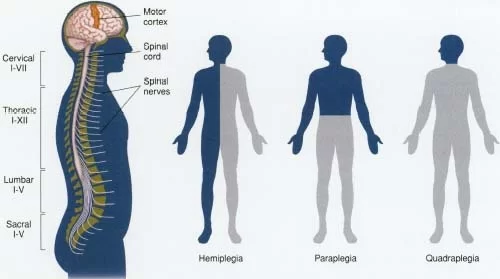
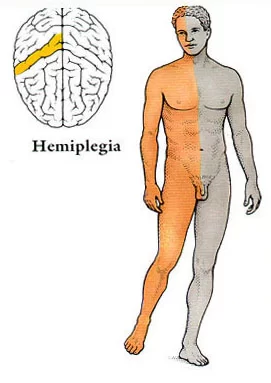
Hemiplegia
Table of Contents
What is a Hemiplegia?
‘Hemiplegia’ means complete paralysis of one half of the body, including one arm and leg.
Any disease or injury in the motor centers of the brain can cause hemiplegia.
Hemiplegia is a more severe form of ‘hemiparesis’ wherein one-half of the body is only weakened.
Causes of Hemiplegia:
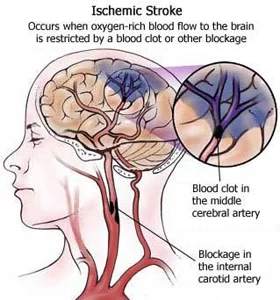
Stroke:
it is the commonest cause of hemiplegia.
The stroke may be caused by:
A clot forms within the blood vessel blocking the blood supply, known as a thrombus.
A thrombus breaks away from its site of origin and forms a block elsewhere in the circulation, known as emboli.
A bleed from a blood vessel supplying the brain is known as hemorrhage.
Head injury
Diabetes
Brain tumor
Infections: meningitis, encephalitis
vasculitis
Diseases affecting the nerves
eg;
Multiple Sclerosis
acute necrotizing myelitis.
cerebral palsy An electroencephalogram may give information about brain injury and its importance.y
Symptoms of Hemiplegia:
Muscle stiffness or weakness in one half of the body
Favoring one side of the body
Keeping one hand fisted
Difficulty balancing and walking
Lack of fine motor skills
Developmental delays, especially with motor skills
Speech and Language
Sign:
The lesion is localized on the side opposite the affected limb: left brain injury causes right hemiplegia and vice versa.
Observed with different depending on the location of the injury.
When the lesion in the brain cortex:
this causes disproportionate hemiplegia: the face and arms are predominantly affected.
When the lesion is located in the white matter of the brain:
this causes proportional hemiplegia: the arm and leg are affected similarly deficient.
A brainstem lesion causes paralysis of one side of the body and involvement of the face on the other side.
Investigation:
CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect the causes (aneurysm, tumor embolism) cause brain damage.
The presence of a Babinski sign by stimulating the outer edge of the sole from the heel to midfoot.
electroencephalogram may give information about brain injury and its importance.
Physiotherapy treatment of Hemiplegia:
Physiotherapy approach:
theory:
Concerned with ‘the interaction of somatic, autonomic, and psychic factors, and their role in regulations of motor behavior’.
Motor and sensory functions are inseparable
Focuses on the developmental sequence of recovery and the use of peripheral input to facilitate movement
principle:
facilitate movement and postural responses of patients in the same automatic way as they occur in normal.
Sequencing of movement from basic to complex. supine lying; rolling; prone lying; kneeling; standing; walking
Sensory stimulation by brushing, icing, tapping, pounding, stroking, slow stretch, and joint compression to stimulate movement at an automatic level
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) or Knott and Voss
Brunnström
Bobath or neurodevelopmental approach (NDT)
Carr and Shepherd or motor learning or motor relearning
Sensory integration.
Rehabilitation and control of disability.
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
High-intensity electrical stimulation is a proven way to maintain size and function, in muscles that must temporarily take a complete break from activity.
The right kinds of electrical stimulation can keep muscles relatively sound, even when they are not being stimulated by the nerves or engaging in any real activity.
Botulinum Toxin injections
Some forms of hemiplegia make the limb muscles very taut and resistant even to passive movements.
Botulinum injections decrease the high muscle tone of these muscles. However, it is only a temporary and expensive solution to a chronic condition.
Intensive physiotherapy sessions:
upper limb exercise
lower limb exercise
passive exercises
active assisted exercise
active exercise
Activities like :
standing
walking is done repetitively under the guidance of trainers to prevent muscle degeneration from prolonged underuse.
weight-bearing exercise
bridging
Treatment of Hemiparesis
Gait Training :
walking in parallel bar
walking out of the parallel bar
Walking with stick
walking with support
walking without support.
Related Other Article Post :





2 Comments