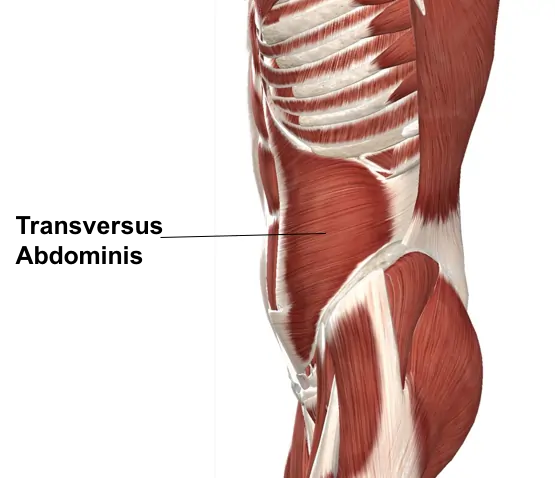
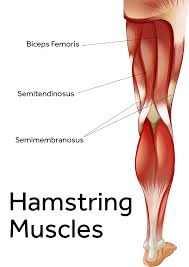
Transverse abdominis muscle
Introduction: The transverse abdominis (TrA) muscle is the deepest of the six abdominal muscles. It extends between the ribs & the pelvis, wrapping around the trunk from front to back. The fibers of the muscle run horizontally, similar to a back support belt. In this way, along with providing postural support, the transverse abdominal muscle…