Neck to Shoulder Pain: Physiotherapy Treatment
Neck to Shoulder pain can be caused by a number of factors including muscle strain, ligament sprains, arthritis, or a “pinched” nerve. Approximately 10 percent of adults have neck to Shoulder pain at any one time.
The majority of patients, regardless of the cause of pain, recover with conservative Physiotherapy treatment. Pain severity may not correlate with abnormalities seen on imaging of the neck.The neck’s susceptibility to injury is due in part to biomechanics.
Activities and events that affect cervical and Shoulder biomechanics include extended sitting, repetitive movement, accidents, falls and blows to the body or head, normal aging, and everyday wear and tear.
Conservative treatment for Neck to Shoulder pain mainly are NSAIDS, Pain relieving Electrotherapy modalities like IFT/TENS/Ultrasound and Shoulder Scapular exercise and Neck Isometric Exercise.
Table of Contents
Neck to Shoulder pain Causes :
Muscle tension and strain :
This is usually due to activities and behaviors such as :
- Poor posture
- working at a desk for too long without changing position
- sleeping with your neck in a bad position
- jerking your neck during exercise
- Over-exercise
Injury around Neck and Shoulder area :
The neck and Shoulder is particularly vulnerable to injury mainly during fall on shoulder to neck, car accidents and sports, where the muscles and ligaments of the neck and shoulder are forced to move outside of their normal range.
If the Neck bones (cervical vertebrae) and /or shoulder are fractured due to sudden jerking of the head and shoulder, Pain and related symptoms are seen.
Cervical Spondylosis :
As you age, the cervical discs can degenerate. This is known as spondylosis, or osteoarthritis of the neck. This can narrow the space between the vertebrae. It also adds stress to your joints.
Cervical disc prolapse :
Sudden jerky movement in Neck causes disk prolapse as from a trauma or injury, it may add pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. This is called a herniated cervical disk, also called ruptured or slipped disk.
Spinal canal stenosis :
It can occurs when the spinal column narrows and causes pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots as it exits the vertebrae. This can be due to long-term inflammation caused by arthritis or other conditions.
Heart attack :
Neck and shoulder pain can also be a symptom of a heart attack, but it often presents with other symptoms of a heart attack, such as:
- Shortness of breath
- sweating
- nausea
- vomiting
- Shoulder arm or jaw pain
If you have other symptoms of heart attack, call an ambulance or go to the emergency room immediately.
Meningitis :
Meningitis is an inflammation of the thin tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. In people who have meningitis, a fever and a headache often occur with a stiff neck and shoulder pain. Meningitis can be fatal and is a medical emergency.
If you have the symptoms of meningitis, seek help immediately.
Rheumatoid arthritis :
Rheumatoid arthritis causes pain, swelling of the joints, and bone spurs. When these occur in the neck and shoulder area and neck and shoulder pain can result.
Osteoporosis :
Osteoporosis weakens bones and can lead to small fractures. This condition often happens in hands or knees, but it can also occur in the neck and shoulder area.
Fibromyalgia :
Fibromyalgia is a condition that causes muscle pain throughout the body, especially in the neck and shoulder area.
Sign and Symptom’s of Neck to Shoulder Pain :
Muscle spasm :
A spasm is a sudden, powerful, involuntary contraction of muscles. The muscles feel painful, stiff and knotted. If you have neck muscle spasms, you may not be able to move your neck, Your doctor or physiotherapist may call it acute torticollis or wry neck. Generally Paraspinal neck muscles, Trapezius muscle and related Shoulder muscles spasm are seen.
Muscle ache :
The neck and shoulder muscles are sore and may have hard knots (trigger points) that are tender to touch. Pain is often felt up the middle of the back of the neck (Trapezeus area), or it may ache on one side only(Left or Right side).
Stiffness of Neck and Shoulder :
The neck and shoulder muscles are tight and if you spend too long in one position they feel even tighter. Neck stiffness can make it difficult or painful to move your neck. Shoulder joint stiffness is also available sometimes.
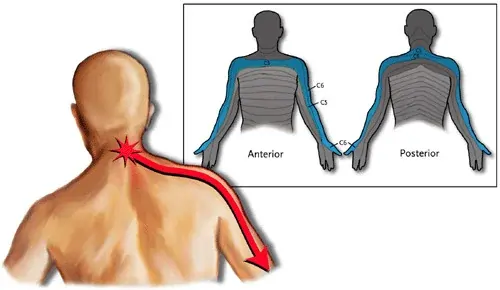
Radiating Nerve pain :
Radiating Pain from the neck can radiate down the arms, and sometimes, the legs. You may feel a sensation of pins and needles or tingling in your arms, which can be accompanied by numbness, burning or weakness.
Cervicogenic Headaches :
Cervicogenic Headaches are common in conjunction with neck problems. They are usually a dull aching type of headache, rather than sharp pain. While the headaches are often felt at the back of the head, the pain may also radiate to the sides, and even the front of the head.
Reduced range of motion :
If you can’t turn your head to the side to the same degree towards each shoulder or you feel limited in how far forward you can lower your head to your chest, or how far you can tilt your head back, you may have reduced range of motion. Shoulder joint Range of motion also reduced in chronic cases.Your doctor will be able to test this.
Weakness of Neck /Shoulder muscles :
Inability to carry objects or use the arm due to severe pain and muscle weakness. Make it difficult to comb your hair or reach behind your back.
How to Diagnose of Neck to Shoulder pain ?
X-rays :-
X-rays can reveal areas in your neck and Shoulder where your nerves or spinal cord might be pinched by bone spurs or other degenerative changes.
CT scan :-
CT scans combine X-ray images taken from many different directions to produce detailed cross-sectional views of the internal structures of your neck.
MRI :-
MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create detailed images of bones and soft tissues, including the spinal cord and the nerves coming from the spinal cord.
Electromyography (EMG) :-
If your doctor suspects your neck to shoulder pain might be related to a pinched nerve, he or she might suggest an EMG. It involves inserting fine needles through your skin into a muscle and performing tests to measure the speed of nerve conduction to determine whether specific nerves are functioning properly.
Blood tests :-
Blood tests can sometimes provide evidence of inflammatory or infectious conditions that might be causing or contributing to your neck and shoulder pain.
Treatment :
Analgesics Medicine : eg. acetaminophen or NSAIDs are recommended to reduced pain.Muscle relaxants are often prescribed and are known to be effective.
Pain reliever topical gel and patches are also effective for some patients.
Cervical collar :— A soft cervical collar is a piece of foam covered with fabric that is worn around the neck to support the head.
Routine use of a cervical collar is not recommended because it may delay recovery or allow the neck muscles to weaken. In addition, collars can make neck pain worse in some people due to the fit of the collar.
At night, a rolled towel under the neck or a neck pillow can provide comfort and keep the neck in a neutral position. The ear should be aligned with the middle of the shoulder when lying on the back. When lying on the side, the nose should be aligned with the middle of the chest bone.
Using one or two regular pillows is not recommended because it can cause too much forward or side-bending of the neck.
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatment is the best option for permanent resolution of your pain. Physiotherapy treatment mainly are Pain relieving Electrotherapy modalities eg. IFT, TENS, Ultrasound, Cervical Traction Machine and Exercise of Neck and Shoulder muscles.
Physiotherapist first do assessment of your symptom’s , take medical history, aggravating and relieving factor and accordingly make a treatment plan.
IFT (Interferential Therapy) : It is a type of electo therapy treatment that uses electric currents to stimulate tissue which provides pain relief, reduction of swelling and many other health benefits.
Cervical Traction also mostly recommended by Physiotherapist to reduce pressure on compressed nerve roots over cervical area which are causing Neck to shoulder pain that are radiating down to hands.
TENS (Trancutaneous Electrical nerve stimulation) : TENS is a method of electrical stimulation which primarily aims to provide a degree of symptomatic pain relief by exciting sensory nerves and thereby stimulating either the pain gate mechanism and/or the opioid system.
Ultrasound Therapy (US) : Use of Sound-wave in Physiotherapy Have Physiological Healing And Pain Relieving Effects is known as a Ultrasound Therapy.
Exercise Therapy :
Exercise of Neck and Shoulder muscle recommended mostly by your Physiotherapist are Shoulder scapular exercise, Isometric neck exercise and Active Shoulder exercise. These exercise strengthen your neck and shoulder area.
Shoulder Scapular Exercise :
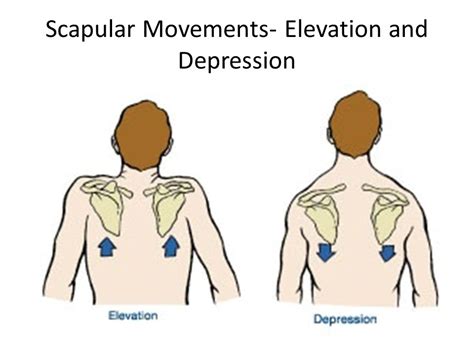
Shoulder Scapular exercise is highly recommended by Physiotherapist in Neck to shoulder pain, This exercise helps to Strengthen and stabilize scapular region and also improve your thoracic posture.
Steps to do exercise :
- Exercise -1 : Place your both hands behind the neck with elbow flexed position and then try to do elbow forward and backward for 10 time and then relax.
- Exercise – 2 : Elevate your shoulder and then depressed and repeat 10 times and relax.
- Exercise – 3 : Protract and Retract your shoulder 10 times and relax.
Isometric Neck Exercise :
Isometric neck exercise helps to strengthen weak neck muscles without aggravating pain. This exercise are easy to do home exercise and also useful in acute pain.
Steps to do Exercise :
In sitting Position, Place both hands behind the neck and try your neck to push pressure on hands and the same time Resist with your neck muscles, both hands maintain align position for 4 to 5 seconds and then relax.
First day do 5 repetitions and second day 10 repetition. do same exercise on your forehead and side of the neck.
Do the exercise again, pressing on the side of your head. Repeat 5 times. Switch sides.
Isometric Neck Exercise Video :



12 Comments