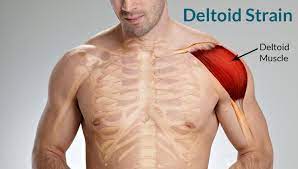
What does a Muscle Strain look like?
Muscle strain, also known as muscle pull or muscle tear, is a common injury that occurs when a muscle is overstretched or torn due to excessive force or repetitive use. This can happen as a result of sudden movements, such as lifting heavy objects or twisting, or as a result of overuse or repetitive strain from sports or other physical activities.
Muscle strains can range in severity from mild to severe, and may cause pain, stiffness, swelling, bruising, and weakness in the affected area. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation of the affected area, as well as over-the-counter pain relievers to manage pain and inflammation.
In some cases, more severe muscle strains may require physical therapy or other medical interventions, such as corticosteroid injections or surgery, to help the muscle heal properly and reduce the risk of further injury.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Muscle strain is a common injury that occurs when a muscle is stretched or torn due to overuse or sudden force. The symptoms of muscle strain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but generally include pain, stiffness, swelling, and weakness in the affected area.
Pain is one of the most common symptoms of muscle strain and can range from mild to severe. The pain may be sharp, dull, or throbbing, and may worsen with movement or activity. Stiffness is another common symptom of muscle strain, and may make it difficult to move the affected muscle or joint.
Swelling is also a common symptom of muscle strain, and may occur immediately after the injury or develop over time. Swelling can cause the affected area to feel warm to the touch, and may also be accompanied by redness or bruising.
Muscle Weakness is another symptom of muscle strain, and may make it difficult to use the affected muscle or joint. In severe cases, weakness may make it impossible to move the affected area at all.
Other symptoms of muscle strain may include a popping or snapping sensation at the time of injury, and muscle spasms or cramping. These symptoms may occur immediately after the injury or develop over time.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if the pain or swelling is severe or if you’re unable to move the affected area. With proper treatment and rest, most muscle strains can heal within a few weeks, but more severe injuries may require longer recovery time and medical intervention.
Diagnosis of Muscle Strain
Diagnosing muscle strain involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests if necessary. During the physical examination, a healthcare provider will evaluate the affected area and assess the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the affected muscle or joint. They may also ask questions about the onset and severity of symptoms, as well as any activities that may have caused or contributed to the injury.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may be ordered to help confirm the diagnosis of muscle strain and rule out other possible injuries, such as bone fractures or ligament tears. These tests can help to identify the location and severity of the injury, as well as any underlying structural abnormalities that may have contributed to the injury.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may also perform a muscle biopsy to evaluate the muscle tissue for signs of damage or inflammation. This may be necessary if the muscle strain is severe or if the symptoms do not improve with conservative treatment.
It’s important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a muscle strain, as early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent further injury and reduce the risk of long-term complications. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most muscle strains can heal within a few weeks, allowing you to resume normal activities without pain or limitations.
Self-Care Tips
If you have a muscle strain, there are several self-care treatments that you can do at home to help manage symptoms and promote healing. These include:
Rest: Resting the affected muscle is important to allow it time to heal. Avoid activities that cause pain or strain to the injured area.
Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help to reduce swelling and pain. Use a cold pack or wrap ice in a towel and apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Compression: Applying a compression bandage to the affected area can help to reduce swelling and provide support. Make sure the bandage is snug but not too tight, and remove it if it causes numbness, tingling, or increased pain.
Elevation: Elevating the affected area above heart level can help to reduce swelling and promote blood flow to the injured area. Use pillows or other props to keep the affected area elevated.
Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Gentle stretching and exercise: Once the initial pain and swelling have subsided, gentle stretching and exercise can help to improve range of motion and prevent stiffness. Ask your healthcare provider or physical therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises for your specific injury.
It’s important to follow these self-care treatments closely to ensure proper healing and prevent further injury. If your symptoms do not improve or worsen, or if you experience severe pain, weakness, or numbness, seek medical attention promptly.
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment for muscle strain may involve prescription medication, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgery. Your healthcare provider may prescribe pain medication or anti-inflammatory medication to help manage pain and inflammation. They may also recommend physical therapy to help restore range of motion, strength, and flexibility to the affected muscle or joint.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may also recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain. If the muscle strain is severe or if conservative treatments do not improve symptoms, surgery may be necessary to repair the muscle or surrounding tissues. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations closely to ensure proper healing and prevent further injury.
Prevention from Muscle Strain
Preventing muscle strain involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury. These include:
- Warm-up: Always warm up before engaging in physical activity to help prepare your muscles for movement and reduce the risk of injury
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strain. Stretch before and after physical activity to prevent injury.
- Proper technique: Make sure you are using proper technique when engaging in physical activity or lifting heavy objects. Poor form can increase the risk of injury.
- Gradual progression: When starting a new physical activity or exercise routine, gradually increase the intensity and duration to allow your muscles time to adapt.
- Rest and recovery: Allow your muscles time to rest and recover after engaging in physical activity. Overuse or pushing yourself too hard can increase the risk of injury.
By following these prevention strategies, you can reduce the risk of muscle strain and other related injuries, allowing you to engage in physical activity safely and without pain or limitations.