Ataxic Gait
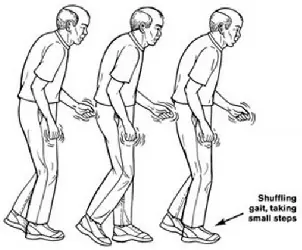
What is Ataxic Gait? A common feature of ataxic gait is the inability to walk straight ahead, as well as lateral veering, poor balance, a wider base of support, irregular arm movements, and lack of repeatability. These signs frequently reflect the way a person walks after drinking.During walking, there are some features of intralimb leg…