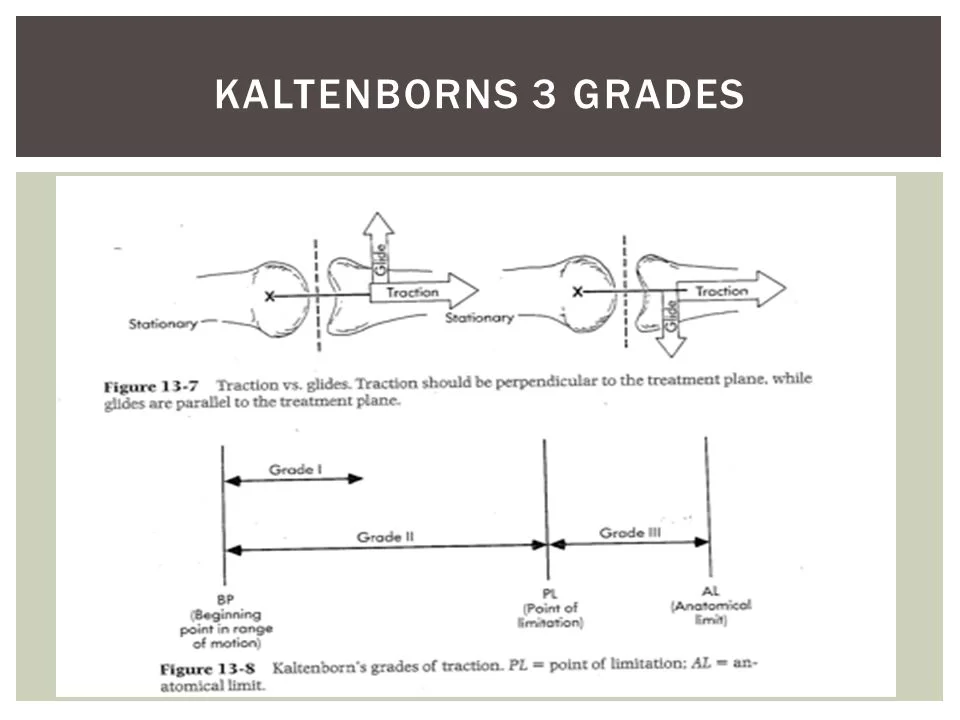
Kaltenborn Traction Grading Scale :
> Grade I – Neutralizes joint pressure without separation of joint surfaces
> Grade II – Separates articulating surfaces, taking up the slack or eliminating play within a joint capsule
> Grade III – Stretching of soft tissue surrounding a joint
MOBILIZATION & MANIPULATION TECHNIQUES :
> Elbow Mobilizations
> Wrist/Hand Mobilizations
> Hip Mobilizations
> Knee Mobilizations
> Ankle/Foot Mobilizations
> Spinal Manipulation
> Shoulder Mobilizations and Manipulation
> Cervicothoracic Manipulation
BENEFITS OF MANUAI THERAPY :
- Cases like back pain, whether they are chronic or acute, can be treated through manual therapy. There are no known side effects because the treatment is hands-on. It also deals with the mobilization of nerves, soft tissue, and fascia. Relief is attained in less time than most therapies and with less financial strain on the patient as well.
Physiotherapy Health clinics use manual therapy techniques performed by skilled and registered physiotherapists. Manual therapy is:
> Effective for acute and chronic pain.
> helpful in relaxing muscles and breaking up scar tissue.
> Useful in increasing joint movement beyond a restricted range of motion.
> Helpful in reducing painful muscle spasms.
USES OF MANUAL THERAPY
> Relieve pain
> Improve movement or ability
> Prevent or recover from a sports injury
> Prevent disability or surgery
> Rehab after a stroke, accident, injury, or surgery
> Work on balance to prevent a slip or fall
> Manage a chronic illness like diabetes, heart disease, or osteoarthritis
> Recover after you give birth
> Control your bowels or bladder
> Adapt to an artificial limb
> Learn to use assistive devices like a walker or cane
> Get a splint or brace



4 Comments