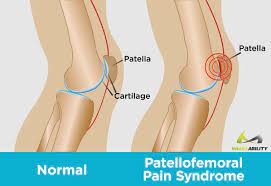
Patello-femoral pain syndrome:
When you feel pain at the front of the knee, around to the kneecap means patella, it indicates pain of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome.
This Patello-femoral pain syndrome is also known as the jumper’s knee & runner’s knee.
This Patello-femoral pain syndrome is more common in the sports people like the running & jumping sport.
You also feel this pain when you do some activities like walking up, sitting for a long period, running, squat & downstairs.
This syndrome most commonly occurs in females & young adults.
You also feel difficulty in your daily activities.
Risk factors of this syndrome are weak quadriceps muscle, trauma & increased training.
Diagnosis of this Patello-femoral pain syndrome is based on the symptoms & examination.
The doctor also conforms this syndrome with the other condition by performing the differential diagnosis of this syndrome like chondromalacia patellae & patellar tendinopathy.
This Patello-femoral pain syndrome pain is relieved by conservative treatment & physiotherapy treatment.
Table of Contents
What is the anatomy of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
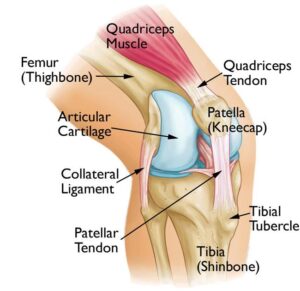
- In our body largest joint is the Knee joint.
- This knee joint is one of the most complex joints of the body.
- This knee joint is made up of three bones.
- Thighbone = Lower end of the femur.
- Shinbone = Upper end of the tibia
- Kneecap = The patella
- This knee joint becomes form 2 joint
- Patellofemoral joint
- Tibio-femoral joint
- Many tendons of the lower legs & ligaments are connected to the femur bone.
- Many Muscles around of knee joint are connected to the knee joint bones by the tendons.
- Quadriceps tendon = this tendon is connected to the muscles in the front of the thigh to the patella bone.
- The patellar reticulation = this reticulation is attached off to the tibia which helps you stabilize the patella bone.
- So that knee joint of several structures become knee joint movement easier.
- Articular cartilage = is a slippery substance of the knee joint.
- This articular cartilage is covered to the ends of the femur bone, trochlear groove, & patella [underside].
- This articular cartilage helps the bones glide smoothly against each other during knee joint movement.
- Synovium = is also a thin lining of the tissue which covers the surface of the knee joint.
- This synovium produces a small amount of the fluid which is given to lubricate the cartilage.
- This Synovium is performed as the cushions of the kneecap means patella & acts as a shock absorbed.
What is the epidemiology /etiology of the patellofemoral pain syndrome?
- This patello-femoral pain syndrome occurs mostly of a patellar trauma but this syndrome is also due to many other factors like overload abnormalities, overuse of the patellofemoral joint, muscular weakness, imbalance & anatomical or bio-mechanical dysfunction.
- Because of this condition, this syndrome becomes worsened.
- The main causes of this patellofemoral pain syndrome are patellar orientation & alignment.
- if the patella stays in a different orientation, it is given to the glide more to one side of the femur bone & apply the overpressure onto the part of the femur bone.
- This cause has produced pain, irritation & discomfort.
- This Patellar orientation varies from one person to another people.
- This patellar orientation is also different on both sides knee joint in all the patients.
- It occurs as a result of anatomical malalignments.
- Patellar deviation
- It is a cause of biomechanical abnormalities & muscular imbalances which also lead to patello-femoral pain syndrome.
- This condition also occurs due to some causes including:
- Tightness in the iliotibial band
- Knee joint hyperextension
- Genu valgum or varus
- Increased Q-angle
- Lateral tibial torsion
- Hamstrings or gastrocnemius
What is the epidemiology /etiology of the patellofemoral pain syndrome?
- This patellofemoral pain syndrome occurs mostly of a patellar trauma but this syndrome is also due to many other factors like overload abnormalities, overuse of the patellofemoral joint, muscular weakness, imbalance & anatomical or bio-mechanical dysfunction.
- Because of this condition, this syndrome becomes worsened.
- The main causes of this patellofemoral pain syndrome are patellar orientation & alignment:
- If the patella stays in a different orientation, it is given to the glide more to one side of the femur bone & apply the overpressure onto the part of the femur bone.
- This cause has produced pain, irritation & discomfort.
- This Patellar orientation varies from one person to another people.
- This patellar orientation is also different on both sides knee joint in all the patients.
- It occurs as a result of anatomical malalignments.
- Patellar deviation:
- It is a cause of biomechanical abnormalities & muscular imbalances which also lead to patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- This condition also occurs due to some causes including:
- Tightness in the iliotibial band
- Knee joint hyperextension
- Genu valgum or varus
- Increased Q-angle
- Lateral tibial torsion
- Hamstrings or gastrocnemius
What are the muscular etiologies of the patellofemoral pain syndrome?
| NO | Etiology | Pathophysiology |
| 1 | Weakness in the quadriceps muscle | this condition is applied to the adverse effect on the PF mechanism. in this condition advised the strengthening of muscle. |
| 2 | Weakness in the medial quadriceps muscle | this condition allows the patella bone to the track too far on the lateral side. this condition needs the strengthening of the VMO muscle. |
| 3 | Tightness of the iliotibial band | this condition is the place of excessive lateral force onto the patella bone & also does the externally rotate to the tibia bone. So that it is applied to upsetting the balance of the PF mechanism. this condition also leads to excessive lateral tracking off to the patella bone. |
| 4 | Tightness of the hamstrings muscles | this condition places to the more posterior force on the knee joint, so that this condition is applied to pressure between the patella bone & the femur bone. |
| 5 | Weakness & tightness in the hip joint muscle | dysfunction of the hip external rotator muscle which is given to results in the compensatory for the foot pronation movement. |
| 6 | Tightness of the calf muscles | this condition is lead to compensatory foot pronation & increases the posterior force onto the knee joint. |
What are the causes of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
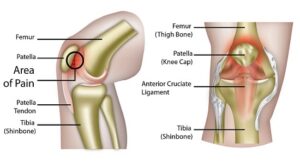
- When you do overuse the knee joint.
- During some activities like running, jumping & other sports which are applied to repetitive stress onto the knee joint.
- When occur to weakness in the muscle & muscle imbalances around to knee joint.
- If the muscles are not properly aligned onto the kneecap – patella.
- Occur to trauma in the kneecap such as dislocation & fracture.
- After the Surgery of the knee cap – patella = mostly surgery of the repair of the anterior cruciate ligament.
- When you use to improper sports for the training equipment & techniques.
- Changes in the footwear for the playing surface
- Malalignment of the patella bone
- Abnormal tracking off to the kneecap – patella bone into the trochlear groove around to knee joint
- when you wear the poorly fitted footwear
- If you are suffering from osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
- If occur to bony tumors around the knee joint.
- Some point around the knee joint increases the pressure on the patella bone.
- When increasing the levels of daily physical activity.
- Quadriceps muscle imbalance
- Tightness of the anatomical structures like the reticulum & iliotibial band.
What are the symptoms of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
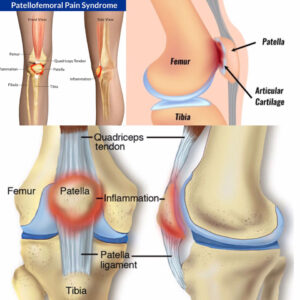
- You are feeling a dull & aching pain in the front of the knee joint.
- This pain starts gradually, more common in activity-related pain.
- Your pain is such as the diffuse vague pain around the kneecap means peripatellar it produces a localized pain that is produced behind the kneecap means retropatellar.
- Some activities which are aggravated your Pain include :
- Down to the stairs
- Squatting
- During the Walking
- Kneeling
- When you are sitting with a bent knee joint for a long period of time
- this syndrome pain is also produced during this exercise.
- this syndrome pain is produced in the front of the knee joint when you sit for a long period in a knee-bending position & this pain is reduced during the knee flexion movement.
- You are heard to popping or crackling sounds during the during to the standing up the form to the prolonged sitting & climbing stairs
- You are also observed with mild swelling around a pain area.
What is a sign of patellofemoral pain syndrome?
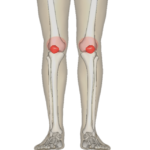
- This syndrome pain mostly occurs around the patella like a circle shape.
- This sign is checked by to the place your hands over the anterior patella.
- This sign is known as to circle sign.
- this syndrome pain is also produced during the prolonged sitting position.
- This sign is known as the theater sign & movie sign.
What is a diagnosis of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
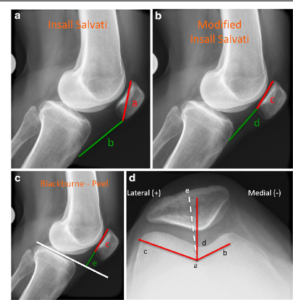
- X-rays :
- It is shown to the outer damage to the bone which is around the knee joint.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans :
- This scan is provided clear images of your body’s soft tissues.
- The doctor is advised to MRI if your symptoms do not improve after physiotherapy treatment & home exercise.
What is the differential diagnosis of patellofemoral pain syndrome?
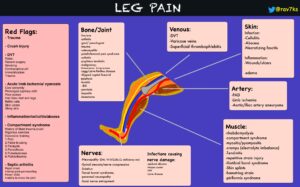
- Chondral lesions
- Osteoarthritis in the knee
- PCL injury/rupture
- Medial overload syndrome
- Hoffa’s pad syndrome
- Chondral lesions
- ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear
- Popliteal Cyst (Baker’s Cyst
- Chondromalacia Patellae
- medial meniscus tears
- Referred pain from the hip joint
- Iliotibial band friction syndrome
- Patellar tendinitis
- medial meniscus tears
- Sinding-Larson-Johansson syndrome
- Referred pain from the lumbar spine
What is the treatment of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
Medical treatment :
- You are taken to anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
- The doctor is also advised of glycosaminoglycan polysulfate (GAGPS).
- This drug inhibits to the degree the polymerization of the hyaluronic acid into the synovial fluid and proteolytic enzymes & increases the synthesis.
Nonsurgical Treatment of this syndrome :
RICE principle :

When you feel muscle pain in the knee joint due to this syndrome doctor is advised to RICE principle as home treatment or primary treatment.
- R – rest = When you feel muscle pain doctor is advised to your rest for sometimes form of activity release to muscle pain, this means doing a total rest or even using the crutches & another mobility aid.
- I- ice = You are applied to ice on the area of the pain for the 20 minutes, release to swellings & muscle pain but always applied to the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice to prevent ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- Compression = to the prevent form the additional swelling you are lightly wrapping to the knee joint with the elastic bandage
- & also leaving to hole in the area of the kneecap or patella & but make sure the bandage is not to fits tight & not produce the additional pain.
- Elevation =if possible, rest with the knee joint raised higher than the heart by applying to pillow under the leg which helps you release swelling.
Orthotics :
- In this orthotic doctor is give you shoe inserts which are helpful to you for the align & stabilize the foot & ankle joint.
- It also helps your form to take the stress off the lower leg.
- Another used custom-made for the foot is called off the shelf.
What are the function measures of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
There are present to 2 function tests that are helpful to you in the examination of pain.
- 10-point of the numeric pain rating scale
- Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS)
The numeric pain rating scale:-
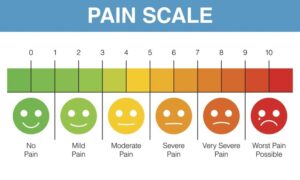
- In this scale, the available range is from ‘0’ to 10.
- On this scale doctor asked to you give the number of your pain between 0 to 10.
- 0 point = no pain.
- 5 points = moderate pain.
- 10 points = worse pain.
Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS):–
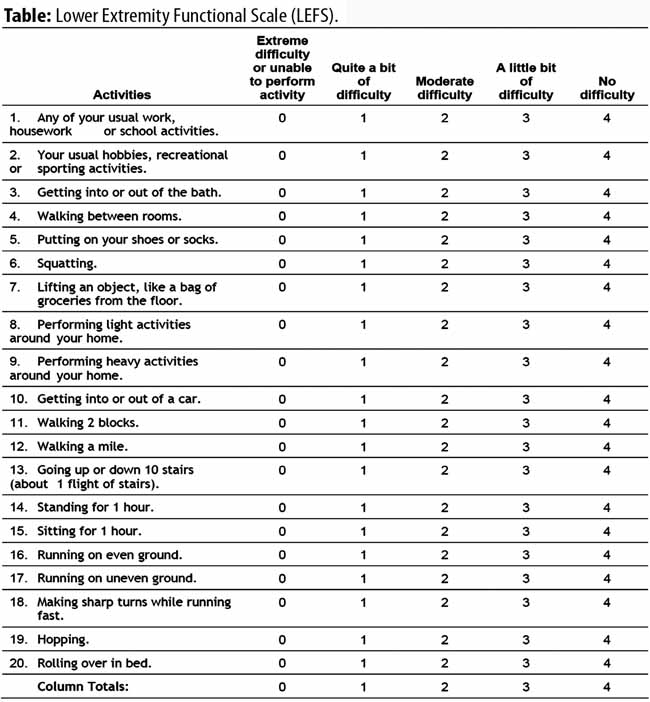
- This scale helps you measure your ongoing progress, the outcome of the wide range of the lower-extremity conditions & initial function.
- On the scale, the therapist asks you some questions about the difficulty of the activities.
Depends on the activity difficulty given to rating on every question :
- When you are unable to Perform any Activity.
- Bit of the Difficulty in any activity.
- Any activity you feel to moderate to the Difficulty.
- Any activity you feel to a little bit of the Difficulty.
- Any activity you feel no Difficulty with to the activity.
What is physiotherapy Examination of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
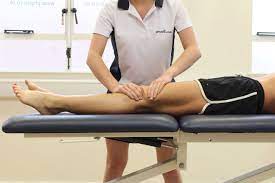
- For the knee, the joint pain physiotherapist is applied to gently press & pull the knee joint in front of the knees & kneecaps – patella.
- A physiotherapist is asked to you perform many activities like the squat, jump & lunge.
- A physiotherapist has also checked the patellar tracking.
- During the examination, the physiotherapist is check your knee joint for problems in patellar tracking.
- In the clinic, the therapist also checks the position of the kneecap = and patella & alignment of the lower leg.
- During the examination, the part therapist checks the Knee joint stability & ROM of the knee or hip joint.
- A physiotherapist also checks the tenderness of the kneecap & strength of the muscles of the knee or hip joint.
- In this syndrome, the physiotherapist checked the Q-angle, lateral hypermobility & J-sign.
- Sometimes also check for tightness of the heel cord & flexibility of the feet during the examination.
- Gait checking is also important for this syndrome.
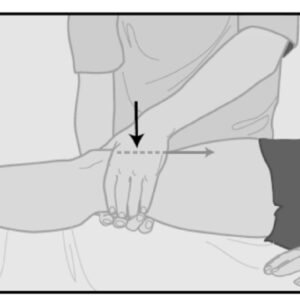
A special test of this syndrome:
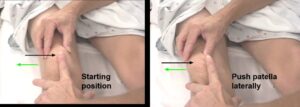
Patellar apprehension test :
- When in you suffer form to lateral instability this condition is assessed by the patellar apprehension test.
- This patellar apprehension test is positive when you feel pain or discomfort which is associated with the lateral translation of to the patella bone.
Active Instability Test :
- This test is used to check the knee joint pain during stair climbing.
Clarke’s test :
- When you feel pain with to the prolonged sitting position.
- You are also feeling pain during the squatting activity.
What is physiotherapy treatment for the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
When this syndrome pain is not relieved after the home treatment & pain medication then the doctor has advised physiotherapy treatment to release syndrome pain.
Physiotherapy treatment is help you relieve pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the muscle.
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy treatment & exercise therapy.
Massage:
- When the trigger & tender points are present in the syndrome pain area physiotherapist is advised to massage therapy release to these tender points.
- Massage is applied after 2 – 3 days of following the RICE principle when you are not feeling to release the syndrome pain.
- Massage is applied with the help of the oil & applied for 5 -10 minutes.
- Massage is applied 3 times per day at home.
Electrotherapy treatment:
After the RICE principle, pain medication & massage if the syndrome muscle pain is not relieved then used Electrotherapy treatment for releasing this syndrome pain.
To relive the swellings, spams & pain physiotherapist is advised to you electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the treatment therapist is used to many machines.
- When the trigger & tender points are present therapists are advised & to apply US = ultrasound therapy for the release of syndrome pain.
- This treatment is applied with the help of gel & applies for 5 to 10 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you release pain & swelling.
- Reduce to pain physiotherapist is applied to SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Interferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on the area of pain.
- SWD = Short wave diathermy is hot therapy for release to spams on the area of muscle pain.
- IFT = Interferential Therapy & TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of muscle pain.
- This therapy is applied for 10 minutes to the area of muscle pain.
Exercise therapy for this syndrome pain :
After following the RICE principle for the 2- 3 days at home & primary treatment & the help of pain medication, you feel released from the pain.
When you feel too comfortable & release from your muscle pain then the physiotherapist is advised to you exercise therapy reduce to muscle weakness & tightness.
The exercise therapy for muscle pain includes stretching & strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to relieve muscle tightness as well as strengthening exercise is help you relieve muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
After the follow of electrotherapy for 2-3 days for release to muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to stretch for release to muscle tightness.
This stretching is applied when your pain is released & when you feel comfortable.
- Quadriceps stretch
- Lunging Hip Flexor Stretch
- Hamstring Stretch in supine
- Wall Hamstring Stretch
- Standing hamstring stretch
- Standing calf stretch
- Iliotibial Band & Buttock Stretch
- Iliotibial band stretch: Side-bending
Quadriceps stretch:

- The starting position of this stretching is the standing position.
- You are standing with the left hand resting gently on something on a sturdy surface, such as to piece of the furniture.
- Try to pull the right foot toward the buttocks or grasp to the top of the right foot with the help of the right hand.
- Then point to the right knee joint toward the floor & you feel a stretch into the front of the leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & perform the 3 sessions per day.
Lunging Hip Flexor Stretch :

- The starting position of this stretching is the kneeling position.
- You are Kneeling on the left knee joint.
- Must be kept to the right shin on the ground.
- When you find it off to the ground is tough onto the back leg so try to the doing stretch on onto the yoga mat.
- Try to move the right leg back to the behind of the body.
- Must be kept to the right foot facing towards the ceiling.
- Then put your both hands on the right knee joint &push the body forward.
- In this situation must be kept to the torso & head in one alignment.
- You feel the stretch in the hip joint in the left leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & perform the 3 sessions per day.
Hamstring Stretch in supine :

- The starting position of this stretching is supine.
- You are lying down on the back.
- Try to extend your right leg form to the front of the body.
- Then bend to the left leg.
- Your hands are wrapped around the back & left thigh.
- Try to pull your leg slowly as you can.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & perform the 3 sessions per day.
Wall Hamstring Stretch :

- The starting position of this stretching is the supine.
- You are lying on the floor with your back facing toward the wall.
- You scoot the body & touch the glutes muscle at the wall.
- Then place your one leg on the wall or extend the leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & perform the 3 sessions per day.
Standing hamstring stretch:

- You are standing upright with the spine in a neutral position.
- Place your leg in front of the body with the foot flexed.
- The heel pushed into the ground & the toe pointing toward the ceiling.
- Then slightly bend the left knee joint.
- Try to gently lean forward & place the hands on the straight leg.
- Must keep a neutral spine.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Standing calf stretch:
- You are facing a wall & put your hands against the wall at about eye level.
- Must keep one leg back with the heel on the floor & the other leg forward.
- Try to turn your back foot slightly inward as you slowly lean into the wall till you feel a stretch in the back of your calf muscle. Hold this stretching position for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Iliotibial Band & Buttock Stretch:
- you are sitting down on the floor with 1 leg bent at a 90-degree angle with your foot flat on the floor & your other leg in a fully extended position.
- try to twist your trunk to the right & use your left arm to gently “push” your right leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Iliotibial band stretch: Side-bending:
- First, you cross one leg in front of the other leg & lean in the opposite direction from the front leg.
- Try to reach the arm on the side of the back leg over your head while you do this stretching.
- Hold this stretching position for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Perform this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow of Electrotherapy & massage for 2 -3 days to release this pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to you do strengthening exercises for muscle weakness.
This strengthening exercise is always advised when you feel to release pain & when you feel comfortable.
This all strengthening exercise helps to you muscle weakness & pain.
- Side-lying leg lift
- Quad sets
- Straight leg raise
- Step-up
- Wall squat with a ball
- Knee stabilization
- Resisted terminal knee extension exercise
- Clam exercise
- Wall Slide
- External Hip Rotation
- Hip circle
- Lateral set ups
- Hip Adductor Strengthening
Side-lying leg lift:

- You are lying on your unaffected side.
- First, you tighten the front thigh muscles on your top leg.
- Try to lift the leg 8 to 10 inches away from the other leg.
- Must keep the leg straight & go too slowly.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Quad sets:
- You are in a sitting position on the floor with your affected leg straight & your other leg is in the bent position.
- Try to press the back of the knee of your affected leg against the floor by tightening the thigh muscles
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Straight leg raise:
- You are lying on your back means in a supine position with your legs are straight out in front of you.
- Try to bend the knee joint on your unaffected side & place the foot flat on the floor.
- First, tighten the thigh muscle of the affected leg & lift the leg about 8 inches off the floor.
- Must keep the thigh muscle tight throughout all exercise.
- Then slowly lower your leg back down to the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Step-up:
- You are standing with the foot of your affected leg on a support such as a small step & block of wood at 3 to 5 inches high.
- Must keep your unaffected foot flat on the floor.
- Try to shift your weight onto your affected leg for support & straighten your knee joint as the unaffected leg comes off the floor. then lower your leg back to the floor slowly.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Wall squat with a ball:
- You are standing with your back, shoulders joint & head against a wall, or look straight ahead.
- Must keep your shoulder joint relaxed & your feet 2 feet away from the wall or a shoulder joint width apart.
- You are placing a soccer & basketball-sized ball behind your back.
- Must be keeping your back upright or slowly squat down to a 45-degree angle.
- Your thigh is not yet parallel to the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Knee stabilization:
- First, wrap a piece of elastic tubing around the ankle of the unaffected leg & tie a knot in the other end of the tubing or close it in a door.
- You are standing facing the door on the leg without tubing & bend your knee joint slightly.
- Must keep your thigh muscles tight during this exercise.
- While maintaining this position try to move the leg with the tubing straight back behind you.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Turn the 90 degrees so that leg without tubing is closest to the door & move the leg with tubing away from your body.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Turn to 90 degrees again so that your back is to the door & move the leg with tubing straight out in front of you.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- Turn your body 90 degrees again so that your leg is closest to the door & move the leg with tubing across your body.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
- You are holding onto a chair when you need help balancing.
- This exercise is made even more challenging by standing position on a pillow while you are moving the leg with tubing.
Resisted terminal knee extension exercise :
- First, make a loop with a piece of the elastic tube by tying a knot on both ends.
- Close the knot in a door at knee joint height.
- Try to step into the loop with your affected leg so that tubing is around the back of your knee joint.
- Then lift the other foot off the ground & hold onto a chair for balance, if needed.
- Try to bend the knee joint with tubing about 45 degrees.
- Slowly straighten your leg must keep your thigh muscle tight.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Clam exercise:
- You are lying on your unaffected side with your hips & knee joint bent & feet together.
- Then slowly raise your top leg toward the ceiling while must keep your heels touching each other.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Wall Slide:
- Start this exercise by standing with your heels about 6 inches away from a wall & your feet about a foot apart.
- Your back & buttock is pressed against the wall.
- Try to slowly slide your hip joint down the wall till your knee joint is bent at roughly a 45-degree angle.
- Hold this exercise position for about 5 seconds & slowly return to starting position.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
External Hip Rotation:
- You are lying on your side with your knee joint stacked & bent at 90-degree angles or your hip joint flexed at an angle of about 60 degrees.
- Must be keeping your heels stacked together & your pelvis anchored or perpendicular to the ground.
- Try to lift your top knee joint as high as you can.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Perform this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Hip Circles:
- You are lying on your side with legs slightly bent & hip joint stacked.
- Try to straighten the top leg & tighten the muscles.
- First circle the leg in a clockwise direction 20 times.
- Then perform 20 circles in a counterclockwise direction.
- Switch to your other side & repeat.
- Always do the circles in medium-sized, neither large & sweeping nor tiny.
- Do the 3 sets of this exercise.
Lateral Step-Ups:
- In this exercise using a step, when you don’t have a platform, you also use a stair-step.
- When your knee joint pain is severe, you use a lower step.
- You are standing beside the platform & lift the adjacent foot or place the step on the platform.
- Step up on the platform & let the other foot come off the ground & hanging loosely.
- Try to lower the hanging foot to the ground & step down.
- Do the 3 sets of 15 step-ups.
Hip Adductor Strengthening:
- You sit in a chair & squeeze a soft ball between your knee joint.
- Hold this squeeze for 5 to 10 seconds then release this exercise.
- Repeat this exercise 5 to 10 times.
- When you don’t have a ball & place your balled fists next to each other between your knee joint & squeeze.
Which exercises are avoided during the patellofemoral pain syndrome?
- Three exercises are avoided in this pain syndrome:
- Lunges
- Leg Extension Machine
- Deep squats
Other activities which are become to worsen your patellofemoral pain syndrome include:
- Any exercise which is involves to kneeling position on your knee joint directly
- Running activities
- When you use the leg press machine
- Some sports activities like Volleyball & Basketball
- When you use any stair stepper machine
- Soccer
What is the Surgical Treatment for this Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
After the medical treatment & physiotherapy treatment pain is not relieved then the doctor is advised surgical treatment.
- Arthroscopy :
- During this treatment, the surgeon inserts a small camera means an arthroscope, into the knee joint.
- This Camera displays pictures of the soft tissue of the knee joint on a television screen.
- With the help of this camera, the surgeon uses as the guide miniature for the surgical instruments.
- Debridement :
- In some cases of this syndrome, doctors are removing the damage of the articular cartilage of the knee joint from the surface of the patella bone which is provide to your pain relief.
- Lateral release :
- When occur to lateral retinaculum tendon is become too tight which is enough to the pull the patella bone out of the trochlear groove,
- So the help of this lateral release procedure, it is loose to the tissue & correct to the patellar malalignment.
- This treatment is performed by a single procedure but for some causes, this surgery is performed as part of the larger surgery which helps you treat a painful & unstable kneecap.
- Tibial tubercle transfer :
- It is necessary for the realigning of the patella by the moving of the patellar tendon which is located along with a portion of the tibial tubercle [ the bony prominence onto the tibia bone ].
- In this surgical treatment, an open surgical incision is required.
- Then the doctor partially & detaches the tibial tubercle so that the bone & the tendon is moved toward the inner side of the knee joint.
- After that doctor’s piece of the bone is reattached to the tibia bone using the screws.
What are the risk factors for the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
- Age:
- This syndrome typically affects adolescents & young adults.
- In the knee, joint problems in older populations are more commonly caused by arthritis.
- Sex:
- In Women are twice common for men to develop patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- It occurs because of a woman’s wider pelvis which increases the angle at the bones in the knee joint meet.
- Certain sports:
- When your participation in running & jumping sports put the extra stress on your knee joint mostly when increasing your training level.
What are the prevention points of the Patello-femoral pain syndrome?
- Maintain strength.
- Always maintain your muscle strength.
- Strong quadriceps & hip abductor muscles help you keep the knee joint balanced during activity, but avoid deep squatting activities during your weight training.
- Think alignment & technique.
- First ask your doctor & physical therapist about flexibility or strength exercises which is to optimize your technique for jumping, running & pivoting.
- It helps the patella track properly in the patella groove.
- Warm-up.
- Before running & another exercise always do the warm-up for 5 minutes.
- Do the stretch & promote flexibility with gentle stretching exercises.
- Then increase to intensity gradually.
- For avoid to sudden changes in the intensity of your workouts.
- Always wear shoe smarts.


9 Comments