Lumbar Lordosis
Table of Contents
What is Lumbar Lordosis?
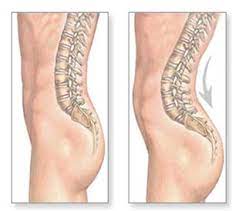
- Lumbar Lordosis is the inward curvature of the lumbar spine. A small degree of lordosis is normal while too much lumbar spine curving is called lordosis (swayback).
- The lumbar spine is support your head, and keep your body stable and normal curves serves to distribute mechanical stress incurred as the body is at rest and during movement.
The lumbar spine help your body:
- absorb shock
- support the weight of the upper body
- align your upper body over your pelvis
- stabilize and maintain body structure
- Allow Back movement and bend flexibly
How to check Lumbar Lordosis?
- You can check for lordosis by lying on a flat surface and checking if there is a lot of space between the curve of your neck and back and the floor. if You have lordosis then you can easily slide your hand between the space.
Common causes of Lumbar Lordosis
- Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: Spondylolisthesis is a spinal condition in which one of the lower vertebra (L1 to L5) slips forward onto the bone below.
- Achondroplasia: Achondroplasia is one of the most common types of dwarfism (a genetic condition)
- Dwarfism is short stature(height) that results from a genetic or medical condition.
- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a bone disease that causes bones to become weak and brittle.
- Osteosarcoma: Osteosarcoma is a bone cancer that develops in the shinbone near the knee, the thighbone near the knee, or the upper arm bone near the shoulder.
- Obesity: Obesity is a complex disease involving an extreme amount of body fat.
What Are the Symptoms of Lumbar Lordosis?
- Low Back Muscle pain.
- Pain that extends into the neck muscle, shoulder muscle, and upper back muscle.
- Limited movement in the neck or lower back.
- Numbness.
- Tingling.
- Electric shock pains.
- Muscle weakness: Hip extensors (hamstrings and gluteus maximus are weak.
Lordosis in children

- lordosis appears in childhood without any known cause. This is called benign juvenile lordosis.
- It happens because the muscles around your child’s hips are weak or tight the muscle.
- Benign juvenile lordosis typically corrects itself as your children grow up.
- Lordosis can also be a sign of hip dislocation, especially if your child has been hit by a car or fallen somewhere.
- Other conditions that can cause lordosis in children are normally related to the nervous system and muscle weakness.
- These conditions are rare and include:
- cerebral palsy: A group of disorders that affect a person is the ability to move and maintain posture and balance.
- Myelomeningocele: An inherited condition where the spinal cord sticks between a gap in the bones of the back
- muscular dystrophy: A group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass.
- spinal muscular atrophy:A genetic condition that causes involuntary movements
- arthrogryposis: A problem that occurs at birth where the joints can’t move nearly normal
Lordosis in pregnant women
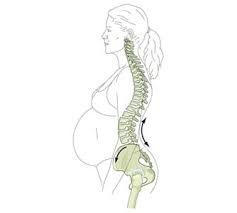
- Many pregnant women experience back pains that is signs of lumbar lordosis, a protruding belly, and buttocks. But according to Harvard Gaze, research and during pregnancy is actually your spine adjusting to realign your center of gravity. Overall back pain may be due to altered blood flow in your body, and the pain will most naturally go away after birth.
How is Lordosis diagnosed?
- Your doctor will show your medical history, perform a physical exam, and ask about other symptoms to help find out if you have lumbar lordosis.
- During the physical exam, your doctor will ask you to bend forward and to the side. They are checking:
- whether the curve is flexible or not
- your range of motion
- if there are any abnormalities
- if your spine is aligned
- They may also ask questions like:
- When did you notice the extravagant curve in your back?
- Is the curve getting worse?
- Where are you feeling pain?
- Is the curve changing shape?
Scanning:
- Test: x-ray
- The patient stands to reveal the whole length of the spine when PA (posterior/anterior, or back and front) and Lateral (side) x-rays are taken.
- MRI and CT:
- Bone scans are conducted in order to rule out possible fractures of the bone and infections.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to terminate the possibility of spinal cord or nerve abnormalities in body.
- Computed tomography scans (CT scans) are used to get a more detailed image of the bones, muscles and affected organs of the lumbar region.
Treatment:
- Initially symptomatic medical treatment with a combination of Physiotherapy treatment & exercise to correct the posture, in severe surgery is the last prescribed option.
Medical Treatment:
- An-inflammatory medicines can relieve back pain.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen, (Advil, Motrin IB), naproxen (Aleve)
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
Braces:
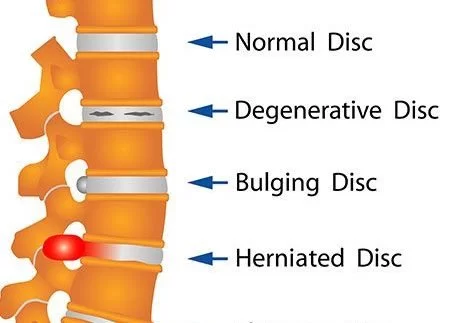
- The Boston brace is a plastic exterior that can be made with a small amount of lumbar lordosis to reduce stresses on discs that have experienced herniated discs. In the case where Ehlers Danlos syndrome is responsible, being properly fitted with a customized brace may be a solution to avoid strain and limit the frequency of instability.
Hip flexor stretches

- To perform a hip flexor stretch, Start from a kneeling position on a slushy surface, such as a yoga mat. Place the right foot in forward of the body so that the knee bends at a 90-degree angle, with the right knee directly over the right foot.
- Drag the shoulders down and back, without bending the back, and keep the pelvis and spine stable and neutral.
- Incline forward into the right hip while keeping the left knee on the ground and with the pelvis facing forward.
- Hold the stretching for 30–45 seconds at a time.
- Repeat 2–5 times for each hip.
Cat-Cow Pose

- To perform the Cat-Cow yoga pose, start on the hands and knees on the ground or a yoga mat.
- Place the knees hip-width apart and directly under the hips, with the toes pushed.
- Place the hands directly under the shoulders, facing forward, and shoulder-width apart.
- Use the abdominal muscles to pass the spine into a neutral position.
- Exhale and slowly arch the spine toward the roof, allowing the head to drop down, and hold the position for 10–15 seconds.
- Inhale and relax the spine and drawing the shoulder blades down the back.
- Hold the position for 10–15 seconds.
- Return the spine to a neutral position.
Plank

- Benefits: This Exercise can help strengthen your abdominal muscles, glutes, shoulders, and upper back.
- To do this exercise:
- Lie faces down on a comfortable soft surface like a yoga mat.
- Push yourself up onto your toes and palms, with your body in a straight line from your head to your ankles. If this is too intense, try starting with a low plank: raise just onto your forearms instead of straightening your arms all the way.
- Remain your abdominal and glutes braced as you hold this position.
- Hold for at least 30 seconds.
Glute bridge

- Benefits: Glute bridge exercise can help strengthen your core muscles and glutes.
- To do this exercise:
- Start by lying on your back, with your knees bent at 90 degrees and your arms flat against the floor by your sides. Turn your feet out slightly.
- Push into the floor with your feet and lift your hips by squeezing your glutes, until there is a straight line from your knees to your shoulders.
- stop for a couple of seconds, then return to the starting position.
- Do one to two sets of 15 repeats to start.
- Try to work up to three sets as you erect your core strength.
Resistance band pull apart
- Benefits: Resistance band pull apart exercise helps strengthen the muscles power in your upper back and shoulders.
- To do this exercise:
- Stand while holding a resistance band tightly between your hands. lift your hands in front of you so that they are shoulder-width apart and similar with the floor.
- Drag the band apart while squeezing your shoulders together, until your arms are stretched out by your sides.
- stop for a moment, then return to the start position
- Do one to two sets of 15 repeats to start. Try to work up to three sets as you erect your upper body strength.
Surgical Treatment
- Surgery for kyphosis would usually be recommended if the curve of your lumbar spine is very pronounced. the curve is causing persistent pain that cannot be controlled with medication. the curve is disrupting your body is other important functions.
Laminectomy:
- A laminectomy is a surgical procedure where parts of the lumbar vertebrae are removed to give access to the spinal cord or nerve roots.
What can you do to prevent Lumbar Lordosis?
- If you sit a long time during the day, take small breaks to get up and stretch.
- If you have to stand for a long time, periodically move your weight from one foot to the other, or from your heels to your toes.
- Sit with your feet flat on the ground.
- Use a pillow or rolled towel to support your lower back when sitting.
- Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes.
- Stick to an exercise program of your choice.



4 Comments