Inflammation: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Inflammation is a complex biological response of the body’s immune system to harmful stimuli, such as injury, infection, or irritation. It is characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain in the affected area. It is a protective mechanism that helps the body to heal and defend against pathogens, irritants, and other harmful substances.
Chronic or excessive inflammation can contribute to the development of various diseases and disorders, such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Therefore, controlling inflammation is an important aspect of maintaining good health and treating many health conditions.
Table of Contents
Types of Inflammation
There are two main types of inflammation: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation is a rapid and short-lived response to harmful stimuli, such as injury or infection. It is characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain, and is typically resolved within a few days. This type of inflammation is a normal and necessary part of the body’s immune response and helps to remove harmful stimuli and initiate the healing process.
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is a long-lasting and persistent response to harmful stimuli. It is characterized by low-grade inflammation that persists over a prolonged period of time and can lead to the development of various diseases and disorders. Chronic inflammation is often caused by ongoing exposure to irritants, pathogens, or other harmful substances, or by underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or allergies.
In addition to these two main types of inflammation, there are also several subtypes of it, including autoimmune inflammation, which occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs, and neuroinflammation, which occurs in response to injury or damage to the central nervous system.
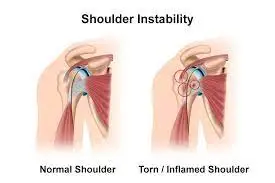
Inflammation and Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term that refers to inflammation in the joints. When it’s in the joints is a hallmark of many types of arthritis, and it is the main cause of joint pain, stiffness, and swelling in these conditions.
In rheumatoid arthritis, for example, the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, leading to chronic inflammation and joint damage. And it causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints, and can also cause damage to bones, cartilage, and other tissues in the joint.
In osteoarthritis, the joints undergo wear and tear over time, and the breakdown of cartilage can lead to inflammation in the joints. The inflammation can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility in the affected joints.
Treatment for arthritis typically involves reducing it in the joints and controlling symptoms. This may involve the use of anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, weight management, and other interventions to help reduce it and improve joint function.
It is important to note that while inflammation is a key aspect of many forms of arthritis, not all forms of arthritis are associated with it. For example, some types of arthritis, such as gout, are caused by deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints, and do not involve significant inflammation.
Symptoms
Acute inflammation is characterized by a rapid and short-lived response to harmful stimuli, such as injury or infection. Common symptoms of acute inflammation include:
- Redness in the affected area
- Heat in the affected area
- Swelling in the affected area
- Pain in the affected area
- Tenderness in the affected area
- Loss of function in the affected area
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is characterized by low-grade inflammation that persists over a prolonged period of time. Common symptoms of chronic inflammation include:
- Fatigue
- Pain and stiffness in joints
- Digestive problems, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhoea
- Skin problems, such as rashes and dry skin
- Respiratory problems, such as asthma and sinusitis
- Mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety
- Sleep problems
- Weight loss
It is important to note that the symptoms of chronic inflammation can be non-specific and may be similar to those of other medical conditions. Therefore, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and to rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
What Causes Inflammation and Its Effects?
Inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Physical injury or trauma
- Infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections
- Exposure to irritants, such as chemicals, pollutants, or smoke
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or other substances
- Chronic diseases, such as arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease
- Autoimmune disorders, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues
- Chronic stress
- Poor diet and lack of physical activity
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
The effects of inflammation can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on the cause and duration of the inflammation. In the short term, it is a protective response that helps the body to heal and defend against harmful stimuli. However, chronic or excessive inflammation can have a number of harmful effects, including:
- Tissue damage and scarring
- Increased risk of chronic diseases, such as arthritis, heart disease, and cancer
- Impaired wound healing
- Decreased function and mobility in affected joints
- Increased risk of infections
- Mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety
It is important to manage and control it in order to reduce its harmful effects and maintain good health. This may involve lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding exposure to irritants and harmful substances. In some cases, medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, may also be necessary to control it.
Diagnosis
Inflammatory diseases can be diagnosed based on a combination of factors, including:
- Medical history: The doctor will ask about symptoms, past illnesses, and family history of inflammatory diseases.
- Physical examination: The doctor will examine the affected area for signs of swelling, redness, heat, and tenderness.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help diagnose it by measuring levels of inflammatory markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP).
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, can help to identify changes in the affected area that are characteristic of inflammatory diseases, such as joint damage in arthritis.
- Tissue samples: In some cases, the doctor may take a tissue sample from the affected area for laboratory analysis, such as a biopsy of skin in psoriasis.
It is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and to rule out other possible causes of symptoms. Some conditions, such as infections, can mimic the symptoms of inflammatory diseases, and a doctor can help to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and provide appropriate treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of inflammatory diseases depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation, the severity of the symptoms, and the individual’s medical history and other health factors. Some general treatment options for inflammatory diseases include:
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, getting regular physical activity, managing stress, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), can help to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms of inflammatory diseases.
- Biologic therapies: Biologic therapies, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitors, target specific molecules in the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damage caused by inflammation, such as joint replacement surgery for severe arthritis.
- Complementary and alternative therapies: Some people with inflammatory diseases use complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and herbal remedies, to manage symptoms.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and preferences. In some cases, a combination of different treatment approaches may be necessary to effectively manage the symptoms of inflammatory diseases.
Home Remedies for inflammation
You may select an anti-inflammatory diet that helps to relieve inflammation. Few research shows that those people who follow a Mediterranean diet have reduce the levels of inflammation in their bodies.
You should select to eat those foods that have anti-inflammatory effects, such as:
- Oily fish, such as sardines. salmon, mackerel
- Leafy greens vegetables like spinach and kale.
- Olive oil.
- Tomatoes.
Eating large amount of certain foods may increase risk of inflammation. If you have chronic inflammation, you may feel good if you avoid certain foods such as:
- Fried foods, like many fast food oily items.
- Cured meats with nitrates, like hot dogs, Burger.
- Highly refined oils and trans fats.
- Refined carbohydrates, such as sugar, pastries or white bread.
How can I prevent inflammation?
You may reduce your risk of chronic inflammation by living healthy lifestyle habits. Few of these health habits tips are:
- Try to Achieving and maintaining a healthy Body weight.
- Quitting smoking.
- Daily Exercising such as Running, walking, cycling, swimming (4 to 6 times per week at least)
- Reduce or Quitting your alcohol intake (maximum 2 ounces per day).
- Managing stress with meditation or journaling.
When should I consult the doctor?
Contact your Doctor immediately if you feel a serious injury. Also consult with Doctor about you have ongoing pain, swelling, stiffness or other related symptoms. A Doctor examine you about the cause and plan a treatment to help you feel better.
Summary
Inflammation is a complex biological response of the body’s immune system to harmful stimuli, such as injury, infection, or irritation. If inflammatory reaction is too long, it may lead to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a symptom of other associated conditions, such as Gout, Osteoarthritis. Your Doctor may prescribe you medication or at-home treatment. You can follow a health diet and lifestyle that helps to reduce inflammation.