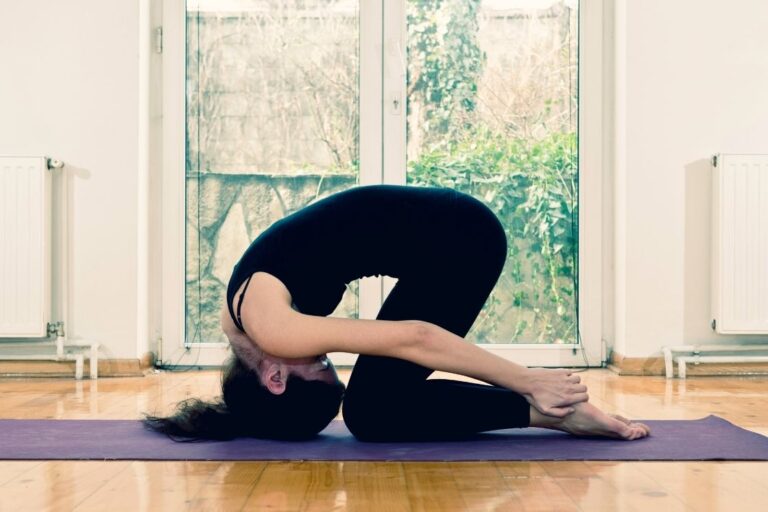
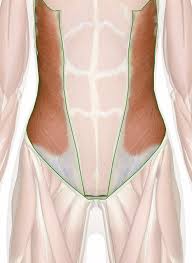
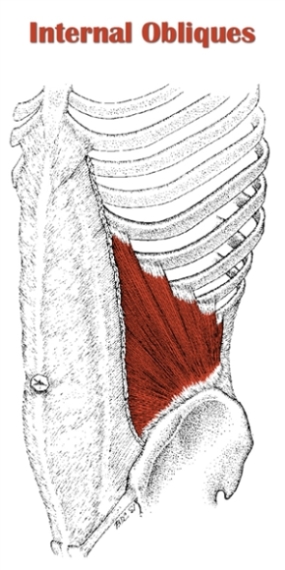
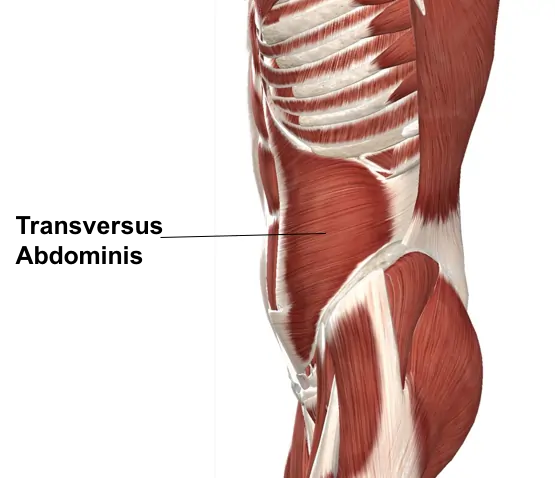
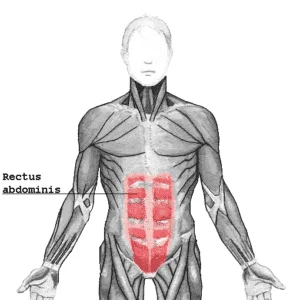
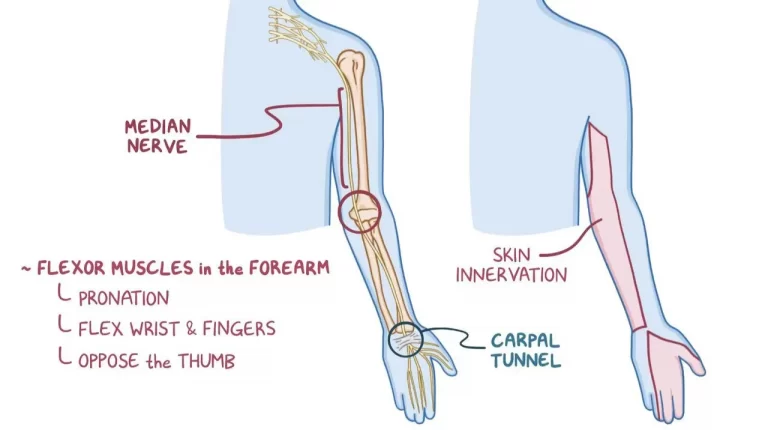
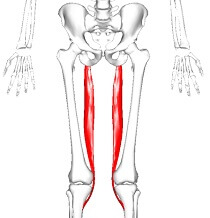
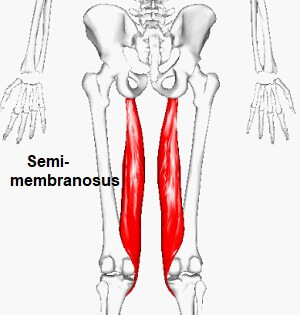
External oblique muscle
Introduction of external oblique muscle: The external oblique muscle is one of the outermost abdominal muscles, extending from the lower half of the ribs around and down to the pelvis. It is broad, thin & irregularly quadrilateral, its muscular portion occupying the side. Together, the external oblique muscles cover the sides of the abdominal area,…