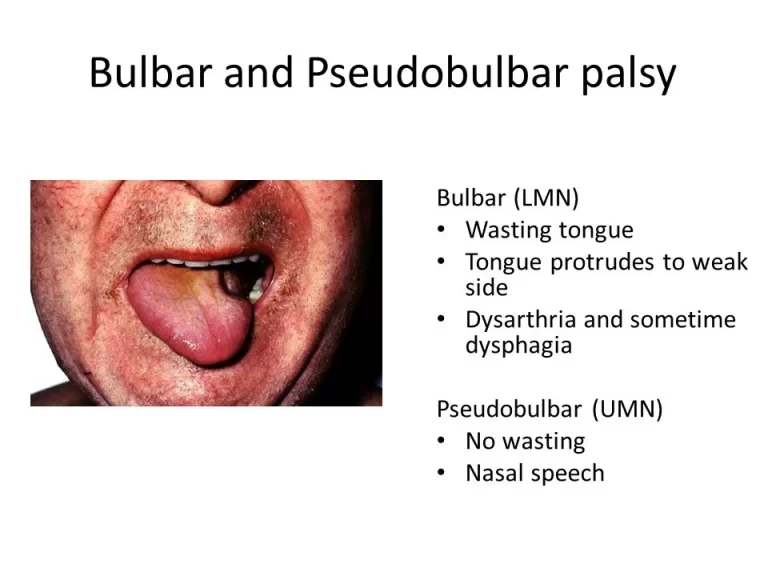
Pseudobulbar Palsy
What is Pseudo-bulbar palsy? Signs and symptoms of the Pseudobulbar palsy Signs and symptoms of pseudobulbar palsy involve: Causes of Pseudo bulbar palsy Rare causes of pseudobulbar palsy prevalence of the Pseudo bulbar palsy Pathophysiology of the Pseudo bulbar palsy Diagnosis of Pseudo bulbar palsy Treatment of pseudo bulbar palsy Dysphagia ( difficulty in swallowing…