Microcephaly
Table of Contents
What is the condition of microcephaly?
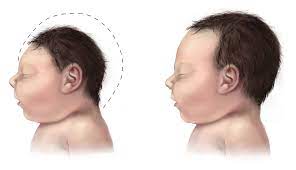
- Microcephaly is a condition where a baby’s head is much lessened than expected.
- During pregnancy, a baby’s head grows because the baby’s brain grows.
- Microcephaly can happen because a baby’s brain has not developed properly during pregnancy or has stopped growing after birth, which results in smaller head size.
- Microcephaly can be an isolated condition, meaning that it can happen with no other major birth defects, or it can happen in combination with other major birth defects.
What is the condition of severe microcephaly?
- Severe microcephaly is a more serious, extreme form of this condition where a baby’s head is much lesser than expected.
- Severe microcephaly can result because a baby’s brain has not developed properly during pregnancy, or the brain started to develop correctly and then was damaged at a certain point during pregnancy.
Other Problems
- Babies with microcephaly can have a range of other problems, depending on how severe their microcephaly is.
Microcephaly has been linked with the following problems:
- Seizures
- Developmental delay, like as problems with speech or other developmental milestones (like sitting, standing, and walking)
- Intellectual disability (decreased ability to learn & function in daily life)
- Problems with movement and balance
- Feeding problems, like as difficulty swallowing
- Hearing loss
- Vision problems.
- These problems can range from mild to severe & are sometimes lifelong.
- Because the baby’s brain is small & underdeveloped, babies with severe microcephaly can have more of these problems, or have more difficulty with them, than babies with milder microcephaly.
- Severe microcephaly also can be life-threatening. Because it is difficult to predict at birth what problems a baby will have from microcephaly, babies with microcephaly sometimes need close follow-up through regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor their growth & development.
How Many Babies Are Born with the condition of Microcephaly?
- Microcephaly is not a usual condition.
- Researchers estimate that about one in every 800-5,000 babies is born with microcephaly in the United States.
What are the Symptoms of the condition of microcephaly?
- The primary symptom of microcephaly is having a head size that is much lesser than that of other children of the same age & sex.
- Head size is a measure of the distance around the peak of the child’s head (circumference).
- Using standardized growth charts, health care providers contrast the measurement with other children’s measurements in percentiles.
- Certain children just have small heads, with a measurement that falls below an established value for children of the same age and sex.
- In children with microcephaly, head size measures much lesser than average for the child’s age and sex.
- A child with more-severe microcephaly may too have a sloping forehead.
Aside from a noticeably smaller head, the following are the most usual symptoms of microcephaly:
- A high-pitched cry
- Feeding problems
- Hearing and vision problems
- Convulsions (seizures)
- Increased movement of the arms & legs (spasticity),
- Hyperactivity (overly active)
- Developmental delays, or problems learning how to speak, stand & walk
- Intellectual disabilities (trouble with learning).
- As the child grows older, his or her face constantly grows while the skull does not.
- This causes the child to develop a large face, a receding forehead & a loose, sometimes wrinkled scalp.
- The rest of the body is sometimes underweight and smaller than normal.
- Certain babies have no visible or noticeable symptoms.
- Also, certain children who have microcephaly go on to develop normally.
What causes the condition of microcephaly in your baby?
- During the pregnancy, your baby’s head grows as her brain grows.
- Microcephaly can occur when a baby’s brain doesn’t develop properly during pregnancy or stops growing after birth.
- We do not know for sure what causes microcephaly in most babies.
But we do know that these things may cause microcephaly in certain babies:
- Genes and chromosomes: Changes in genes (also called mutations) that affect the brain’s growth & development. This is the most common cause of microcephaly. Genes are part of your body’s cells. They supply the instructions for the way your body grows & works. Genes are passed from the parents to the children.
- Chromosomal conditions, like Down syndrome. Chromosomes are the structures that hold the genes. Babies with chromosomal conditions have a problem in 1 or more of their chromosomes.
- Untreated maternal PKU. This is a condition passed through genes in which a woman’s body can not break down an amino acid called as phenylalanine. Most women with PKU can have healthy babies if they follow a special meal plan that is low in phenylalanine.
- If your baby’s microcephaly is caused by a gene change or chromosomal condition, you may want to see a genetic counselor. This is a person who is trained to assist you to understand genes, birth defects & other medical conditions that run in families, and how they can affect your health and your baby’s health.
Exposures in the womb: Being exposed to alcohol or some drugs or chemicals in the womb. Being exposed to certain infections in the womb, involving Zika virus, chickenpox (also called varicella), rubella (also called German measles), toxoplasmosis, or cytomegalovirus.
Brain problems: Cerebral anoxia- This is when a baby’s brain does not get enough oxygen. Complications during pregnancy, birth or afterward birth can cause problems with oxygen flow to a baby’s brain.
Craniosynostosis- This is a birth defect in which the joints (also called sutures) between the bones in a baby’s skull fuse together also early before the brain stops growing. This can cause problems with brain development.
Traumatic brain injury- This occurs when a head injury causes brain damage.
Metabolism or nutrition problems
Metabolic disorders: These are health conditions that harm a body’s metabolism. Metabolism is the way your body changes food into the energy it needs to use oxygen, digest food & grow.
Severe malnutrition in the womb. This means a baby does not get enough food or nutrients during the pregnancy.
How is the condition of microcephaly diagnosed in a child?
- Microcephaly may be diagnosed at a previous birth by prenatal ultrasound.
- This imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves & a computer to make images of blood vessels, tissues, & organs.
- Ultrasounds let healthcare providers show the internal organs as they function.
- They also see blood flow through blood vessels.
- In many cases, microcephaly may not be seen with ultrasound till the third trimester.
- After birth, the healthcare provider will question about your child’s health history.
- He or she may question your pregnancy and health history, and your family’s health history.
- The provider will give your child a physical examination.
Your child may have tests, like as:
Head circumference measurement: The measurement is compared with the scale for normal growth and size.
CT scan: This test uses a series of X-rays & a computer to create images of the inside of the body. A CT scan sees more detail than a regular X-ray.
MRI: This test uses large magnets, radio waves, & a computer to create images of the inside of the body.
Blood tests: These involve genetic tests. Genetic tests check for the conditions that tend to run in families.
Urine test: This is done to look for a substance that may show some type of microcephaly.
When to see a doctor?
- Chances are your health care provider will discover microcephaly at your baby’s birth or at a regular well-baby checkup.
- However, if you think your baby’s head is less for the baby’s age & sex or is not growing as it should talk to your provider.
How is the condition of microcephaly treated in a child?
- There is no cure for microcephaly.
- Treatment options depend on how exaggerated your baby’s condition is.
- Babies with mild microcephaly often do not have other health problems, yet they still need regular check-ups so their health care provider can check their growth & development.
- Babies with severe microcephaly may need special care & treatment.
- Babies with craniosynostosis may need to have surgery to assist separate the fused bones in their heads and give the skull the ability to expand as the brain grows & develops.
- Certain babies need to take medicines to treat seizures or other health problems.
- If your baby has microcephaly & has developmental delays, he should show a child neurologist.
- This is a doctor who treats the brain, spine & nerves in children.
- Getting early intervention services as soon as possible can assist to improve your child’s development.
- These services can assist children from birth through 3 years old to learn important skills.
- Services include therapy to assist a child talk, walking, learning self-help skills, and interacting with others.
- The healthcare team will give support & teach you how best to manage your child’s health.
Over time, your child may see healthcare providers such as:
- Pediatrician or family doctor.
- This is the child’s primary healthcare provider.
- Neurologist: This is a healthcare provider who treats conditions of the brain, spinal cord, & nerves.
- Rehabilitation team: This involves physical, occupational, speech, and audiology therapists.
- Talk with your child’s healthcare providers about the risks, benefits, and possible side effects of all treatments.
Physiotherapy Treatment could include for the condition of microcephaly:
- Strengthening exercises can be used to treat weak muscles, improving your child’s function as the muscle will be stronger & have the ability to perform better.
- Breaking a task down can be beneficial for your child as it can make them more independent and give them confidence, it also shows the physiotherapist what they are struggling with & they can prescribe exercises to assist this.
- Proprioception exercises are exercises to assist your child’s awareness of their body in space, for example, standing on one leg.
- Balance exercises help reduce the risks of falls and assist to improve movements such as walking.
What can you do to assist prevent the condition of microcephaly in your baby?
- You can not always prevent microcephaly in your baby.
- But there are things you can do to assist reduce your baby’s chances of having it.
Here is how:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Alcohol includes beer, wine & liquor.
- Do not use street drugs or abuse prescription drugs.
- Tell your provider if you need assistance to quit using drugs.
- Protect yourself from harmful chemicals.
- Wear gloves or a face mask if you have to use them.
- Open a window or door to let the clean air in.
- If you have PKU, get the treatment & follow your meal plan.
- Cure yourself from infections.
Here’s what you can do to assist protect yourself from infections before and during pregnancy:
- Protect yourself from Zika.
- Do not travel to a Zika-affected area unless absolutely necessary.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
- If your male or female partner may be infected with Zika, do not have sex.
- If you do have sex, use a condom.
- If you work in a health care setting, follow safety rules to protect yourself from exposure.
- Talk to your provider to make sure your vaccinations are up to date.
- Have safe sex to protect you against sexually transmitted diseases (also called STDs) & other infections, involving Zika.
- Safe sex means using a condom if you have sex with more than one partner.
- If your male or female partner may be infected with Zika, use a condom every time you have sex or do not have sex at all.
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom, sneezing or coughing, changing a diaper, or preparing food.
- Do not eat raw or under-cooked food, including lunch meats.
- Cook meat, chicken & fish until done.
- Wash food previous you cook or eat it.
- Do not touch cat poop or change a cat’s litter box to help protect you from toxoplasmosis.
- Get regular dental checkups to assist prevent gum infections.
How can I assist my child to live with the condition of microcephaly?
- The full range of issues is typically not known right after birth.
- Issues can be revealed as a child grows and develops.
- Children born with microcephaly need to show their healthcare team frequently.
- They will require tests to track the growth of the head.
- Their motor, social, intellectual, & language functions will be tracked over time.
- You can assist your child to strengthen his or her self-esteem & be as independent as possible.
- Your child may require physical and occupational rehabilitation.
- He or she may require extra support in school.
- The healthcare team will talk with you about the best ways to assist your child.
When should I call my child’s healthcare provider?
Call the healthcare provider if your child has:
- Symptoms that do not get better, or get worse
- New symptoms
Key points about the condition of microcephaly in children
- Microcephaly is a condition where a baby’s head is much lesser than normal.
- It is most often present at birth (congenital).
- Most children with microcephaly have a small brain & intellectual disability.
- Certain children with small heads have normal intelligence.
- Microcephaly may be caused by problems during the woman’s pregnancy.
- In certain cases, it may be caused by inheriting an abnormal gene.
- Microcephaly is a lifelong condition that has no prevention.
- Treatment focuses on preventing or reducing problems & maximizing a child’s abilities.
- Children born with microcephaly require to see their healthcare team often.
- They will require tests to track the growth of the head.
- Their motor, social, intellectual, & language functions will be tracked over time.
- Your healthcare provider may advise genetic counseling.
- You can learn more about the risk for microcephaly in a future pregnancy.