Pudendal nerve entrapment syndromes : Physiotherapy Treatment, Exercise
Table of Contents
What is Pudendal nerve syndrome ?
- It is also known as the Pudendal neuralgia & Alcock syndrome.
- It is an unusual of the condition which is arises from to the compression of to the pudendal nerve (S2) .
- It is a chronic & severely disabling neuropathic pain syndrome.
- It is a presents in to the pudendal nerve region & affects to the both of the males & females.
- It is a mostly inappropriately treatment & underdiagnosis and also affect to the impairment of the quality of the life.
- In this condition patient feel to the pain, discomfort & numbness in the pelvis ,genitals , perineal, perianal area.
- It is happen when to the major nerve of the lower body is damage or irritate & it is make to it hard for the use to the bathroom ,during sex & In the sit to down.
- This pain is come & go.
- This syndrome is one of form to the vulvodynia which is mostly common in women.
- This syndrome is also affect to the men.
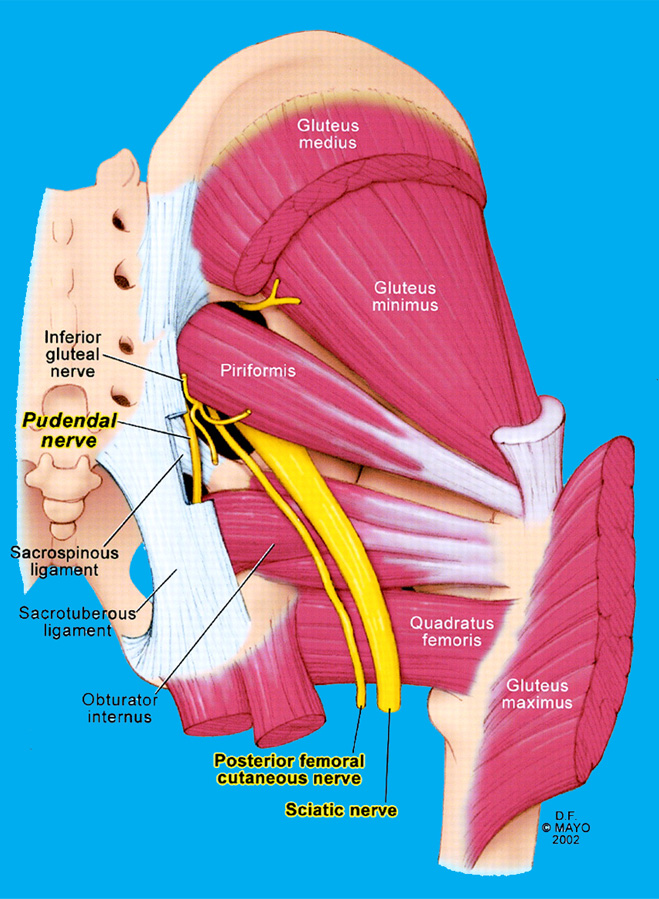
Anatomy of the Pudendal Nerve :
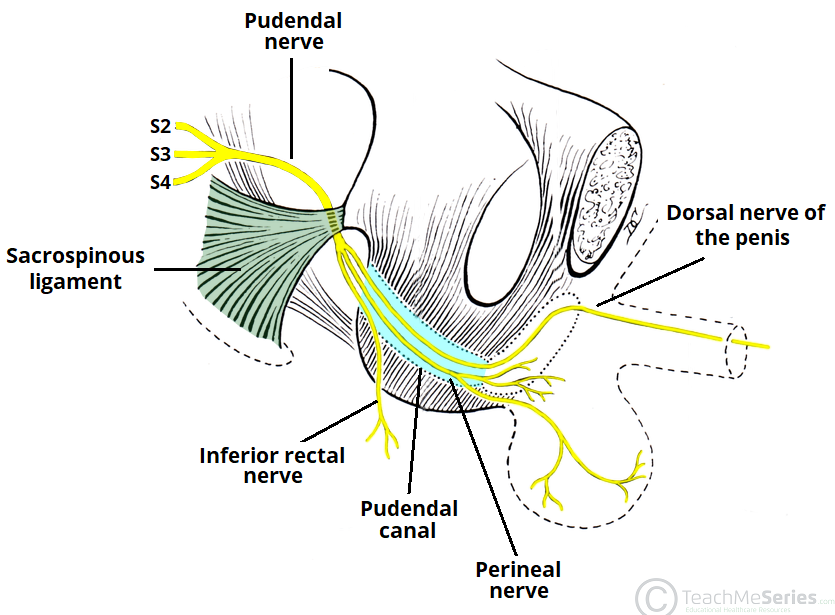
- This nerve is in paired, meaning to there are to the two nerves, one for the left & one for the right side of to the body.
- This nerve is emerges from nerve roots to the S2, S3, S4 roots of the ventral rami of to the sacral plexus.
- It is carries to the sensory, motor, & autonomic fibers .
- So that in this an injury to this nerve sensory is more affected than the motor.
- Courses of this nerve is between the two muscles, the piriformis & coccygeus muscles.
- It is departs to the pelvic cavity through to the greater sciatic foramen ventral to the ligament sacrotuberous .
- It is pass to the medial side to & under to the sacrospinous ligament to the level of the ischial spine for to the re-enter of the pelvic cavity through to lesser sciatic foremen.
- In This nerve courses also a pudendal canal, which is also to the Alcock canal.
- The last three branches of this nerve terminate in to the fossa of ischioanal .
- In three branches include the perineal branch, inferior rectal branch, perineal branch, & the dorsal sensory nerve of to the penis / clitoris.
- Sensory fibers = it is innervates in to the external genitalia of the both of the sexes & to the skin around of the anus, anal canal & perineum
- Motor fiber = it is innervates to various to pelvic muscles, to the external urethral sphincter & the external anal sphincter.
- Autonomic fibers = it is carries to sympathetic nerve fibres of the skin of to the S2-S4 of the dermatology region.
- This nerve compression is based on to the anatomy .
- This syndromes is subdivide into the four types based on to the level of compression.
- Type I – Entrapment is below to the piriformis muscle when the pudendal nerve is exits form the greater sciatic notch.
- Type II – Entrapment is between to the sacrospinous & sacrotuberous ligaments , it is the most common cause of the nerve entrapment.
- Type III – Entrapment is in the Alcock canal.
- Type IV – Entrapment is of the term inal branches.
Etiology of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome:
- It is arise from to the non-mechanical or mechanical injury.
- Mechanical injury is due to the compression, stretching or transaction,.
- In the mechanical causes compression is the most common cause of this symdrome .
- Non-mechanical causes is in this symdrome
- Viral infections such as HIV , herpes zoster
- Multiple sclerosis
- Diabetes mellitus
Epidemiology of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome:
- This is to a rare syndrome
- This prevalence is to unknown.
- This condition is may be occurs to 1 per 100,000 .
Pathophysiology of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome:
- Exact mechanism of this nerve dysfunction & damage is to dependent on to its etiology.
- It is may be to the unilateral or the bilateral.
- Patient is feel the stretch & compression .
- This nerve is compressed to during prolong sitting & cycling.
Clinical Presentation of of the Pudendal Nerve:
- In this situation include to pelvic pain with the sitting which is increases throughout to the day & decreases with to the standing or to lying down.
- Sexual dysfunction & difficulties with the urination & defecation.
- To confirm this syndrome by the Nantes criteria.
- This pain & sensations are to similar to the other entrapment nephropathy.
Causes of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome:
- There are to many several things which can damage the pudendal nerve.
- It is happen due to when the if any is injured,
- In past clear to the surgery,
- During to the birth.
- Tumor & any infection which is squeeze or irritate to it
- Sometimes some exercise, like as to spending a lot of the time on to the bicycle, it is produce to the problem.
- Genitoanal surgical scarring
- Mishaps in to the pelvic region,
- Trauma to the pelvis,
- Pregnancy,
- Anatomic abnormalities.
- Vaginal birth is also reason of the damage & stretch of this nerve
- Cesarean section,is also cause of the nerve injury.
- In the cyclists, is present to this symdrome due to the both of the reason [compression + stretching ]
- If use the inappropriately shaped or the incorrectly position of the bicycle seat
- Repeated of to the mechanical injury
- Trauma of to the pelvic area, for example during childbirth
- Any cause of the development of the peripheral neuropathy such as the diabetes or vasculitis .
Symptoms of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome :
- Patient feel the neuropathic pain feel the cutaneous dysaesthesia
- Burning or sharp pain [ dysaesthesia ]
- Increase to sensitivity
- patient feel to the Numbness , pins & needles feeling, like when the leg falls in a asleep
- A feeling of swelling
- This feelings is become to worse when the patient sit down.
- This symptoms is feel on to the both sides of the body & they this pain is go into the belly, buttocks, /legs.
- Need to go sudden or frequent in to the bathroom
- Feel the trouble or pain during the sex
- Patient feel the Genito-anal numbness,
- Gecal & urinary incontinence is occur in the patient .
- People feel the burning pain in the perinatal or the genital areas.
- May be Pain is present is during the sitting and also relieved by in the standing, lying down or the sitting to the toilet seat.
- In the systematic symptoms of this syndrome implicated in the various sexual dysfunctions such as to PGAD = persistent genital arousal Disorder
- Erectile dysfunction,
- Premature ejaculation,
- Vestibulodynia.
- Sexual dysfunction by to the disturbing of to the testosterone signaling
- Constipation
- Painful of the bowel movements,
Diagnosis of the Pudendal Nerve syndrome :
Physical examination :-
- In this examination doctor is put the finger into the vagina / rectum & apply the pressure on to the nerve for check this symdrome .
High-frequency ultrasonography :-
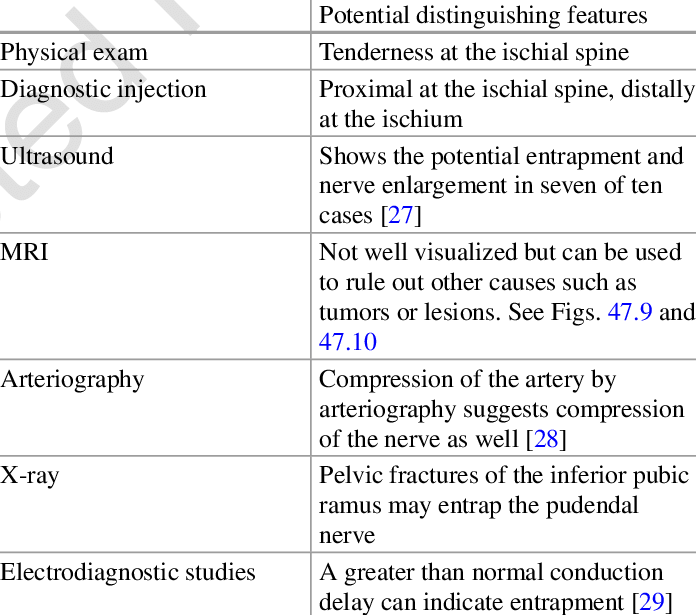
- It is helpful in to the detection of the site [ location ] of this compression.
- Compressed nerve is appear to the flat, when to the inflamed nerve is appear edematous.
Doppler ultrasound :-
- It is a most of the use of for the diagnosis of this syndrome .
- As of the pudendal nerve & vessels course together to in a become to neurovascular bundle & the assumption is produce due to if there is a Present to nerve compression & also present of the vein compression .this is diagnosis by the Doppler ultrasound
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) :-
- It is help into the running out of the other causes of the chronic pain.
- The advancement of the MRI techniques is to evaluating of the peripheral nerves which is provides to a detailed description of to the anatomy,
- Fascicular details,
- To the blood supply of the nerve & to the 3-D anatomy.
- It is also help to for the diagnosis in to the localizing the site of entrapment.
- Functional MRI is assesses to nerve integrity based on to their biological properties.
- There are to no specific & consistent radio logical findings of in the patients with this syndrome so that the further research is to necessary.
Pudendal nerve blocks :–
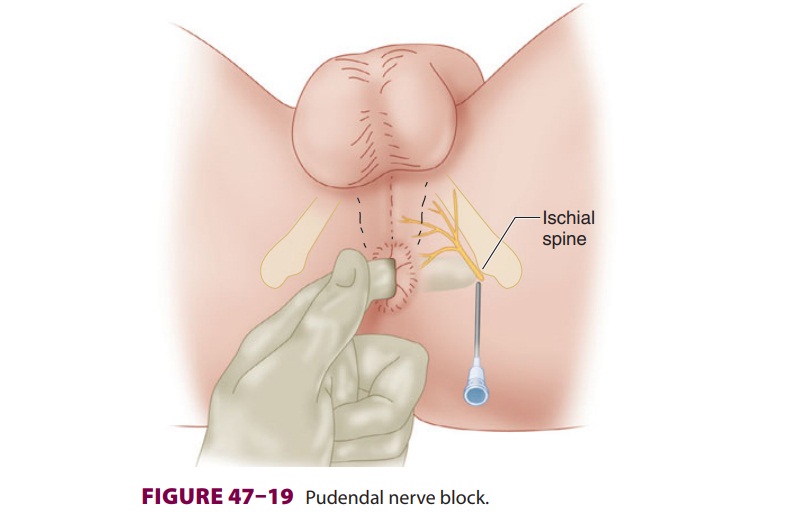
- This blocks is used to for confirm of this nerve
- In this procedure patient is feel to pain relief .This blocks is also used to during delivery in place of the spinal anesthesia.
- In This procedure given to a shot in the pelvis to the numb of the nerve & check the symptoms is relief or not .
Quantitative sensory threshold testing :-
- It is used in to the detect of the inability of sense temperature changes.
Skin rolling test :-
- It is a helpful for the clinical sign.
- In to this test , a thick roll or fold of skin is just below & lateral to the anus is to the pinched & then rolled to forwards.
- If the patient feel the pain is to elicited, so that the this syndrome is compressed.
Nerve studies :-
- Small device is to the inserted into to the rectum .
- In these study stimulate to the nearby nerves with the mild electrical impulses to the check how to it react .
Nantes Criteria for diagnosis :
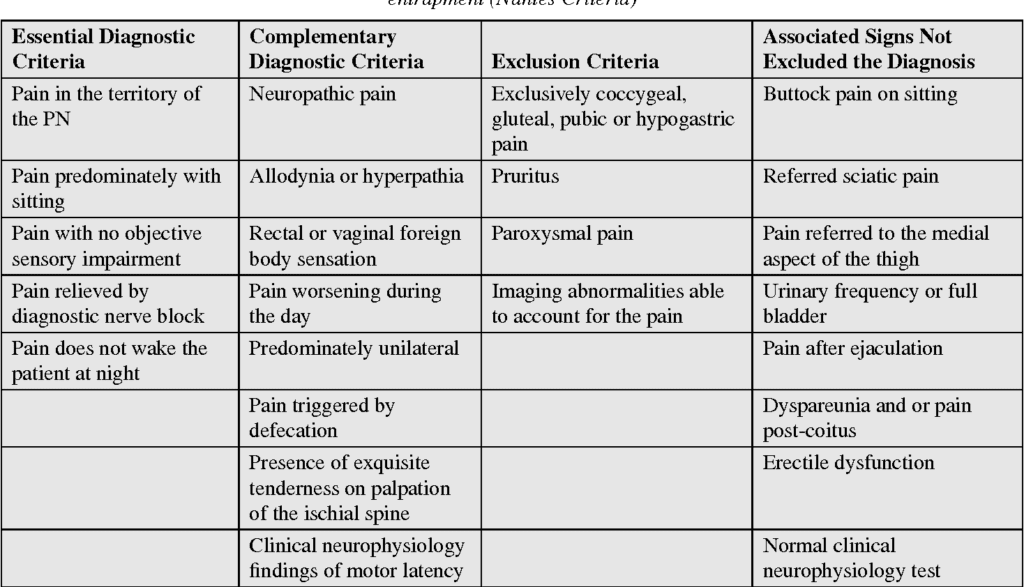
- This syndrome is difficult for the diagnose & there are no a viable of specific exams which is clearly to confirm of the diagnosis.
- So that the Dr Roger Robert posted to the “Nantes Criteria” , which is help & guide to the physicians in to the diagnosis of this syndrome .
- It this Criteria consists of the inclusions, exclusions, & complementary characteristics of this syndrome.
Inclusion of this criteria :-
- Pain is produce to anatomically associated with to the pudendal nerve .
- Patient feel the Pain in a sitting position .
- Pain is not to cause of the nocturnal awakenings .
- Function of sensory is to intact .
- Pudendal nerve block is used to for diagnosis test of the in pain relief .
Exclusion of this criteria :-
- This Imaging results is used for the exclusion .
- Pain in Unilateral .
- This test results is of an abnormal diagnostic .
- In this criteria pain is acute .
Complementary of this criteria :-
- Nerve to pain is associated with the extreme sensitivity to the touch .
- It is described to burning or shooting pain .
- Defecation following to the posterior pain .
Associated signs:-
- Pain in the buttock .
- Referred sciatica pain .
- Pain in the medial thigh (indicates obturator nerve) .
- Pain in the supra pubic region .
- Increased frequency of urine or pain with a full bladder .
- Pain after ejaculation .
- Pain worsens hours after sexual intercourse.
- Erectile dysfunction .
- A normal result on electrophysiological tests .
Differential Diagnosis of the pudendal nerve syndrome :-
- A tumor & metastasis in the external source
- Superficial infections of to the skin in the dermatomes which is covered to in this nerve
- Sacral region of this neuropathy which is due to damage to this sacral nerve plexus.
- During Childbirth to a stretch of to the perineum
- Pain syndrome in complex regional , chronic pain in to the limbs .
- Interstitial cystitis.
- Prostatitis in males,
- Uterine diseases in females,
- Abacterial chronic prostatitis in male
- Idiopathic proctalgia in male
- Vulvodynia in female
- Endometriosis in female
- Endometriosis in female
Function measurement of the pudendal nerve syndrome :-
- Visual Analogue Scale (VAS)
- McGill Pain Questionnaire(MPQ)
- DN4 (which stands for Douleur Neuropathique 4)
- Brief Pain Inventory – Short Form (BPI-sf)
Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) :-
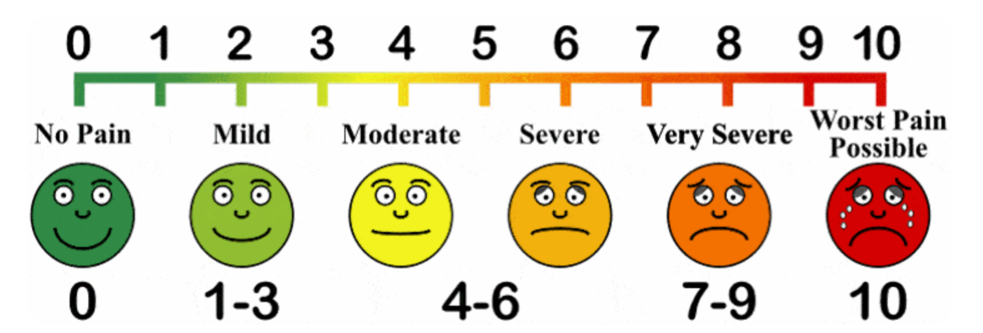
- It is used for the check the pain intensity of the patient .
- First all give the all the information about this scale to the patient .
- In this scale tell the patient give to the number how many number like their feel the pain .
- All see the face of the patient .
McGill Pain Questionnaire(MPQ) :-
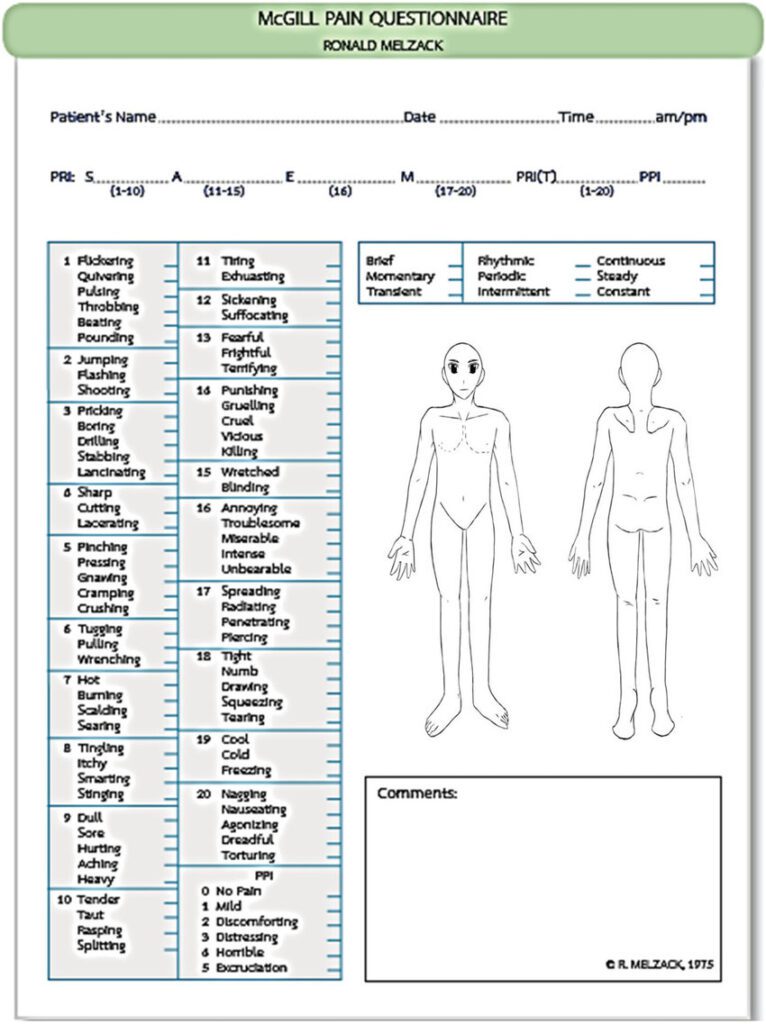
- It is used for the check the pain of the patient .
- First all give the all the information about this scale to the patient .
- In this scale ask to question the patient about to the pain .
Douleur Neuropathique 4 (DN4) :-
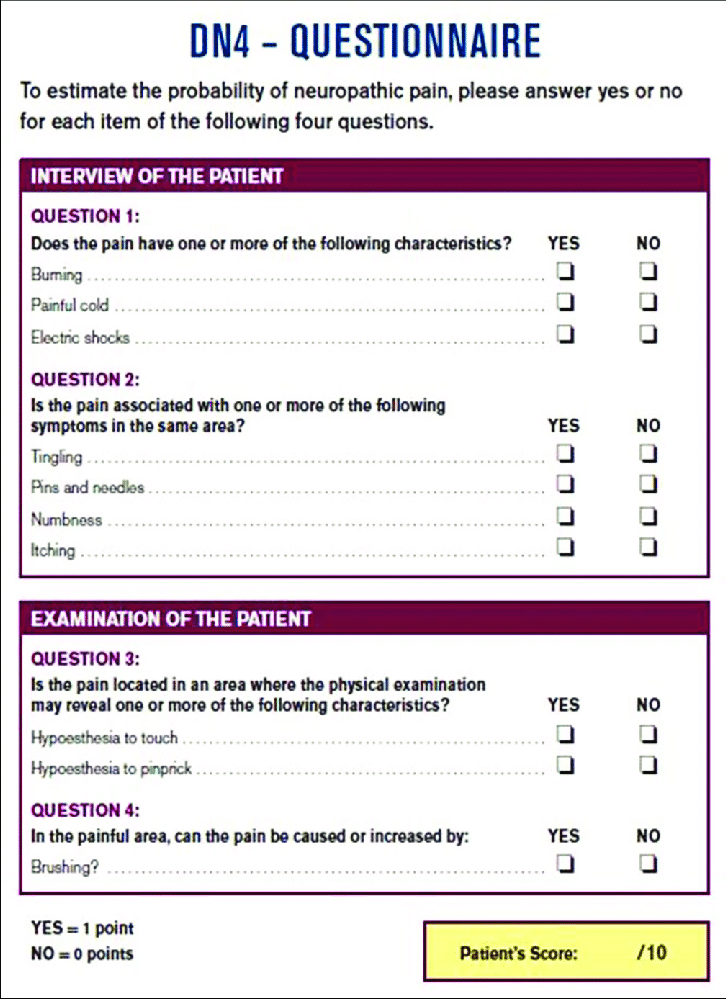
- It is a screening question naire to the help for the identify neuropathic pain (NP) .
- It is used to the in clinical practice & research.
The Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) :-
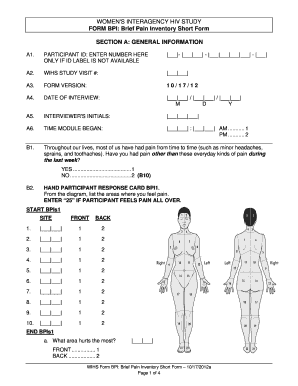
- It is rapidly assesses to the severity of the pain & its to impact on to the functioning.
- In this scale ask to the patient 9 question for the pain relief .
Treatment of the pudendal nerve syndrome :
Medical treatment :-
- Give to the patient analgesics, anticonvulsant & muscle relaxants
- Give to the patient anti-epileptics drug = gabapentin ,
- Antidepressants drug = amitriptyline & palmitoylethanolamide.
- Tricyclic antidepressants = amitriptyline
- Anticonvulsants = carbamazepine & sodium valproate
- Nerve stabilizers = gabapentin & pregabalin.
Conservative treatment :–
- Avoidance of to the painful stimulus is one of the most important parts of this treatment.
- If the cycling is produce to the pain so that the patient is use to proper padding or the cease of the activity.
- Do the lifestyle modifications for the minimize of sitting.
Surgical treatment :-
- This treatment is decompression is the best treatment for this symdrome .
- Four different approaches are used for this symdrome .
- Transperineal,
- Transgluteal,
- Transischiorectal
- Laparoscopy.
- Superior retrosciatic
- Medial transgluteal
- Inferior retrosciatic
- Superior transgluteal
- Transischial entryinferior transglutealand.
- in all tenchinque remove to the nerve fiber .
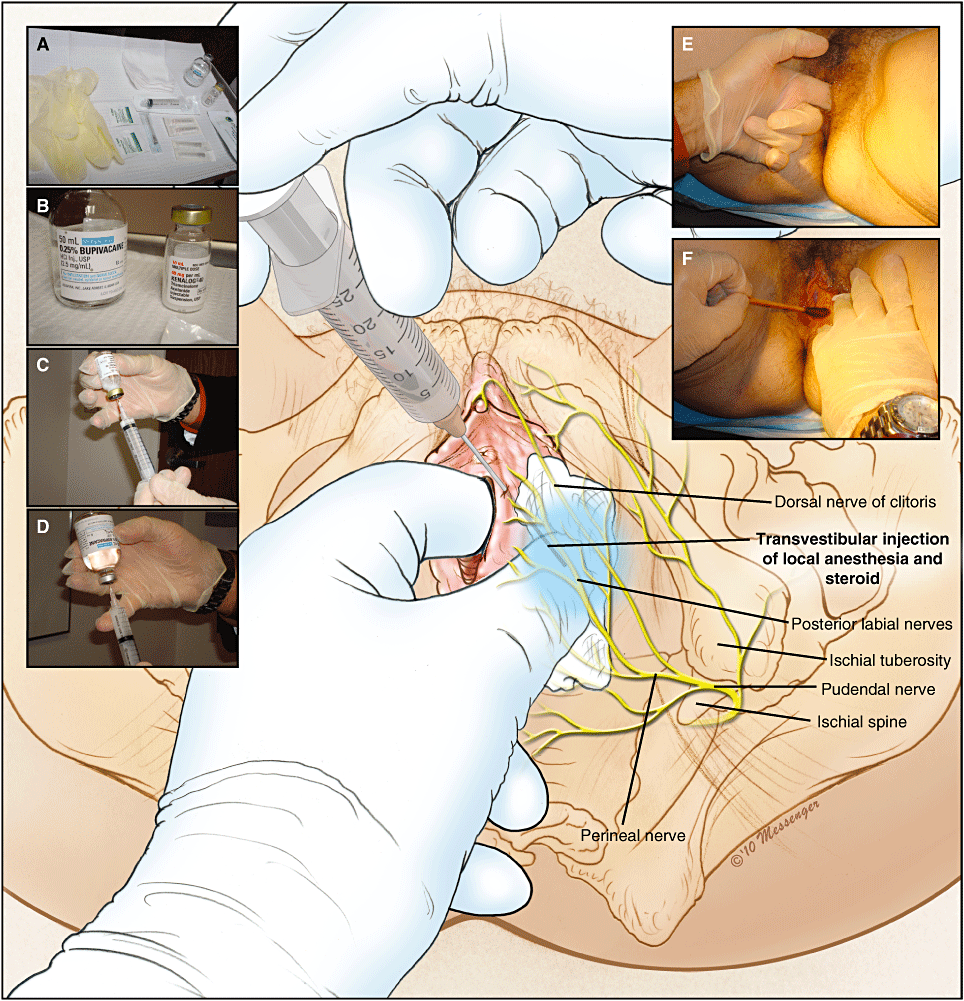
Pudendal nerve block :
- In to the other treatment of the modality is to infiltration with to local anesthetic or to a steroid in to this area encircling the pudendal nerve.
- This block is given to unguided or with to the aid of the ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT) scan & fluoroscopy,.
- Mostly used this technique is with to the use of the CT scan.
Neuromodulation:–
- In the latest treatment includes to the using a peripheral nerve stimulator
- Which is stimulat the pudendal nerve in to the ischioanal fossa.
Pulsed radiofrequency:–
- It is a relatively to new neuromodulation technique &
- It is a considered to safer than the continuous radiofrequency .
- It is also useful for the chronic refractory neuropathic of the pudendal neuralgia.
- It is manage to chronic pain & give to the long-term benefits
Lipofilling:–
- It is a relatively to new technique of the treatment of the pudendal neuralgia.
- In this techinqe give to the patient autologous injection of the adipose tissue along with the stem cells in to the pudendal canal.
Nerve protection :-
- It is a form of the self treatment to the keep pressure off to the pudendal nerve.
- In this involves to avoiding the any activities which is increase to pain in the pelvic area.
- If the remove the seat cushion of the center area is help to provide relief & prevent form the further pain.
- Used to a wider seat when do the cycling ; which is prevent to damage of the nerve.
- For use to the cycling include to having soft & wide seat in to a horizontal position & setting to the handlebar height lower than to the seat.
- For the bicycle used to seat designed for to the prevent of this nerve compression so that the seat is usually to a narrow channel in the middle of to them.
- For the other recommendations include to wearing padded during bike shorts, standing on to the pedals, periodically, shifting to the higher gears & take to frequent breaks.
- Avoid to the prolonged periods of the sitting, particularly in to the in cyclists who have to this condition.
- Use to a foam ring-cushion which is no apply to pressure on to the center when to the sitting
- Avoid to straining when to the passing the urine or opening of the bowels
CT-guided nerve block Injections :-
- It is used to in to identify & alleviate pain associated with to the pudendal nerve .
- During in this procedure bupivacaine hydrochloride drug which is a long-acting local anesthetic & a methylprednisolone [ corticosteroid ] are give to as injected for to the provide a immediate pudendal anesthesia.
- This nerve blocks inserted from several to different anatomical locations like as the : transvaginal, transperitoneal& perirectal.
- A reduction of the pain following to this injection is typically felt to quickly.
- Side effect of this block injection is site irritation.
- This is also Relief the chronic pain , by the reduced of the inflammation around the nerve .
Physiotherapy treatment of the Pudendal nerve syndrome :
- Pelvic floor exercise is works for the patients in the pain & muscle spasms.
- Exercise is helps in to the relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles by the releasing of spasm & muscle lengthening.
- It is give to the stretches the muscles of the lower end of the pelvis, which is known as the pelvic floor muscle .
- This stretch is also give to easy pressure on that to irritate by to this nerve.
- It is also help in control of the bladder or bowels by the exercise.
- Give to the patient neural mobilization for the nerve entrapment by the therapist .
- Goal of this mobilization is to the restore the functionality of to the nerve & muscles through to a variety of exercises .
- Do the strengthening exercise of the muscle .
- Apply to TENS (trans-cutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machine for relieve of the pain but apply to electrode in correct position .
Exercises of the pudendal nerve syndrome :
- Wide leg bridges
- Standing backward leg lifts
- Side-lying hip abduction and extension
- Hip extension in the quadruped position
- Cobra pose
- Arch Backs
Wide leg bridges :-

- It is strengthens to the glutes & hamstrings muscle while enhancing to core stability.
- Tighten to the abdominal & buttock muscles by the pushing the low back in to the ground.
- Raise to the hips to the create a straight line from to the knees to the shoulders.
- Squeeze the core and pull the belly button back toward the spine.
- Hold for the 20 to 30 seconds.
- Do the Lower the hips and return to in the starting position.
Standing backward leg lifts :-

- Starting position of the standing .
- Then the left the leg in the backward .
- Do this exercise for the 10 times in one session .
- Repeat this exercise 3 session per a day .
Side-lying hip abduction and extension ;-
- Starting position is the side lying
- One leg is bend and other leg to raise .
- It is called the abduction .
- For the extension other leg is extended form the hip .
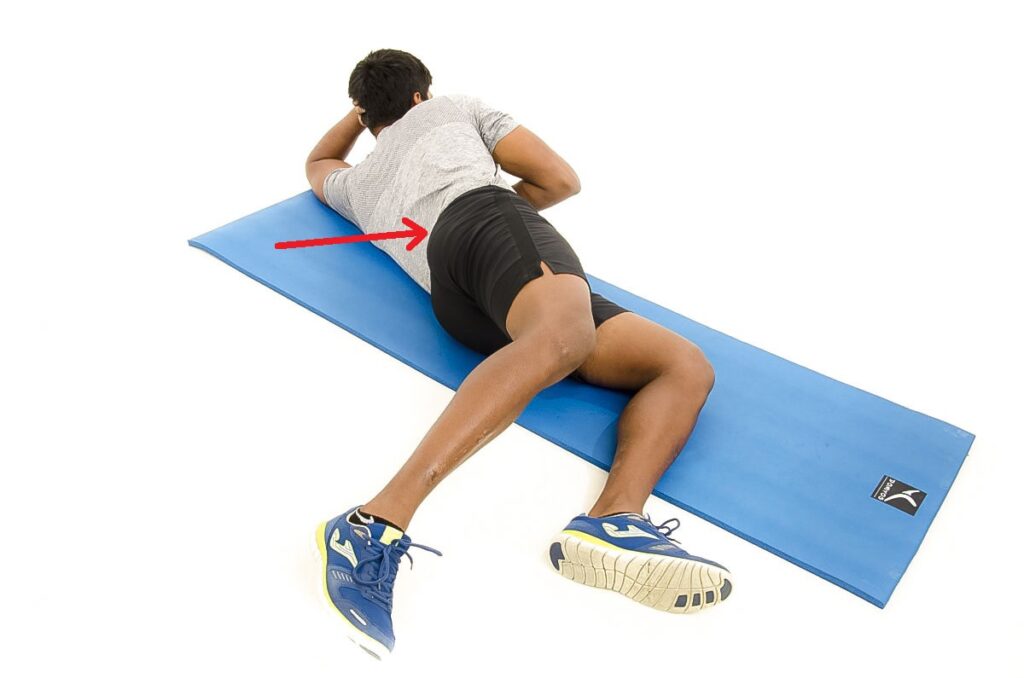


Hip extension in the quadruped position :-

- Starting position is the quadruped position
- Then the extended the leg form this position
- Hold for the 10 second .
- Repeat this exercise for the 10 times & 3 times per a day .
Cobra pose :

- Lie prone on to the floor.
- Stretch the legs , back, tops of to the feet on to the floor.
- Spread to the hands on to the floor under the shoulders.
- Hug to the elbows back into the body.
- Then Press to the tops of to the feet & thighs & the pubis firmly in the floor.
- During the inhalation, begin to the straighten the arms for to lift the chest off to the floor.
- Go to the height at which the maintain a connection through to the pubis to the legs.
- Press to the tailbone toward to the pubis & lift to the pubis toward to the navel.
- Narrow to the hip points.
- Lift through to the top of the sternum & avoid to pushing the front ribs to forward
- Hold this pose anywhere from to the 15 to 30 seconds breathing to easily.
- Release to back the floor with the exhalation.
Arch Backs :-

- This all exercise perform to the relive to the back pain .
Complications of the pudendal nerve syndrome :
- Infection .
- Laceration of to the vaginal mucosa .
- Intravascular injection of to a local anesthetic is cause to cardiovascular & CNS toxicity.
- Hematoma of the injury of to the pudendal artery .
- Urinary problems like as the frequency & urgency .
- Sexual dysfunction including to a painful sex .
- High levels of the stress .
- Anxiety & depression .
- Difficulty to opening the bowels .


2 Comments