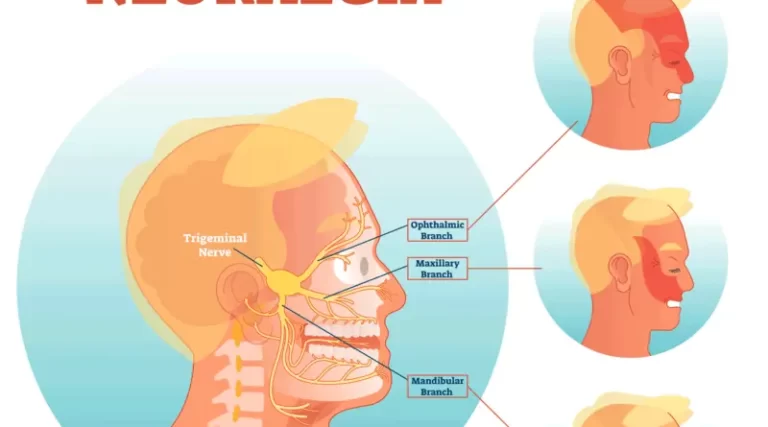
Trigeminal Neuralgia
What is Trigeminal neuralgia? What are the symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia? This disorder is distinguished by episodes of severe facial pain along the trigeminal nerve divisions.A flare-up of trigeminal neuralgia may start with tingling or numbness in the face. Pain occurs in intermittent bursts that last from a few seconds to two minutes, becoming more…