Vitamin E deficiency
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin E deficiency?
Vitamin E deficiency is incredibly rare in humans as it is improbably caused by a diet consisting of low vitamin E. Rather, it manages to be led by irregularities in dietary fat absorption or metabolism. Vitamin E is a lipid-soluble nutrient. Vitamin E may have an important role in decreasing atherosclerosis and lowering rates of ischemic heart disorders. Premature infants have low vitamin E help due to vitamin E being only able to cross the placenta in small parts.
Vitamin E is all the ensuing eight compounds alpha, beta, gamma, and delta-tocopherol & alpha, beta, gamma, & delta-tocotrienol. Alpha-tocopherol is the only combination of the 8 that is known to meet human dietary needs. All of the vitamin E conditions are absorbed in the small intestine, & then the liver metabolizes just alpha-tocopherol. The liver then releases & excretes the remaining vitamin E conditions.
Pathophysiology
Vitamin E functions as an antioxidant, immunomodulation, & antiplatelet effect.
Antioxidant Effect
Vitamin E contains propagated oxidation of saturated fatty acids within membranes. Also, vitamin E may contain oxidative modifications to LDLs, decreasing coronary heart diseases.
Immunomodulation
Vitamin E reduces the production of prostaglandin E2 & serum lipid peroxides while improving lymphocyte proliferation.
Antiplatelet Effect
Vitamin E interferes with platelet adhesion by controlling oxidative changes to LDL & inhibiting platelet aggregation by decreasing prostaglandin E2. Another effect is inhibiting protein kinase C generating smooth-muscle proliferation.
Even though analysis has shown that vitamin E helps with the prevention of heart conditions & atherosclerosis, it has not been approved for this service by the United States Food & Drug Administration [ FDA ].
Causes of vitamin E deficiency
Genetics
Vitamin E deficiency usually runs in families. Understanding family history can make diagnosing certain infrequent, inherited conditions easier.
Medical conditions
Vitamin E deficiency can also result from conditions that severely decrease the absorption of fat. This is because the body needs fat to absorb vitamin E perfectly.
Some of these conditions include:
- chronic pancreatitis
- celiac disorder
- cholestatic liver disorder
- cystic fibrosis
Deficiency is also common in newborns & babies born prematurely who have lower birth weights & less fat.
Premature babies are at particular risk because an immature digestive tract can interfere with fat & vitamin E absorption.
Vitamin E lacks in these infants can also cause hemolytic anemia, which eliminates red blood cells.
Signs and symptoms of deficiency
Vitamin E deficiency may lead to disorientation & vision issues.
Low levels of vitamin E can cause:

Muscle weakness: Vitamin E is important to the central nervous system. It is among the body’s main antioxidants, & a lack of results in oxidative stress, which can cause muscle weakness.
Coordination & walking difficulties: A insufficiency can lead to certain neurons, named the Purkinje neurons, breaking down, hurting their capability to transmit signals.
Numbness and tingling: Injury to nerve fibers can prevent the nerves from transferring signals correctly, resulting in these feelings, which are also named peripheral neuropathy.
Vision deterioration: Weaken the light receptors in the retina & many different cells in the eye because of vitamin E insufficiency. This can generate a loss of eyesight over time.
Immune system problems: Some analysis indicates that a deficiency of vitamin E can interfere with the immune cells. More aging adults may be especially at risk.
Muscle deficiency & problems with coordination are neurological symptoms that show damage to the central and peripheral nervous systems.
The peripheral system is the network of nerves encountered beyond the brain & spinal cord and these neurons pass messages throughout the body.
The central nervous system displays between the brain & the spinal cord.
The sheaths of neurons are mostly comprised of fats. It includes fewer antioxidants that guard these fats, & the function of the nervous system breaks down when the body has too slight vitamin E.
Hair fall: Eating a diet rich in vitamin E will reverse the injuries brought about by hair fall. If experiencing abnormal hair fall, it is a clear sign that may not be conscious of taking a Vitamin E-rich diet.
Vitamin E can restore & refurbish dead hair cells & hair follicles.
Dry, flaky skin: Dry skin is generally a byproduct of severe weather conditions especially in the winter months. However, do not be surprised if easy to dry skin even otherwise. This is an obvious indicator of a deficiency of Vitamin E.
Eye problems: These contain weakening of eye muscles, fluctuating powers, etc. An early diagnosis can hit the nail on the head and measures can be taken out to control eye damage.
Hormonal imbalance: Any kind of hormonal inequality can create devastation in the body & it is very hard to analyze what may be leading to the imbalance. In such cases, Vitamin E could be lacking. Whether it is an inequality like PCOD, PCOS, or pre-menopause, a Vitamin E-rich diet is necessary to combat the problem holistically.
Why do you require Vitamin E?
Vitamin E assists in Anti-ageing: The dangerous ultraviolet rays of the sun are known to lead to a great deal of damage to the skin, releasing forces that cause wrinkling of the skin. Being an antioxidant, vitamin E raises the skin in a way that supplies oils, which control the aging of the skin. Most everyday use products for the skin consist of vitamin E. We generally fight dryness of the skin with moisturizing creams, but little do we recognize that these creams have vitamin E as an important element. Vitamin E has the possibility of rejuvenating dead skin cells, thereby raising them & giving them a younger outward impression.
Vitamin E is an Antioxidant: Free revolutionaries break down healthy cells in the human body. The best immunity against free radicals is a diet rich in antioxidants. Vitamin E is rich in antioxidants & helps decrease the damage done by free radicals.
For Hair Care: Vitamin E is known to be helpful for hair care too. A hair oil rich in Vitamin E can maintain moisture & help maintain dryness away.
Balancing Hormones: Vitamin E also maintains equilibrium within the hormones of the body. Any imbalance in the hormones is followed by ill health.
Benefits reduce Inflammation: Vitamin E is known to be an adequate anti-inflammatory nutrient as well.
Vitamin E can be found in all kinds of green leafy vegetables, in fruits like papaya, dry fruits & nuts, and seeds.
The greatest sources of Vitamin E include:
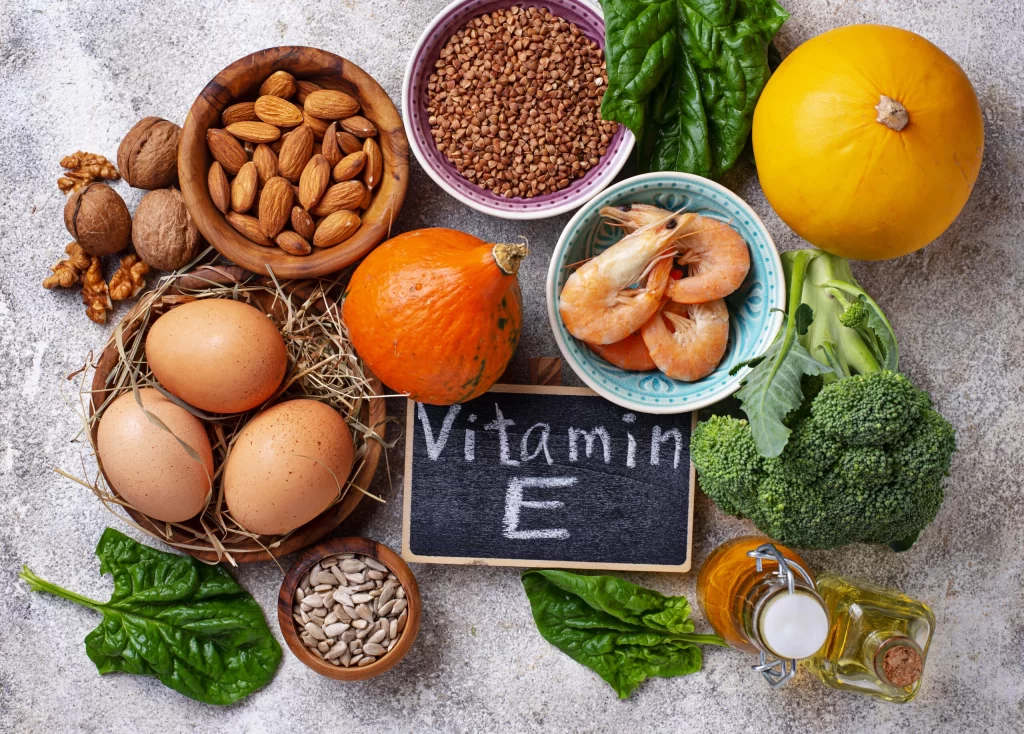

- Flaxseeds
- spinach
- peanuts
- avocado
- almonds
- broccoli
- asparagus
- shrimp
Contain at least one of these in the diet every day. Here is the guide to diagnosing which vitamin may be lacking. There are many explanations why Vitamin E should be part of a normal diet. It is an antioxidant that restricts the process of aging and acts as an obstacle to easy cell damage.
Diagnosis of vitamin E deficiency
While developing a differential diagnosis, clinicians must evaluate other possible vitamin defects as well as the following:
- Friedreich ataxia
- Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency (AVED)
- Stroke
- Cerebral palsy
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- Biliary disease
- Short-Bowl syndrome
- Mutations in the tocopherol transfer protein cause impaired fat metabolism
- Cystic fibrosis
- Chronic cholestatic hepatobiliary disease
- Crohn disease
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- Liver disease
- Abetalipoproteinemia
- Isolated vitamin E deficiency
Prognosis
If left untreated, symptoms may worsen. However, once analyzed, the outcome is very good as most signs will settle quickly. However, as the deficit becomes more enunciated, the therapy will be more limited. Patients who are at threat of vitamin E deficiency should be tested and considered regularly.
Treatment of vitamin E deficiency
The best food sources of vitamin E
Below are some of the best vitamin E-rich foods to contain in your diet. This can help control deficiency.
- wheat germ oil
- sunflower seeds
- almonds
- Many vegetable oils like sunflower oil, safflower oil, corn oil, soybean oil
- hazelnuts
- peanut butter
- peanuts
- spinach
- broccoli
- kiwi
- mango
- tomato
- fortified breakfast cereals
Supplementing vitamin E
If the doctor recommends supplementing vitamin E, be certain to buy from a reputable brand. Although vitamin E supplements are monitored by the FDA, they’re not as precisely regulated as pharmaceuticals, so supplements aren’t always safe & sufficient.
Eating vitamin-E-rich nutrition could be safer & more effective than taking a supplement.
However, some people, like those with medical conditions that affect vitamin E absorption, may require a vitamin E supplement to maintain healthy levels. And if deficient in vitamin E then you may need a high-dose supplement as recommended by the doctor.
The role of fat in absorption
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, like its buddies vitamins A, D, & K. This means they dissolve in organic solvents, making them more comfortable to absorb and transport throughout the body, just like fats. Peeps with diseases that mess with fat absorption are more possible to produce vitamin E insufficiency than those without.
Vitamin E contains 8 naturally happening fat-soluble nutrients named tocopherols.
Complications
Taking vitamin E supplements can inhibit and react with other medicines that might be taken.
These include:
- Anticoagulants
- Antiplatelet medicines
- niacin
- Chemotherapy medicines
- Radiotherapy medicines
- Cholesterol-lowering medicines
If a doctor recommends vitamin E supplementation, make sure to let them know about any current prescription drugs you take.
Vitamin E has a few dealings with medications that are detailed below:
Anticoagulation & antiplatelet medications: Due to vitamin E deterring platelet aggregation & disrupting vitamin K clotting factors, there is a protentional increased risk of bleeding
combining these two.
Simvastatin & niacin: Vitamin E can decrease the amount of high-density lipoprotein [ HDL ], which is the opposite expected effect of taking simvastatin & niacin.
FAQ
Human vitamin E insufficiency symptoms contain a progressive neurologic disease, spinocerebellar ataxia, which occurs as a result of a dying rear of peripheral nerves, especially sensory neurons.
Dietary vitamin E insufficiency is common in nations with high rates of food insecurity: insufficiency among adults in other nations is uncommon and usually due to fat malabsorption.
You should be able to get the amount of vitamin E you require by eating a various & balanced diet. I take vitamin E supplements but do not take too much as this could be harmful. Taking 540mg (800 IU) or negligibly a day of vitamin E supplements is doubtful to lead to any damage.
The body requires sufficient vitamin E to fight oxidative stress in the scalp that is associated with hair loss. Vitamin E can also boost blood flow to the scalp, which will stimulate hair growth. Vitamin E also creates a protective wall on the skin.