FIFTH CRANIAL NERVE- TRIGEMINAL NERVE
Table of Contents
TRIGEMINAL THE FIFTH NERVE:
The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the largest of the cranial nerves.
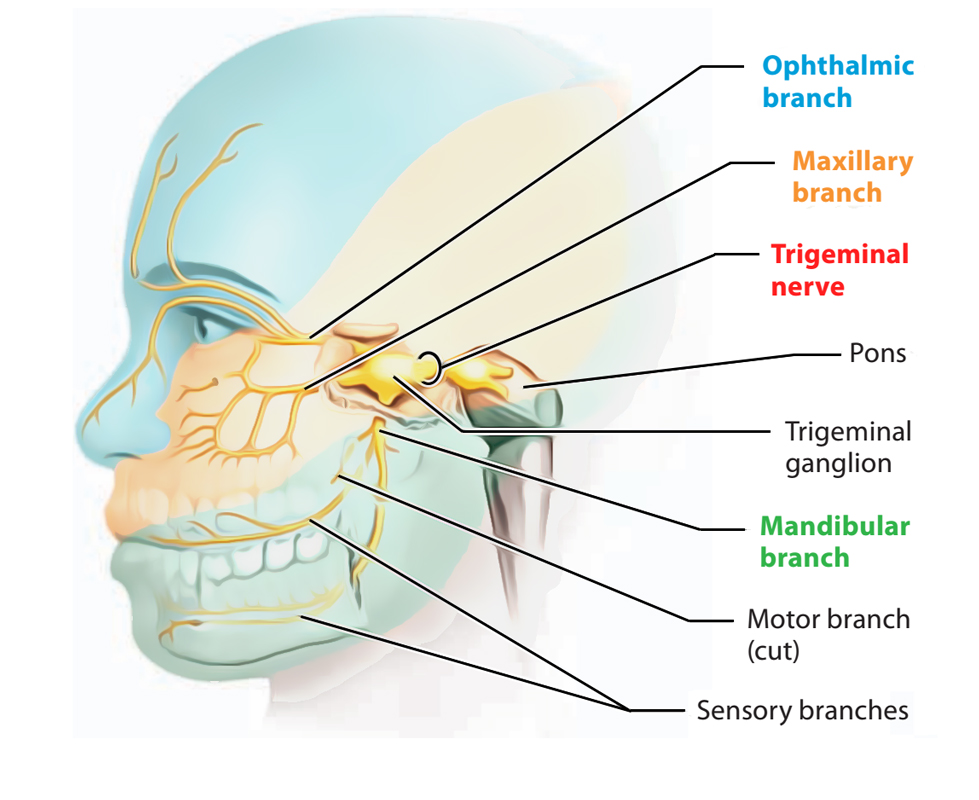
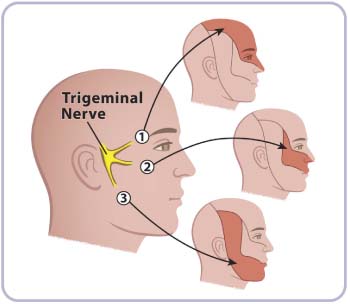
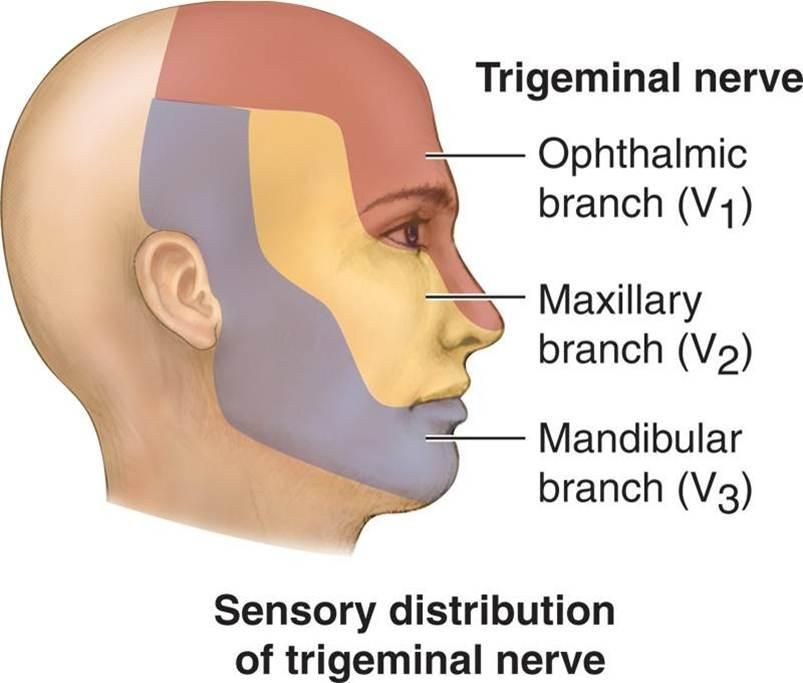
It has three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or “cutaneous”) functions.
The ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular branches leave the skull through three separate foramina: the superior orbital fissure, the foramen rotundum, and the foramen ovale, respectively.
The opthalmic nerve(v1):
-carries sensory information from the scalp and forehead, the upper eyelid, the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye, the nose (including the tip of the nose, except alae nasi), the nasal mucosa, the frontal sinuses and parts of the meninges (the dura and blood vessels).
The maxillary nerve (V2):
-carries sensory information from the lower eyelid and cheek, the nares and upper lip, the upper teeth and gums, the nasal mucosa, the palate and roof of the pharynx, the maxillary, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses, and parts of the meninges.
The mandibular nerve (V3) :
-carries sensory information from the lower lip, the lower teeth and gums, the chin and jaw (except the angle of the jaw, which is supplied by C2-C3), parts of the external ear, and parts of the meninges.
FUNCTION:
The sensory function of the trigeminal nerve is to provide tactile, proprioceptive, and nociceptive afference to the face and mouth. Its motor function activates the muscles of mastication, the tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid, and the anterior belly of the digastric.
TEST:
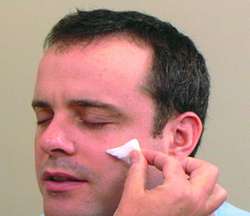
Pin or cotton swab test:
One or both sides of the face are touched with either a pin or cotton swab. The person will then be asked whether they felt anything, and if so, where they felt it. A doctor may also lightly touch the cornea of the eye with a cotton swab to test the ophthalmic division. If the person doesn’t blink, the ophthalmic division of their trigeminal nerve may be damaged.
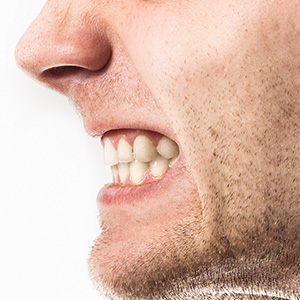
Clenching test:
A doctor will ask someone to clench their teeth or try to open their jaw when resistance is applied. They’ll check muscle tone and movement for any signs of trigeminal nerve damage.
DISORDER :
TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA:
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia, even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain.
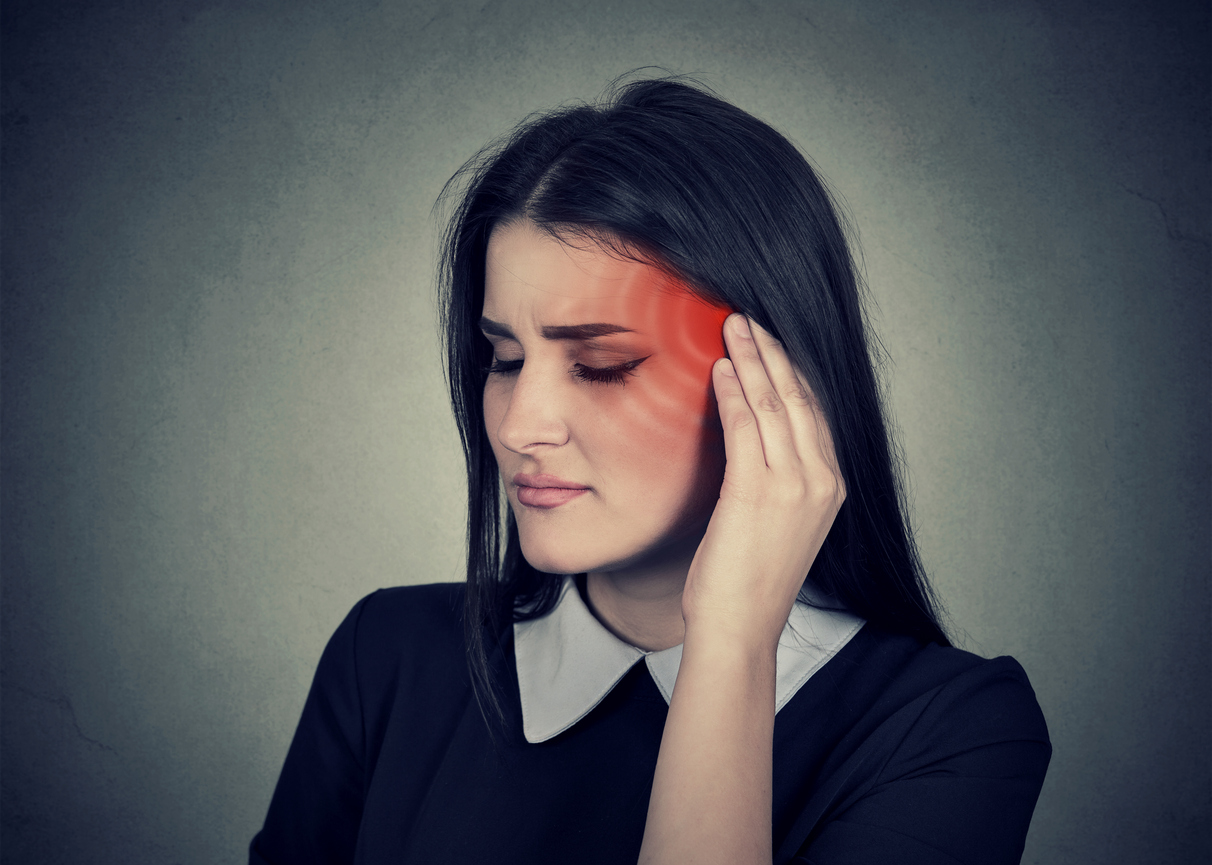

SYMPTOMS :
-Episodes of severe, shooting, or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock.
-Bouts of pain lasting from a few seconds to several minutes.
-Pain in areas supplied by the trigeminal nerve, including the cheek, jaw, teeth, gums, lips, or less often the eye and forehead.
-Pain affecting one side of the face at a time, though may rarely affect both sides of the face.
-Pain focused in one spot or spread in a wider pattern.
-Attacks that become more frequent and intense over time.
CAUSES:
Trigeminal neuralgia can occur as a result of aging, or it can be related to multiple sclerosis or a similar disorder that damages the myelin sheath protecting certain nerves. Trigeminal neuralgia can also be caused by a tumor compressing the trigeminal nerve.
TREATMENTS:
Anticonvulsants:
Doctors usually prescribe carbamazepine (Tegretol, Carbatrol, others) for trigeminal neuralgia, and it’s been shown to be effective in treating the condition. Other anticonvulsant drugs that may be used to treat trigeminal neuralgia include oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), lamotrigine (Lamictal) and phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek). Other drugs, including clonazepam (Klonopin) and gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others), also may be used.
Antispasmodic agents:
Muscle-relaxing agents such as baclofen (Gablofen, Lioresal) may be used alone or in combination with carbamazepine. Side effects may include confusion, nausea, and drowsiness.
Botox injections :
Botulinum toxin A (Botox) injections may reduce pain from trigeminal neuralgia in people who are no longer helped by medications.
SURGERY:
This procedure involves relocating or removing blood vessels that are in contact with the trigeminal root to stop the nerve from malfunctioning. If a vein is compressing the nerve, your surgeon may remove it. Doctors may also cut part of the trigeminal nerve (neurectomy) during this procedure if arteries aren’t pressing on the nerve.


I am 78 yrs old, what is recommended to do, if medications are not good.
Please you can contact nearby Doctor for Proper diagnosis and Treatment!
What Doctor do you recommend in Jordan , for this 5th nerve,
Medicines are not functioning well.