TARSAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
Table of Contents
What is Tarsul Tunnel Syndrome?
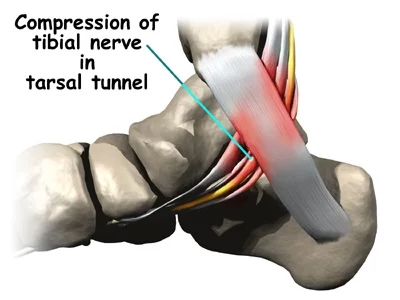
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is condition in which posterior tibial nerve is compressed/Damaged in tarsal tunnel , is a part of ankle joint, narrow space is covered by with a thick ligament (the flexor retinaculum) that protects and maintains the structures contained within the tunnel—Nerves,arteries, veins and tendons.
Anatomy Of Tarsal Tunnel :
To Understand tarsal tunnel syndrome we must understand tarsal tunnel anatomy and posterior tibial nerve.
- The Tarsal tunnel contains:
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- Posterior tibial artery & vein
- Tibial nerve
- Flexor hallucis longus tendon
- The tibial nerve divides into two terminal branches – the medial and lateral plantar nerves – as it passes through the tarsal tunnel. The medial calcaneal nerve branches from the tibial nerve at or superior to the flexor retinaculum.
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a rare compressive neuropathy of the tibial nerve or one of its branches as they pass under the flexor retinaculum.
- In the TTS literature, the tibial nerve is also referred to as the posterior tibial nerve and TTS is also known as Posterior Tibial Nerve Neuralgia. Some authors refer to compression of the deep fibular nerve as “anterior tarsal tunnel syndrome”.
- Posterior Tibial Nerve is Branch of sciatic nerve.
Which Are Common Cause of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome ?
Incidence is unknown. A higher prevalence is reported for women than men. It can be seen at any age. Causes of TTS include:
- Repetitive stress activities such as running, excessive walking or standing
- Traumas such as fracture, dislocation or stretch injuries
- Heel varus or valgus
- Fibrosis
- Excessive Weigh
- Space occupying lesions in tarsal tunnel region such as a ganglion, tumors, edema, osteophytes or varicositie
- Tendonitis
- Systemic diseases that cause ankle inflammation or nerve compromise (ex: diabetes mellitus, arthritis
- Many cases (20%-40%) are idiopathic.
- severely flat feet, because flattened feet can stretch the tibial nerve
- benign bony growths in the tarsal tunnel
- High diabetes, which makes the nerve more vulnerable to compression.
- varicose veins in the membrane surrounding the tibial nerve, which cause compression on the nerve
SYMPTOMS OF TARSAL TUNNEL SYNDROME :
- People with tarsal tunnel syndrome may experience pain, numbness, or tingling. This pain can be felt anywhere along the tibial nerve, but it’s also common to feel pain in the sole of the foot or inside the ankle.
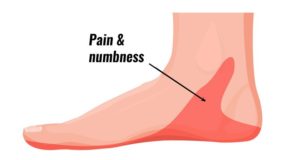
This can feel like:
- sharp, shooting pains
- pins and needles
- an electric shock
- a burning sensation
- Symptoms vary greatly depending on each individual. Some people experience symptoms that progress gradually, and some experience symptoms that begin very suddenly.
- Pain and other symptoms are often aggravated by physical activity. But if the condition is long-standing, some people even experience pain or tingling at night or when resting.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome results from compression of the tibial nerve, and it’s often caused by other conditions.
How to Deferentially Diagnoses the Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome ?
- TTS can present similarly to other lower extremity conditions with the most common differential diagnosis being plantar fasciitis as these patients also present with plantar heel pain. In addition to Plantar fasciitis (in which TTS is thought to be commonly misdiagnosed as), polyneuropathy, L5 and S1 nerve root syndromes, Morton metatarsalgia, compartment syndrome of the deep flexor compartment will have to be distinguished from tarsal tunnel syndrome as well.
Medical Treatment :
1) CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT :
- One of the mechanical causes of tarsal tunnel syndrome is believed to be excessive calcaneal eversion leading to collapse of the medial longitudinal arch (over pronation) which puts traction stress on the posterior tibial nerve and compression by the flexor retinaculum. Scherer proposes that custom fit orthoses will correct the over pronation and therefore decrease the stress on the posterior tibial nerve. Although there is no clinical outcome studies documenting the effectiveness of orthotics, it may be an important technique to consider when treating patients with tarsal tunnel syndrome.
- Several articles listed basic techniques for conservative management of tarsal tunnel syndrome as a guideline to rehabilitation, but did not provide patient outcomes.
2) POST-OPERATIVE TREATMENT :
1)Rest: The easiest and most immediate way to reduce inflammation anywhere in the body is to stop using and putting pressure on the affected area. How long an individual should rest the foot depends mostly on the severity of symptoms. For minor cases, rest may mean replacing running with swimming. For more severe cases, resting the nerve may require completely refraining from exercise and activity.
2)Ice: An ice pack covered with a cloth or towel can be applied to the inside of the ankle and foot for 20-minute sessions to reduce inflammation. It is best to have the foot elevated during this time. Icing sessions can be repeated several times daily, as long as breaks of at least 40 minutes are taken.

3) Compression and elevation: Compressing the foot, and keeping it raised above the heart, helps reduce blood flow to the foot, and so reduces inflammation. Try wrapping the foot with an ACE wrap, and resting it on a pillow while sitting and sleeping.
4) Over-the-counter pain and anti-inflammatory medications: These can include ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
5) Full immobilization: For severe cases, especially those involving physical damage to the nerve, a cast may be necessary to restrict movement completely, allowing the nerve, joint, and surrounding tissues a chance to heal.
6) Injection therapy: For very painful or disabling symptoms, anti-inflammatory medication, such as corticosteroids and local anesthetics, may be directly injected into the nerve.
7) Orthopedic devices and corrective shoes: Podiatrists can make specialized shoes, and inserts that help support the arch and limit motions that can further irritate the inflamed nerve and surrounding tissues. Shoes also exist to help prevent pronation or inward rolling of the foot.
8) Reducing foot pressure: In some cases, wearing looser or larger fitting footwear and socks may help reduce tightness around the foot.
9) Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy exercises can often help reduce symptoms of TTS long-term, by slowly stretching and strengthening the connective tissues, mobilizing the tibial nerve, and opening the surrounding joint space to reduce compression.
Physiotherapy Management :
Physiotherapist play a key role in treatment of TTS to relieve symptoms and maintain their daily function and activities.
Physiotherapist will assess the patient first and then make a treatment plan to according to symptoms/sign of patient specific needs and goals.
Because the signs and symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel syndrome can vary, the treatment plan will also vary.
Basic Physiotherapy Treatment are as per following :
- Nerve stretching / Mobilization Exercise : Gentle exercises that move and “stretch” the nerves may help reduce symptoms and improve function.
- Muscle Strengthening Exercises : Affected muscle become weak and require Strengthening activities, mainly tibialis posterior muscle in the back of lower leg.
- Balance and Co-ordination Activities : Work to improve patient balance and co-ordination, which are also affected in Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome.
- Orthotics /Taping / Bracing : Ankle taping, a custom orthotic, or bracing to position the foot to reduce stress on the posterior tibial nerve.

Other types of physiotherapy used for TTS include:
- Ultrasound therapy
- Electrical Stimulation
- acupuncture
- manual therapy
- taping or bracing
- Ultimately, surgery may be performed for very severe or chronic cases of TTS that do not respond to any conservative Medical/Physiotherapy Treatment
Preventive Measure :
However, there are no fix strategies for preventing Tarsal Tunnel syndrome, there are few tips helps to minimize stress to the foot and ankle, eg. choosing appropriate footwear, wearing custom orthotics, minimizing the amount of time spent standing on hard surfaces, and improving and maintaining strength in the muscles of your legs, ankles, and feet.
Early Diagnosis of the signs and symptoms of TTS will helps doctors starts proper treatment of the condition, which may improve faster and reducing further damage.
Other Heel Pain Related Article :


Please upload note about tardys ulnar nerve palsy