Hip Osteoarthritis
Hip osteoarthritis condition is sometimes called to wear- and – tear arthritis.
It is a common condition that is developed with the age.
This condition occurs in any joint in the body but most often develops in weight-bearing joints such as the hip joint.
This condition produces pain & stiffness.
Due to this condition become to make hard to do everyday activities such as rising from a chair, bending over to tie a shoe & taking a short walk.
Osteoarthritis is gradually worsened with time so always start treatment as soon as possible, because it is an impact on your life.
There is no cure for osteoarthritis but many ways to treat this condition which is to help you manage pain & stay active.
Table of Contents
What Is Osteoarthritis?
- Arthritis means occur to inflammation in the joint.
- It produces pain & swelling in the body’s joints like the knees or hip joint.
- There are occur to many types of arthritis, but osteoarthritis is the most common in the joint.
- This condition is also known as degenerative joint disease & age-related arthritis.
- This osteoarthritis condition is more developed in older people.
- This condition occurs when inflammation & injury to a joint which is lead to the breaking down of cartilage tissue.
- So the breakdown of this tissue produces pain, swelling & deformity.
- Cartilage is a firm, rubbery material which covers the ends of bones in normal joints.
- Cartilage is primarily made up of water & proteins.
- The primary function of the cartilage is to reduce friction in the joints & serve as a shock absorber.
- This shock-absorbing quality of normal cartilage comes from the ability to change shape during compression.
- Cartilage has not undergone some repair when damaged so the body does not grow new cartilage after being injured.
- Changes in osteoarthritis usually occur slowly over many years.
There are two main types of osteoarthritis include :
- Primary osteoarthritis: More generalized osteoarthritis that affects the fingers, thumbs, spine, hips & knees.
- Secondary osteoarthritis: this condition occurs after injury & inflammation in a joint & as a result of another condition that affects the composition of the cartilage, like hemochromatosis.
What is the anatomy of the hip joint?
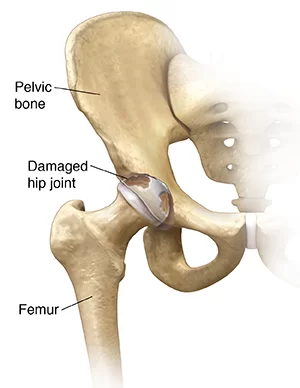
- The hip joint is one of the body’s largest joints.
- This joint is a ball-and-socket joint.
- The acetabulum forms this socket, it is part of the large pelvis bone.
- The ball is the femoral head, which is the part of the upper end of the femur – thighbone.
- The bony surfaces of the ball & socket are covered with the articular cartilage, a slippery substance, a smooth which is provides to cushions the bones & enables move easily.
- This surface of the joint is covered by a thin lining which is known as the synovium.
- In the healthy hip joint, this synovium produces a small amount of fluid which is given to lubricate the cartilage & movement.
What are the causes of hip osteoarthritis?
- Osteoarthritis does not occur due to a single specific cause, but some certain factors are developing the disease, including:
- If occur to the previous injury to the hip joint
- Obesity
- Increasing with age
- Improper formation of the hip joint at birth, this condition known as developmental dysplasia of the hip joint.
- Family history of osteoarthritis
What are the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis?
- The most common symptom of this condition is pain around the Hip area.
- This hip joint pain develops slowly & worsens over time & sudden onset pain is possible.
- You feel pain & stiffness in the morning &after sitting or resting position.
- These painful symptoms occur more frequently, including during rest or at night.
- You also feel pain in your groin & thigh which radiates to your buttocks or your knee joint.
- This pain is flaring up with the vigorous activity
- Due to stiffness, you feel too difficult during the walk or bending activities
- In this condition occur to Locking & sticking of the joint which produces a grinding noise means crepitus during movement due to loose fragments of cartilage & other tissue interfering with the smooth motion of the hip joint.
- Decreased ROM – range of motion in the hip joint which affects the ability to walk & a limp
- This pain is Increased in rainy weather.
What are the pain characteristics of hip osteoarthritis?
- Slowly progressive hip pain & hip-related groin pain radiate into the thigh, buttocks, or knee joint.
- This pain is worse at night, at rest & with strenuous activity which is reducing the range of motion – ROM & limiting walking distance.
- It is associated with stiffness, particularly in the morning & after rest.
What is the epidemiology of hip osteoarthritis?
This hip pain is most common in elderly ladies & it is the most common problem in Western society.
- Due to this hip OA 7%–25% of people older than 55 years.
- The number of affected hip osteoarthritis increases with the aging of the population.
- Risk for symptomatic hip OA is in men = 18.5% & women = 28.6%.
- This 25% risk is developing in hip osteoarthritis for people who live to the age of 85.
What is the etiology of hip osteoarthritis?
- The etiology includes:
- Previous trauma
- Idiopathic or unknown
- Other etiology include:
- Acetabular dysplasia
- Femoroacetabular impingement
- Inflammatory joint disease – septic arthritis;
- Hemochromatosis
- Hemophilia
- Iatrogenic = multiple intra-articular steroid injections.
What is a diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis?
- When you meet the doctor, the first doctor is asked some questions about your symptoms & medical history.
- Then the doctor does the physical examination & advice diagnostic tests like X-rays.
In the physical examination of the hip joint follow the assessment :
- Subjective part :
- Complaints of pain, deformity, stiffness & limp
- Take to the Previous history which is linked with hip pain means congenital or childhood problems & previous trauma.
- Physical examination:
- Perform in Standing and Supine position
- Check the leg length discrepancy, antalgic gait & Trendelenberg gait.
- Objective observation:
- Observe to
- Posture
- Muscle atrophy
- Deformities
- Palpation:
- Palpate to tenderness at the hip joint
- Check the pain & sensitivity over the greater trochanter
- Range of motion:
- Early signs of this hip osteoarthritis have limited the abduction & rotation.
- With the disease progression flexion, extension & adduction movement becomes more difficult.
- Normally you feel too painful to end ROM.
- Check the crepitus with movement
Imaging Tests of the hip joint include :
- X-rays:
- X-rays provide detailed pictures of dense structures like bones.
- It helps to show a narrowing of the joint space, the formation of bone spurs & changes in the bone.
- Result of this x-ray :
- In the normal hip joint = the space between the ball & socket indicates healthy cartilage.
- In the arthritic hip joint = you are showing in the x-ray severe loss of joint space.
- Bone spur:
- In this X-ray of hip arthritis, the arrow indicates a large bone spur (osteophyte) at the bottom of the femoral head.
- Other imaging tests:
- A computerized tomography (CT) scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan helps to better determine the condition of the bone & soft tissues of the hip joint.
What are the variables for detecting hip osteoarthritis?
- Squatting is aggravating the pain
- Active hip flexion produces lateral hip pain
- Perform the hip Quadrant test with adduction which is produced by lateral hip or groin pain.
- The active hip extension also produces pain
- Your passive internal rotation movement is less than or equal to 25°
- When the patient presents 3/5 variables it is indicated to OA is 68%.
- With 4-5/5, it is indicated to OA is 91%.
What is the clinical presentation of hip osteoarthritis?
- Osteophytes
- Subchondral thickening
- Cyst
- Joint space narrowing
What is the treatment for hip osteoarthritis?
There is no cure for hip osteoarthritis but there are many numbers of treatment options that are helpful to you relieve pain & improve mobility.
- Your healthcare provider recommends treatment based on:
- The severity of symptoms
- Motion and weight-bearing limitations
- The severity of joint involvement
- Your overall health
- Other individual factors.
RICE principle:
When you feel pain in the hip joint due to hip osteoarthritis doctor is advised to RICE principle as home treatment or primary treatment.
- R – rest = When you feel pain doctor has advised you to your rest for sometimes form of activity release to the pain, this means doing a total rest or even using crutches & another mobility aid.
- I- ice = You are applied to ice on the area of the pain for 20 minutes, release to swellings & muscle pain but always applied to the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice to prevent ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C – Compression = to prevent form additional swelling you are lightly wrapping the knee joint with the elastic bandage
- & also leaving to hole in the area of the kneecap or patella & but make sure the bandage is not to fits tight & not produce additional pain.
- E – Elevation =if possible, rest with the knee joint raised higher than the heart by applying to pillow under the leg which helps you release swelling.
Nonsurgical Treatment:
- Lifestyle modifications
- You are doing some changes in your daily life which helps you protect your hip joint & slow the progress of hip osteoarthritis.
- Minimizing your activities which is aggravate the condition like climbing stairs.
- Stop the high-impact activities like jogging or tennis & do the lower-impact activities like swimming or cycling which is applied to less stress on your hip joint.
- Lose the weight which reduces your stress on the hip joint which is given to result in less pain & increased function.
Pain Medications:
When your hip osteoarthritis pain affects your daily routine & not relieved by other nonsurgical methods then your doctor advises Pain Medications.
- For mild arthritis, a pain doctor is advised to over-the-counter drug = Acetaminophen.
- These all over-the-counter pain relievers drug produce side effects so that you are also taken to other medications.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) also help you relieve the pain & reduce inflammation.
- In the NSAIDs include to naproxen & ibuprofen.
- Corticosteroid drugs are powerful anti-inflammatory agents which are taken by mouth or injected into a painful area.
- Opiates are avoided in hip osteoarthritis.
Weight management:
- High body mass index (BMI) = it is a higher risk for osteoarthritis because this additional weight put extra strain on the joints.
- So that needs to be weight loss.
- For weight loss, you can follow a diet & exercise.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for hip osteoarthritis?
When this pain is not relieved after the home treatment & pain medication then the doctor has advised physiotherapy treatment to release the pain.
Physiotherapy treatment helps you relieve pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the muscle.
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy treatment & exercise therapy.
Massage:
- When the trigger & tender points are present in the pain area physiotherapist is advised to massage therapy release to these tender points.
- During a massage, a physiotherapist uses their hands to apply pressure on the tendons, muscles, and ligaments of the knee joint. Massage is applied after 2 – 3 days of following the RICE principle when you are not feeling to release the syndrome pain.
- Massage is applied with the help of the oil & applied for 5 -10 minutes.
- Massage is applied 3 times per day at home.
- You are used to various types of massage such as:
- Trigger point massage
- Deep tissue massage
- Swedish massage
Electrotherapy treatment:
After the RICE principle, pain medication & massage if the syndrome muscle pain is not relieved then used Electrotherapy treatment for releasing this pain.
To relieve the swellings, spasms & pain, a physiotherapist is advised to you electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the treatment therapist is used to many machines.
- When the trigger & tender points are present therapists are advised & to apply US = ultrasound therapy for the release of syndrome pain.
- This treatment is applied with the help of gel & applies for 5 to 10 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you release pain & swelling.
- Reduce to pain physiotherapist is applied to SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Interferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on the area of pain.
- SWD = Short wave diathermy is hot therapy for release to spams on the area of muscle pain.
- IFT = Interferential Therapy & TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of muscle pain.
- This therapy is applied for 10 minutes to the area of muscle pain.
Assistive devices:
A physiotherapist is advised to you assistive devices for weight-bearing.
- You are using walking supports for a walk like a cane, crutches & a walker which help you improve mobility & independence.
- You are also using assistive aids like a long-handled reacher & pick up low-lying things which help you avoid the movements and reduce pain.
Walking aid:
- This walking aid is taken to pressure on the hip joint & provides additional support to the joints.
- It also reduces your risk of falling by helping you maintain stability & balance.
- The walking aid includes:
- A walking frame
- A cane
- Follow some steps for using a cane:
- Must be sure the cane is not too tall or short.
- You are not to slump or slouch over when is use a cane.
- Cane’s height comes to the top of your wrist.
- You are using the cane on your “strong” side.
- If the affected hip side is your right side then, hold the cane with your left hand.
- If you step forward with your right side then a cane is provided to support you.
- The cane is placed at the appropriate distance & move the cane about 2 inches to the front or side of you because If you place the cane too far from your body it is to lose your balance.
Exercise therapy for hip osteoarthritis :
After following the RICE principle for the 2- 3 days at home & primary treatment & the help of pain medication, you feel released from the pain.
When you feel too comfortable & release from your muscle pain then the physiotherapist is advised to you exercise therapy reduce to muscle weakness & tightness.
The exercise therapy for muscle pain includes stretching & strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to relieve muscle tightness as well as strengthening exercise is help you relieve muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
After the follow of electrotherapy for 2-3 days for release to muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to stretch for release to muscle tightness.
This stretching is applied when your pain is released & when you feel comfortable.
- Forward fold
- Knee pull
- Extended leg balance
- Cobra
- Standing hip flexor stretch
- Knee to chest
- Iliotibial band stretch
- Hamstring stretch
- Inner leg stretch
- Hip and lower back stretch

Forward fold:
- Start this exercise with your feet shoulder-width apart & sit in a chair.
- Try to slowly lean forward.
- Must be keeping your upper body relaxed.
- You feel the stretch in your hip joint & lower back.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Knee pull:
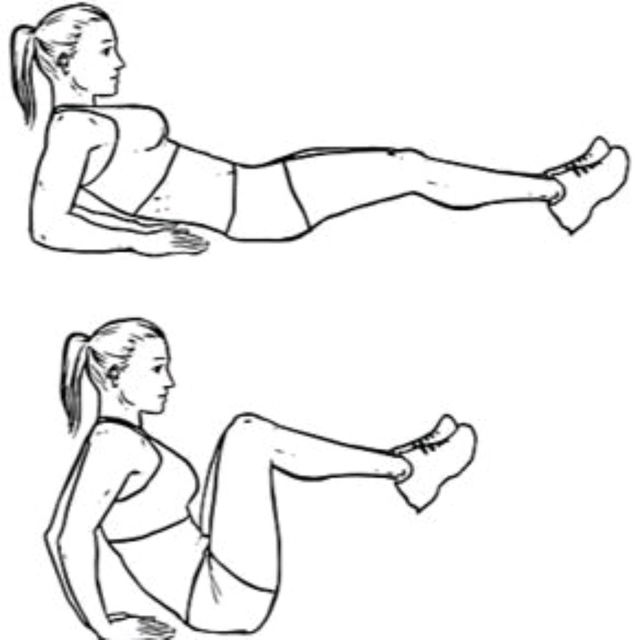
- You are lying on your back.
- Try to pull your bent knee up toward your chest till you feel a stretch.
- When your body allows you to use your other leg to deepen the stretch.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Extended leg balance:
- It is the same exercise as the knee pull exercise, but you start this exercise from a standing position.
- First, place one hand along the wall for support.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cobra:
- Start this exercise by lying facedown on the floor.
- Your palms are on the floor at shoulder or chest height.
- Try to push against your palms to lift your chest off the floor.
- You feel the stretch in your lower back & hip joint.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing hip flexor stretch:
- First, step one foot forward so that your feet are hips-distance apart.
- Bend your back leg slightly & slowly bend your front knee joint.
- Must keep your upper body upright.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- You also need to hold onto a wall & the back of a chair for support.
Knee to chest:
- You are lying on your back with your knees bent & feet flat on the floor.
- Bring one knee joint into your hands.
- Try to gently pull your knee joint toward your chest.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Iliotibial band stretch:
- You are standing next to a wall for support.
- Try to cross the leg which is closest to the wall behind your other leg.
- Then lean your hip joint toward the wall till you feel a stretch at the outside of your hip joint.
- Hold the stretching exercise for 30 seconds.
- Then cross the leg that is further from the wall behind your other leg.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Hamstring stretch:
- You are lying on the floor with both knee joints bent.
- Try to lift one leg off of the floor & bring the knee joint toward your chest.
- Must clasp your hands behind your thigh below your knee joint.
- Then straighten your leg & pull it gently toward your head till you feel a stretch.
- Hold the stretching exercise for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Inner leg stretch:
- You are sitting with your knee joint bent & the soles of your feet touching.
- Try to hold your shins or ankles joint.
- Then bend your upper body forward slightly.
- Try to gently press your knees down with your elbows.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Hip and lower back stretch:
- You are lying down on your back with legs outstretched.
- With your neck on the floor.
- Try to turn your chin toward your chest.
- Then bend your knee joint & hold them with your hands.
- Must pull your knees toward your shoulders joint as far as you can.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow of Electrotherapy & massage for 2 -3 days to release this pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to you do strengthening exercises for muscle weakness.
This strengthening exercise is always advised when you feel to release pain & when you feel comfortable.
This all strengthening exercise helps to you muscle weakness & pain.
- Leg raise
- Bridging
- External hip rotation exercise in sitting position
- External hip rotation exercise in lying position
- Heel slide
- Hip flexion
- Hip extension
- Hip abduction exercise
- Heel to buttock
- Squats
- Short arc quadriceps exercise
- Quadriceps exercise
- Stomach exercise
- Knee lift
- Clock tap
- Sit-and-Stand
- Standing jacks
- Cross-body leg raises
- Double hip rotation
Leg raise:
- You are lying face down though you might want to turn your head to one side if this is more comfortable.
- Tighten your stomach & buttock muscles to lift one leg slightly off the floor, while must be keeping your hips flat on the ground.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Bridging:
- You are lying on your back with your knee joint bent & feet flat on the floor or bed.
- Try to lift your pelvis & lower back off the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
External hip rotation exercise in sitting position:
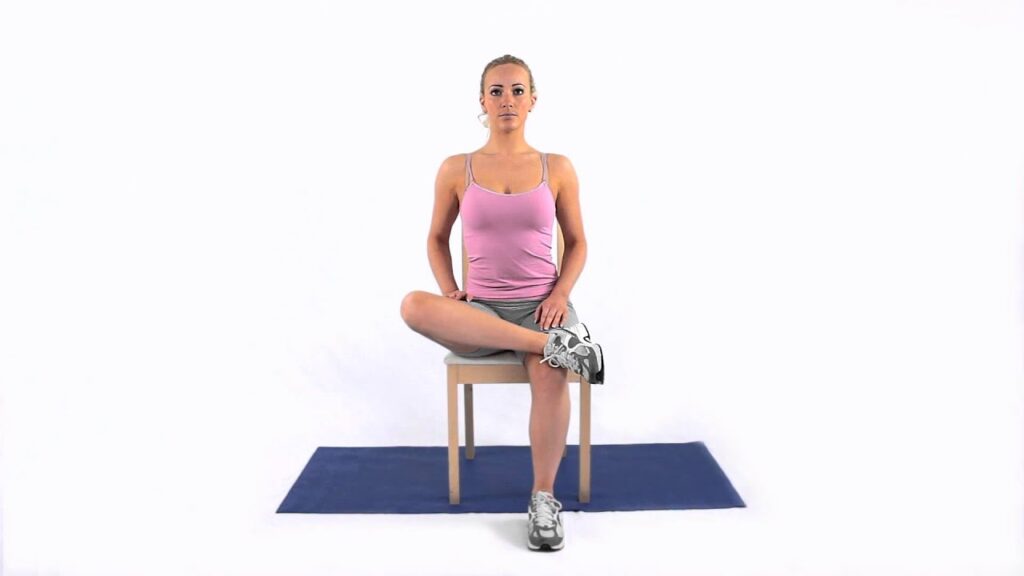

- you are sitting with your knee joint bent & feet together.
- then press your knees down towards the floor with the use of your hands.
- Alternatively for this exercise:
- You are lying on your back & part of your knee joint.
- Must keep your feet together.
- Do the movement up to the point you feel a stretch.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
External hip rotation exercise in lying position:
- You are lying with your knee joint bent & feet flat on the bed, hip-width apart.
- Try to let one knee joint drop towards the bed then bring it back up.
- Must keep your back flat on the bed throughout.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Heel slide:
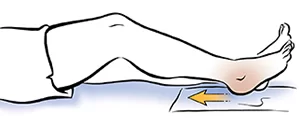
- You are lying on your back.
- Try to bend your leg & slide your knee joint towards your chest.
- Slide your heel down again & straighten your knee joint slowly.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
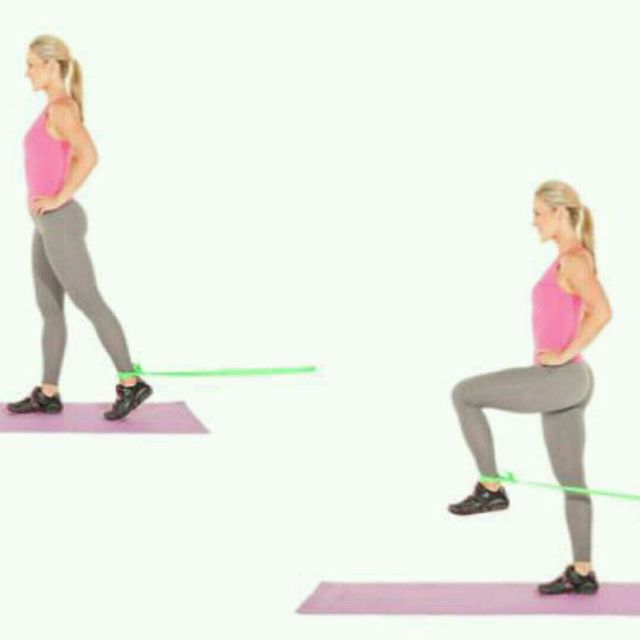
Hip flexion:
- You are in a standing position.
- Hold on to a work surface & march on the spot to bring your knee joint up towards your chest alternately.
- Your physiotherapist is recommended that you do not raise your knee joint above hip level.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Hip extension:
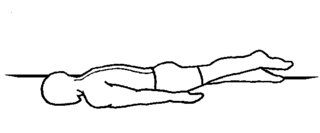
- You are in the prone position.
- Lie flat on your stomach.
- Must keep the legs straight.
- Try to tighten the muscles in the bottom & the hamstring of one leg.
- One leg is lifted toward the ceiling.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Hip abduction exercise in a standing position:
- You are standing with one hand resting on the back of a chair & a work surface for support.
- Try to lift your leg straight up to the side.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
You are also performing this exercise in the side-lying position.
- You are lying on to one side with the legs stacked.
- Try to bend to the bottom leg for support.
- Then straighten to the top of the leg & raise to 45 degrees.
- Hold this position for 10 seconds & then brief to relax.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Heel to buttock:
- You are in the supine position.
- Bend your knee joint to pull your heel up towards your bottom.
- Must keep your knee joint in line & your kneecap pointing towards the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Squats:

- First, hold onto a chair & work surface for support.
- You are in a standing position.
- Squat down till your kneecap is directly over your big toe.
- Your knee joint is not going in front of your toes.
- Then return to your normal standing position.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Short arc quadriceps exercise:
- First, roll up a towel & place the towel under your knee joint.
- Must keep the back of your thigh on the towel.
- Try to straighten your knee joint to raise your foot off the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Quadriceps exercise:
- First pull your toes & ankles towards you, while keeping your leg straight & pushing your knee joint firmly against the floor.
- You feel the tightness in the front of your leg.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
You are also performing this exercise from a sitting position when you find this exercise more comfortable.
In stomach exercise:
- You are lying on your back with your knee joint bent.
- Must put your hands under the small of your back.
- Try to pull your belly button down towards the floor or bed.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Knee lift:
- You are lying on your back.
- Pull each knee joint to your chest, in turn, must be keeping the other leg straight.
- Try to take the movement up to the point you feel a stretch.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- If this is difficult for you, try sliding your heel along the floor towards your bottom.
Clock tap:
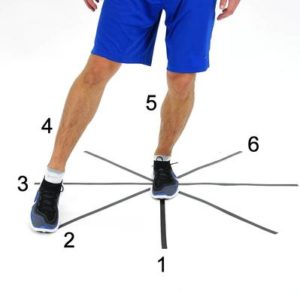
- You are standing next to a wall & door frame for support.
- Try to balance on the right foot.
- First hold on to the wall or door frame to stay steady, if needed.
- Must keep your knee joint straight over your ankle, with a slight bend.
- Tap your left foot around your right foot, as when your right foot is the centerpiece on a clock.
- Your left side is touching numbers on a clock face.
- Start at noon, then tap at 11, 10 & 9.
- Try to retrace the numbers back to 12 then tap 1 and 2 & retrace back to 12.
- Repeat this sequence 4 times; then complete with the opposite foot.
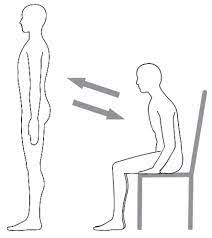
Sit-and-Stand:
- You are standing in front of a sturdy chair, feet planted on the floor about hip-distance apart.
- Try to press your hips back & bend your knee joint a little to lower yourself into a sitting position.
- Then tip forward from the hip joint, push through your feet & up with your legs to a standing position.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing Jacks:
- You are standing with your right arm holding onto a chair & countertop for support.
- Try to raise your left leg out to the side, as though you are doing the bottom half of a jumping jack.
- Do the repetition as many as you can then switch to the other leg.
Cross-body leg raises:
- You are standing with your right arm holding onto a chair & countertop for support.
- Try to raise your left leg forward & to the right, so it crosses your midline.
- Do this exercise slowly & try to raise your leg steadily.
- You are feeling a slight tension in your hip joint, which is normal.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Chair stand:
- First set a chair against the wall & sit towards the front of the chair with your feet flat on the floor.
- Try to recline back with arms crossed & hands on your shoulder joint.
- With your head, neck & back straight, bring your upper body forward.
- Then slowly rise to a standing position & return to your original sitting position.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
In the Double hip rotation:
- You are lying down on your back, with the knee joint bent & feet flat toward the floor.
- With your shoulders joint on the floor.
- Try to slowly lower your knee joint to one side while turning your head to the other.
- Bring the knee joint back.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
What is the Surgical Treatment for hip osteoarthritis?
After the medical treatment & physiotherapy treatment pain is not relieved then the doctor is advised surgical treatment.
- Total hip replacement:
- in the surgery remove both the damaged acetabulum & femoral head and position new metal, plastic & ceramic joint which is to restore the function of your hip joint.
- In the surgery both the head of the femur & the socket which is replaced with an artificial device.
- Hip resurfacing:
- In the hip replacement procedure, the damaged bone & cartilage in the acetabulum (hip socket) is removed which is replaced with a metal shell.
- when the head of the femur is not removed but instead capped with a smooth metal covering.
- Osteotomy:
- the head of the thighbone & the socket is cut & realigned to take pressure off of the hip joint.
- This surgery is used only rarely to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
What are the complications of hip osteoarthritis surgery?
- Blood clots
- Limb length inequality
- Hip dislocation
- Infection
- Damage to blood vessels or arteries
- Excessive bleeding
What are the risk factors for hip osteoarthritis?
- Previous hip trauma mostly give to result in unilateral hip osteoarthritis
- Primary inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis & ankylosing spondylitis
- Genetics
- Subchondral bone defects
- Joint morphology
- This hip osteoarthritis is Increase in age
- Metabolic diseases & acromegaly
- Femoroacetabular impingement
- Obesity is given to result in bilateral hip osteoarthritis
- Menopause
- Congenital & developmental hip disease
- Avascular necrosis of Hip joint
- The occupation which is applied to excessive strain on the hip joint
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Diet low Vitamin D, C & K levels
What are self-care routines for hip osteoarthritis?
Health care provider says that self-management also help in treating hip osteoarthritis.
Some things include in self-care:
- Try to learn as much about your condition
- Take to the advice of a doctor & knowing the treatment options for hip osteoarthritis.
- Do the active part in managing your pain & other symptoms
- Always follow a good healthcare provider
- Follow the diet & nutrition, restorative sleep & appropriate exercise during your daily routine.
Some lifestyle factors that contribute to hip arthritis include:
- Always follow good dietary choices
- Use of tobacco and alcohol
- Establishing healthy sleeping habits
- Getting appropriate care for other mental &physical health conditions
- Type & level of physical activity
- So always staying active or making positive lifestyle choices which help to reduce the risk of depression & anxiety with osteoarthritis.
Some self-care tips which help you with pain relief:
- Do enough rest.
- Always follow regular sleeping habits & rest when your symptoms feel worse than usual.
- Manage stress
- Exercise, meditation & listening to music helps you relax, avoid stress & lift your mood.
- Follow a healthy diet.
- In diet use to in fresh fruits & vegetables.
- Low in added sugar & fat which is help you feel better & maintain a healthy weight.
- Use fresh, whole foods rather than processed food.
- Stay in touch.
- You are meeting with friends & perhaps for exercise which is helpful to you relieve stress or must be keeping you healthy.
- Avoid tobacco & limit the alcohol.



10 Comments