Ape Hand Deformity:
Table of Contents
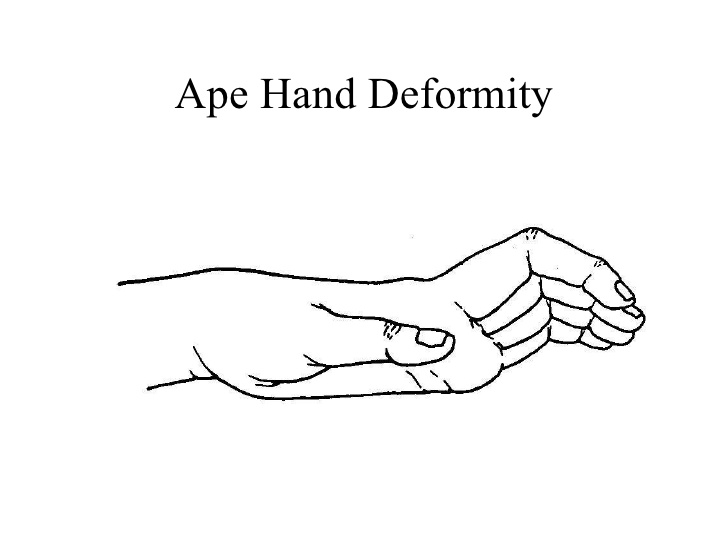
What is Ape Hand Deformity?
Ape hand deformity is one type of deformity of median nerve palsy, which is caused by serious injuries to the arm, forearm, and wrist area.
The ape hand is a movement deformity in people. That causes an unable to abduct or oppose the thumb so that the thumb movement is little or no. In Abduction movement of the thumb is the ability to move the thumb perpendicular (90°) away from the palm plane. The opposition movement is the ability of the thumb to touch the tip of all fingers and is in contact through the swing of the palmar surface so that the pinch grasp movement is also affected. The flexion and extension movements are also limited.
The term “ape hand” is misleading as apes have opposable hand movement but because of the limitations of the thumb functional movement, people believe the hand looks like an ape.
The Ape Hand deformity is caused by injury to the distal median nerve (also known as a Median Claw lesion) and loss of opponens pollicis muscle function. It can occur with an injury of the median nerve at the elbow or the wrist.
Why is it called An Ape Hand?

When the thumb lost its ability to touch against a finger or make an O shape (pincer grasp activity) and the hand muscles are atrophied. Due to the inability of the opposition movement of the thumb, the hand looks like an ape.
Apes have opposable thumb movements and ape hand is a contradictory name.
Mechanism of deformity:
The mechanism for this deformity is a deep injury to the arm, forearm, and wrist part that causes damage to the median nerve so that the affection of the thenar muscles and opponents policies muscle.
Anatomy of Median Nerve:
The median nerve is one branch of the brachial plexus and starts from the spinal cord. The nerve roots are C6, C7, C8, T1, and sometimes C5 of the spinal cord. Median nerve formation is in the axilla by a branch from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus, on either side the axillary artery fuse together to create the nerve anterior to the artery.
The median nerve is related to the brachial artery within the arm, from the axilla it goes down and enters the cubital fossa. The nerve runs into the cubital fossa medial to the brachialis tendon and passes between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle. The nerve continues to run down the forearm between the flexor digitorum profundus muscle and the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
The median nerve is together in between the flexor digitorum superficialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscles just above the wrist. In the wrist region, the nerve gives the palmar cutaneous branch that supplied the skin of the center portion of the palm. The nerve continues through the carpal tunnel into the hand, situated anterior and lateral to the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle’s tendon in the carpal tunnel.
In the hand, the nerve divides into a muscular branch and palmar digital branches. The muscular branch supplies sensation to the thenar eminence muscles and the palmar digital branch supplies the sensation to the lateral 3 ½ digits and the lateral two lumbricals.
The four thenar muscles are the:
- Abductor pollicis muscle
- Adductor pollicis muscle
- Opponens pollicis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
Branches of Median Nerve:
The median nerve has many different branches in the different parts of the whole upper limb.
The forearm gives 2 branches.
1)Muscular branches
2)Anterior interosseus nerve
On the hand, it gives 3 branches.
1)cutenues branch
2)palmar digitorum nerve
3)Recurrent branch
Median nerve injury:
The Median nerve injury is mainly divided into high and low median nerve injury. High median nerve injury is located above the elbow and Low median nerve injury is located below the elbow.
If the median nerve injury is due to any reason at the wrist or the nerve is compressed in the wrist and affects the thenar muscles this deformity occurs.
What are the causes of Ape Hand Deformity?
The ape hand usually occurs because of median nerve palsy, it is commonly caused by deep injury to the wrist or forearm. so that impairs the function of the thenar muscles. A 2018 study reported that median nerve mononeuropathy is the most common neuropathy of peripheral nerve neuropathy.
The median nerve runs down from the arm to the forearm and then reaches into the hand through the carpal tunnel. the median nerve provides a motor function to the forearm and provides both motor and sensory function to the wrist and hand, including the: thumb, index finger, middle fingers, and half of the ring finger, does not affect the little finger.
The thenar muscles are commonly affected in simian ape deformity. thenar muscles allow the pinch grasping movement.
Symptoms of Ape Hand Deformity:
- Pain in the wrist or lateral side of the palm.
- Weakness in the thumb.
- May decrease the sensation of the thumb.
- Can’t move the thumb on the inner side of the palm(opposition movement restricted).
- Sometimes inflammation is present in the thumb.
- Thenar muscle wasting.
A condition similar to the ape hand:
Many different types of hand conditions are associated with an ape hand deformity:
Carpal tunnel syndrome:
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the result of compression of the median nerve which travels through the carpal tunnel into the wrist.
CTS symptoms are pain, tingling, or numbness in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger. sometimes symptoms feel in the forearm.
De Quervain’s tendinosis:
De Quervain’s tendinosis, also known as Quervain’s tenosynovitis, in this condition the inflammation of tendons in the thumb. It’s caused by any trauma to the thumb, repetitive grasping activity, or any inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. In this condition, the symptoms are pain and tenderness at the base of the thumb.
According to the one reported, women are affected with this condition 8 to 10 times more than men.
Trigger finger:
Trigger finger or trigger thumb, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, it occurs when a finger or thumb becomes stuck in a bent position.
A trigger finger is characterized by soreness at the base of the thumb or finger. the person feels a popping or snapping when any movement of the thumb or finger. The stiffness is present and may be worse in the morning, decreasing stiffness when the thumb and fingers are used or do any movement.
Pronator Syndrome:
Pronator syndrome occurs when the median nerve compression in the pronator muscle in the forearm.
The patient complains of sensation loss over the thenar eminence muscle and limitation of forearm movement.
Clinical Presentation:
This condition is a part of median nerve palsy and in this condition movement affection of the thumb in various planes. most commonly opponent’s movement is restricted so that person cant does touch the thumb to the tip of every finger of the hand.
Diagnosis and Evaluation Ape Hand deformity:
Physical examination:
To check the “bottle sign”, for example; when a person grasps a long object(like a bottle) in the hand, some gap is present between the skin of the hand and the object. This sign indicates the weakness of the thenar muscles due to median nerve injury.
Another one is the doctor asked the patient to touch the tip of every finger by the thumb and see if it is possible or not. If the patient can’t do that and the thumb is in the ape position this sign is present.
After the physical examination, another diagnostic procedure can be used to check the electrical activity of the median nerve. that is the following:
- NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity): If the median nerve is affected some impairment is present in the electrical conductivity of the median nerve.
- EMG Test: Any pathology of the muscles supplied by the median nerve can be identified by this test. This will also help to find other causes like polyneuropathy.
Treatment of Ape Hand Deformity:
Treatment mainly depends upon the etiology of median nerve injury. In the case of carpal tunnel syndrome, splints can be used.
Some other treatments are:
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical treatment
- Physiotherapy treatment
Conservative treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief.
- Manual therapy techniques are given to encourage thumb movement.
- Avoiding the activity which produces pain and stress on the thumb.
- Apply the ice massage or heat therapy.
- Dynamic splints are advised to allow the movement of the thumb.
Surgical Treatment:
Surgery may be done depending on the severity of the deformity. Surgery improves the function of the affected area in the hand.
Surgical treatment may consist of:
Nerve decompression
Nerve repair
Nerve graft
If nerve repair is not done then tendon transfer surgery is recommended. Tendon transfers borrow extra tendons from other areas of the hand or forearm to perform a function lost due to the nerve injury.
Physiotherapy Treatment in Ape Hand Deformity:
The goal of Physiotherapy treatment:
- Regain muscle strength.
- Improve muscle functions.
- Improve the sensitivity of the affected area.
- Decrease the pain.
- It helps to regain muscle strength while splints (C-splints) and braces help to recover.
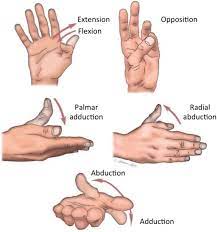
Passive movement Exercise:
The patient cant does the whole movement properly so the therapist does the whole movement of the thumb passively. Like; Thumb flexion movement, Thumb extension movement, Thumb abduction movement, and Thumb adduction movement.
Active movement Exercise:
Doctor asked the patient to do the active movement of the thumb.
Thumb flexion movement: the patient does the thumb in towards the palm.
Thumb extension movement: the patient does a thumb movement away from the palm.
Thumb abduction movement: the patient does thumb away from the lateral line of the palm.
Thumb adduction movement: the patient does the thumb near the lateral line of the palm.
Thumb Opposition movement: the patient does the opposition movement like thumb touching every tip of the fingers sequence.
Strengthening Exercise:

The first patient does the movement actively then the therapist go for the strengthening exercise.
This exercise does by a finger spring, rubber, or small stretchable belt. The patient does the thumb opposition movement by the use of the finger spring. spring is held in the thumb and finger and then compressed the spring by every finger.
The patient wears rubber on the thumb and finger and then does the thumb’s movement to strengthen the muscles.
Hot and Cold therapy:
It helps to reduce the pain and inflammation, and improve the sensation.
Electrical modality:
Therapists give the electrical stimulation first in Ig current given on to the thenar muscles to stimulate the opponent’s muscle. then gradually go to the SF current which helps to strengthen the muscle.
Prognosis of the Ape hand Deformity:
The prognosis is usually good and early. It depends upon the severity of the nerve injury and the patient age and awareness of that, Conservative therapies help in the early improvement of symptoms. The condition is improving within two to six weeks. After the surgery, the complete healing time is four months to two and a half years.
FAQ
Which nerve injury can lead to an ape-like hand?
The thumb is mostly rotated and adducted and called an “ape-like hand.” ape-like hand deformity is caused due to damage to the median nerve in the mid-forearm which leads to paralysis of flexor digitorum superficialis.
What is the difference between the ape hand and the claw hand?
The thumb is mostly rotated and adducted and called an ape-like hand while the Claw hand is a condition in which the fingers are curved or bent. This can lead to difficulty to pick up or grasping objects with your hand. It can affect one or all fingers on one hand or Both hands.