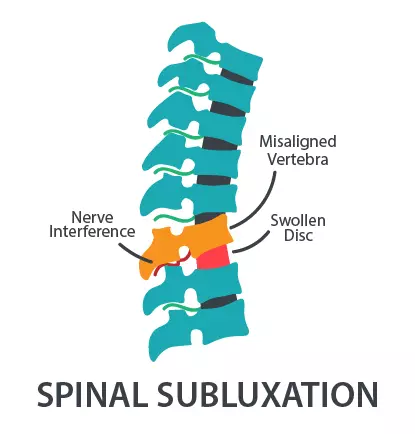
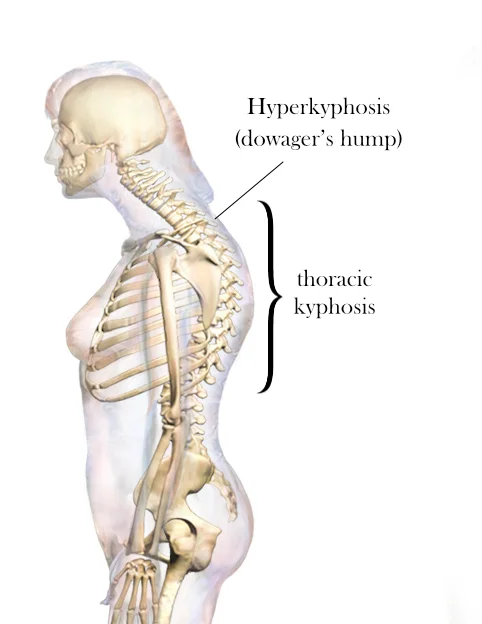
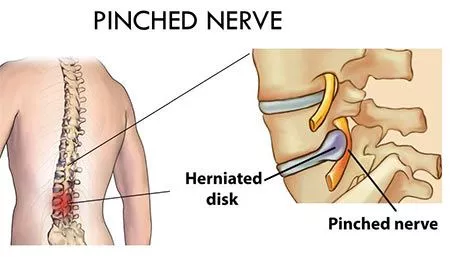
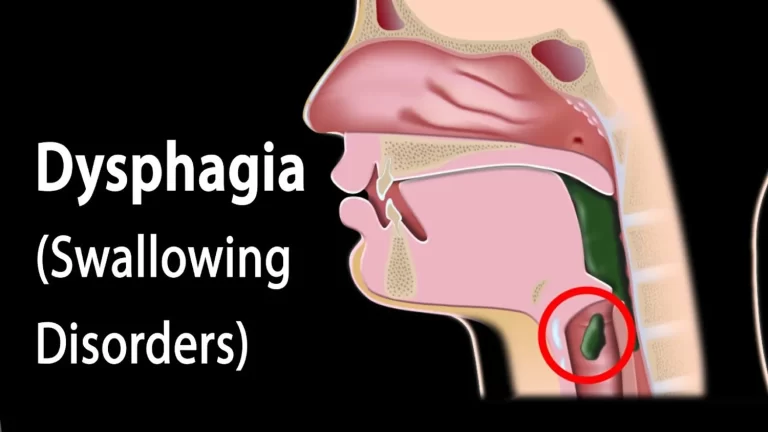
Spinal subluxation
Introduction Spinal subluxation is a condition that occurs when one or more of the vertebrae in the spine become misaligned or move out of their normal position. This can cause pressure on the nerves and interfere with the normal functioning of the body. While chiropractors and some other healthcare providers believe in the concept of…