Sweater Finger Sign (Jersey Test)
Table of Contents
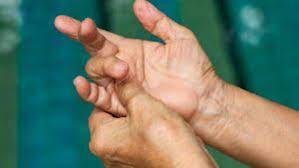
What is the importance of the Sweater Finger Sign test?
This sweater finger sign is used to determine whether the Flexor Digitorum Profundus Tendon has ruptured or is still intact.
Relevant Anatomy:
- The flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) muscle is a fusiform muscle that is seen in the deep muscle within the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm.
The FDP = Flexor Digitorum Profundus muscle separates into four tendons that are run down on the forearm & it closer to the bone.
All of the patient’s hand fingers have these Flexor Digitorum Profundus tendons implanted into the base of the distal phalanges. - This Sweater Finger Sign examination helps with finger bending, or flexing, at the fingertip joint.
The Flexor Digitorum Profundus (FDP) tendon originates at or below the wrist joint, allowing a power grip through contraction of the wrist joint muscle.
Sweater Finger Sign exam
Patient Position: The patient is in a seated position during the exam.
The Sweater Finger Sign test is performed using the following technique:

- It is requested of the examiner (therapist) to make a fist.
- The flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon has ruptured if the distal phalanx of one of the fingers cannot be extended.
- The findings of the Sweater Finger Sign test can be interpreted as positive when the finger is not bent, indicating that it is not flexed, and when the loss of flexion at the DIP indicates that one of the hand’s fingers has flexor digitorum profundus or FDP.
- primarily in the hand’s ring finger.
- Test for the sweater finger sign’s clinical indications:
- The Jersey test, also known as the sweater finger sign test, is used to diagnose severe damage to the flexor digitorum tendon.