Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) : Causes,Symptoms and Physiotherapy Treatment.
Table of Contents
Overview :
Guillain-Barre Syndrome is a rare disorder in which your body’s immune system attacks your own nervous system.
it is an autoimmune disorder that leads to progressive paralysis.
it is the most common cause of acute flaccid , neuromuscular paralysis worldwide.
Definition :
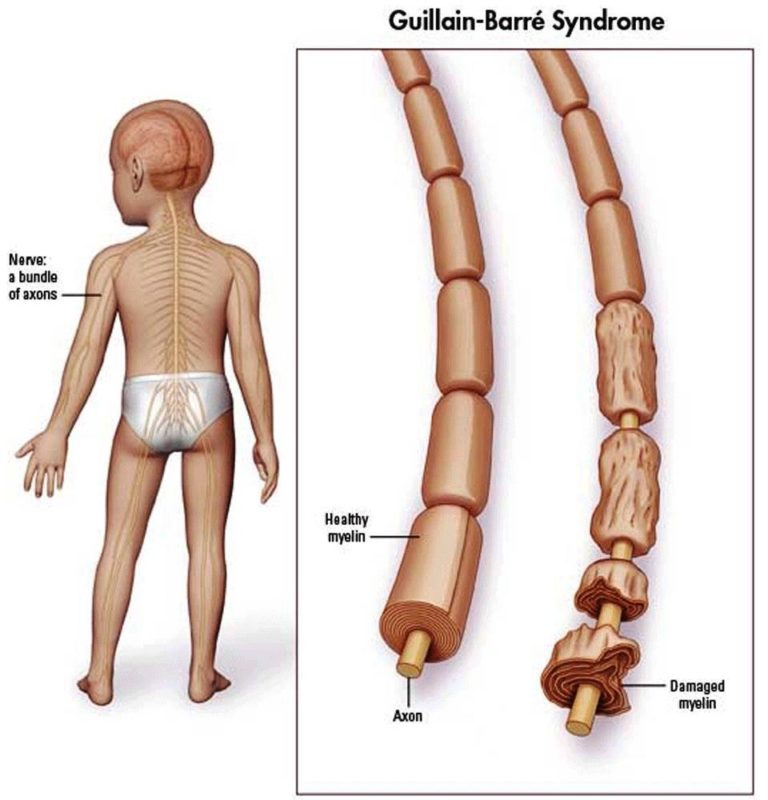
it is the disease of Demyelinating of the peripheral nervous system.
it is also called as : “Acute inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy “
Epidemiology :
0.4 to 2 cases per 100,000.
Causes of Guillain-Barre Syndrome:
The actual cause of the GBS is not known.
but it is known to develop after bacterial or viral infections.
bacterial infections like :
- Complobacter jejuni
- Mycoplasma ineumoniae.
What is the Mechanism of breakdown of myelin sheath ?
myelin is produced by the schwann cell.
because of myelin the fast conduction of signals occurs.
in GBS demyelination happens , because immune system improperly attack on myelin sheath.
so communication between two neurons breakdowns.
it will also lead to sensory , motor and cognitive problems.
bacteria and viruses don’t directly damage the sheath.
antigens that look similar to the lipids in the sheath, so immune cells mistakes in identification .
so because of that they destroys the myelin sheath.
in early GBS , schwann cells make new myelin so Remyelination occurs .
but overtime schwann cells cannot keep up and there’s become irreversible.
so nerve impulses become slow and sluggish.
What are the symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome ?
- Feeling of pain in whole body
- Muscular weakness
- Unsteady walking
- Issues with coordination
- Feeling of fatigue
- Changes or abnormality in your heart rate
- Difficulty in talk
- Difficulty in swallowing of food
- Affection of facial muscles
- Diminished reflexes
- Breathing abnormalities
- Sensations of tingling and burning
- Bowel and Bladder involvement
- Urinary incontinence
- Constipation
- Orthostatic Hypotension ( decreased blood pressure in standing position )
Types of GBS :
Guillain-Barre syndrome has many forms.
The main types are as below :
Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP) :
- The most common type seen in North America and Europe.
- The common sign of AIDP is muscular weakness which starts in the lower extremities first and then spreads upward.
Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS) :
- in this type first paralysis starts into the eyes.
- MFS is also associated with unsteady gait cycle.
- it is most commonly seen in Asia.
Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN) :
- in this type acute paralysis occurs.
- there will be loss of reflexes without any sensory changes.
Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN) :
- it is serious neuropathy in comparison with AMAN.
- it is associated with ascending muscular weakness with sensory changes.
- there will be also respiratory issues.
How to do Diagnosis of GBS ?
It is difficult to diagnose the disease in early stages.
the symptoms are different from one patient to another patient.
the doctor recommend you for the following investigations :
Investigations :
(1)Lumbar puncture :
The CSF is obtained .
it will show the increased level of proteins or albumins without increase in WBCs.
(2) Nerve conduction studies and ElectroMyoGraphy :
this tests are used to assess the functions of the nerves and muscles .
(3) Pulmonary function tests :
this tests are recommended to evaluate respiratory functions.
Treatment of the Guillain-Barre Syndrome :
There is a no cure for GBS.
The ultimate goal of the treatment is to prevent breathing problems and relieve in the symptoms.
The Medicines are used to control pain .
To suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation the following treatment should be done.
(1)Plasmapheresis :
It is the procedure of the removal of the plasma from the body. and replacement of it via other fluids.
Anti bodies are also removed.
so it will help in resolution of the symptoms.
(2)Immunoglobuline transfer :
It contains healthy antibodies from blood donors.
It is given via intravenous route.
Which orthosis are used for the GBS patients ?
Orthosis to prevent foot drop and aid for walking.
Insole to improve alignment of the joints, proprioceptions and gait.
Resting splints to maintain alignment of the joints within available range.
Day and night splints for prevention of contractures.
Modification of shoes to improve mobility .
Physiotherapy Treatment for Guillain-Barre Syndrome :
Goals and treatment plan explained in brief :
To improve muscle strength :
strengthening and mobilization exercises.
To reduce muscle stiffness and spasm :
stretching exercises.
To cope up with postural instability and balance issues :
balance training
core stability exercises.
postural re-education
use of different mobility aids
To reduce risk of falls :
balance workout
gait re-education or gait training.
Fatigue management and advice.
increase independence and quality of life.
Physiotherapy exercise :
(1) Range of motion exercises :
Ankle joint ROM exercises :
Position of the patient : sit on the floor with legs straight. wrap a towel around your feet.hold the both ends of the towel in your hand.
Ankle dorsi flexion :following the position gently points the toes toward your body , slowly return to starting position.
Ankle plantar flexion :point the toes away from the body.
Eversion :movements of the foot outside.
Inversion:movements of the foot inside.
Ankle circumduction : movements of the foot in circular motion.
Knee joint ROM exercises :
Position of the patient :supine lying
Heel slides :
bend your hip and knee by sliding your heel up toward your buttocks while keeping your heel on the bed.
slide your heel back down to the starting position and relax.
you can use a plastic bag under your heel to slide it easily.
Hip joint ROM exercises :
Position of the patient :supine lying
Hip flexion :move your leg towards the sliding with knees straight.
Leg slides ( Hip Abduction ) :slide your leg out to the side.
( Hip Adduction ) :slide your leg back to the starting position .
Hip extension :
Position of the patient : standing
push your leg towards your back.
Shoulder joint ROM exercises :
Position of the patient : sitting position
Shoulder flexion :raise your arm forward over up to your head.
Shoulder extension :bring your arm back to your side.return it to the starting position.
Shoulder movement slide to slide :
(Shoulder Abduction) :raise your arm to the side and then up over your head as far as possible.
(Sholder Adduction) : return your arm to your side.
Shoulder Rotation :roll your sholders in a smooth circles. clockwise and anticlock wise.
Elbow joint ROM exercises :
Elbow flexion :with your palm facing forward, just bend your elbow.
Elbow extension :return your arm to the starting position.
Wrist joint ROM exercises :
Wrist flexion :bend your hand back towards your wrist so that your fingers point towards celling.
Wrist extension :bend your hand down so that your fingers points towards the floor.
Wrist side to side movements :move your hand to side to side.
Wrist rotation : roll your hand in circles , clock wise and anticlock wise.
Hand and Fingers exercises :
Fingers bands :make a tight fist and then relax it.
Fingers spread :open your hand and stretch the fingers as far apart as possible.
bring your fingers together again.
Finger to Thumb touch : touch each finger tip with the pad of your thumb.
Thumb to palm stretch :move your thumb across your palm.
Neck ROM exercises :
position of the patient :sitting or standing with face forward.shoulder sholud be straight and relaxed.
Neck flexion :gently bow down your head and try to touch your chin to your chest.
Neck extension :tilt your head back as you are looking towards celling.
Neck side flexion :tilt your head to the side.do not raise your shoulder.
Neck rotations :turn your head to look over your shoulder.
Note :
All above mentions ROM exercises should be repeated for 5 to 10 times per session.
and it should be done 2 to 3 times in a day.
(2) Static quadriceps :
tighten the muscles on the top of your thigh, by pushing the back of knee down into the towel.
hold for 5 to 10 secs and then relax.
(3) Cat and Camel exercises :
begin from 4 point kneeling. back in neutral position.
tuck your chin in and round your back upward one segment at a time.
reverse by letting back one segment at a time.
but keep your neck in neutral at the end.
hold 30 secs and 3 repetitions /session.
(4) Bridging :
lie on your back with knees bend and feet flat.
slowly lift your hips off from bad ,as you feel comfort.
hold for 5 to 10 secs and then gently return back.
make sure that your head and neck remain straight during lift.
(5)Knee to chest :
lie on your back with knees bend towards your chest.
wrap your arms around your legs to hold your hands in the position.
gently tuck your chin to the chest.
hold the position for 30 secs, repetition 2 to 3 times.
(6) Knee roll :
lying flat with knees bend and foot flat on the ground.
roll your knees side and stretch diagonally across trunk.
come back to the middle , and repeat it over the another side.
(7) Chair stand :
sit to stand from the chair.
repetition 5 to 10 times.
(8) Gait Training :
gradually increase the distance you walk.
Life Style Modification and Home care :
- built a strong support system for the patient.
- provide education of the patient and caregivers for prevention of contractures , DVT and bed sores.
- frequent change in position.
- support your weak extremities.
- introduction of breathing exercises to maintain good airway .
- multiple rest between treatment.
- place computer or monitor at eye level.
- reduce level of stress. so do meditations and yoga regularly
- apply gentle massage to the affected area.
- maintain a healthy weight.
- do regular physical activity.
Complications of GBS :
- Muscular weakness
- Tingling and Numbness
- Feeling of some kind of sensations even after recovery
- Cardiac problems
- Pain Sensations
- Disturbed in bowel or bladder function
- Bedsores




10 Comments