Wernicke’s Aphasia
Table of Contents
What is Wernicke’s aphasia?
- Aphasias are conditions of the brain that affects a person’s communication abilities, particularly speech. Wernicke’s aphasia causes problems speaking in coherent sentences or understanding others’ speech.
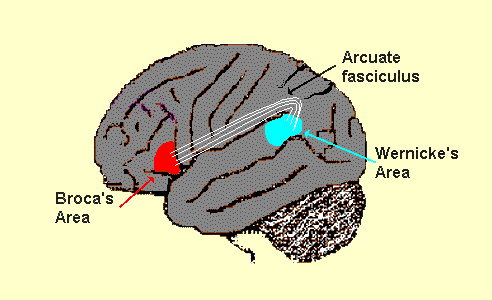
- Wernicke’s aphasia is the most usual type of fluent aphasia. It happens when the left middle side of the brain becomes harmed or altered. This area of the brain is known as Wernicke’s area, named after Carl Wernicke, a neurologist. Wernicke’s part of the brain controls human language. It is also near where we store our personal dictionaries. Someone with Wernicke’s aphasia may have trouble processing the meaning of spoken words.
- Wernicke’s aphasia is a language disorder that makes it difficult for you to understand words and communicate.
- This disorder is caused by damage to the area of your brain that controls language. It conducts in a loss of language ability and can be very frustrating.
What are the symptoms of Wernicke’s aphasia?
Concerning speech & comprehension, people with Wernicke’s aphasia may:
- string words together to make sentences that do not create sense,
- makeup words that have no meaning
- be unknowing of the mistakes in their speech
- deliver words in a usual melodic line, even though the content may not create any sense
- articulate their words normally
- have difficulty repeating phrases
- add words when trying to repeat someone
- interrupt others and speak rapidly
- Saying many words that do not create sense
- Unable to understand the meaning of words
- Able to speak well in long sentences but they do not make sense
- Using the wrong words or nonsense words
- Unable to understand written words
- Trouble writing
- Frustration.
- Others might have difficulty understanding you if you have Wernicke’s aphasia because of paraphrastic errors. These errors are when you restore a word or sound with other words or sounds.
- You might say “telescope” contrary to “glasses” or “classes” instead of “glasses.” You might even create a new word. The rest of the sentence could be correct or it may be a mess of words.
- People with Wernicke’s aphasia typically do not realize they’re not making sense. This can conduct to frustration as they are continually misunderstood.
- Trobling with spoken language may not carry over to other aspects of brain functioning. Aphasia varies from a disease like Alzheimer’s, in which many of the brain’s functions diminish over time.
Those with Wernicke’s aphasia may:
- have seriously impaired reading and writing abilities,
- understand visual materials good than written or spoken words,
- keep cognitive abilities other than those associated with language.
What are the causes of Wernicke’s aphasia?
- Lesions or harm in the middle of the left side of the brain causes Wernicke’s aphasia.
- Stroke is one potential cause of this condition because it contacts blood flow to the brain. If blood does not reach Wernicke’s part of the brain, it can kill brain cells, resulting in this type of aphasia. Aphasia harms 25 to 40 percent of people who experience strokes.
Other conditions that may affect this area of the brain involve:
- head trauma
- tumors
- infections
- Stroke
- Encephalitis, or brain inflammation
- Head injury
- Brain infection
- neurological disorders.
- It is also possible to have aphasia that comes and goes. This may be reasoned by migraines, seizures, or other medical conditions. Progressive damage in your brain conducts to worsening aphasia in some cases. These can involve a growing brain tumor or dementia. Your aphasia might get worse as your illness advances.
How it is diagnosed?
- You should always look to a doctor if you suspect you have Wernicke’s aphasia or any type of aphasia. This condition may specify a significant alteration in the brain. Depending on your diagnosis, you may require to undergo medical interventions for the underlying cause of the aphasia.
- Your doctor will require to perform tests to determine what has caused Wernicke’s aphasia. This will likely involve brain imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan. These tests can also assist your doctor to determine if other parts of your brain have been affected.
- It may be required to have a neurological evaluation as well as a comprehensive speech and language examination. These tests will assist the doctor to determine your receptive and expressive language deficits.
Some of the tasks may involve:
- asking you to perform certain commands,
- asking a question for you to answer,
- asking you to name or repeat objects,
- engaging in conversation,
- testing your reading and writing.
Once diagnosed, your doctor may recommend you see a speech-language pathologist who can assist you improve your language abilities.
What is the treatment for Wernicke’s Aphasia?
- There are not any standard treatments for Wernicke’s aphasia. Your doctor might recommend various treatments or therapies.
- Treating other causes: If you have another condition such as an infection, treating it might help. The treatment turns on the problem. For example, when your doctor recommends steroids for lesions in certain areas of your brain that are causing aphasia symptoms.
- Speech therapy: This is an important treatment for aphasia. The goal of speech therapy is to assist you to gain better use of the language ability you still have, improving your language skills, and learning how to communicate in various ways. Group speech therapy can be useful to practice skills with others and reduce your feelings of isolation.
- Speech devices: Technology that utilizes pictures or speech can help you communicate. These do not improve your language skills but are another way to express yourself. Speech devices can also assist caregivers to communicate with you and understand your needs better.
Physiotherapy treatment
- Physiotherapists get to manage patients with neurological conditions that may and often conduct to aphasia. It is important to be knowledgeable about the condition and its types to aid appropriate referral if or when detected by the physiotherapist in the course of patient care, and to optimize interaction with patients.
What is the outlook for Wernicke’s aphasia?
- Wernicke’s aphasia may diminish your language abilities, but it is possible that you will regain them over time with medical intervention. If the brain has been damaged, it will try to recover over the course of a certain month. Speech and language intervention is most effective when it begins soon later the brain injury.
- Someone with profound aphasia needs more medical intervention than someone with a milder diagnosis. Going to therapy to assist your language skills and learn new communication strategies to use with family and friends may be necessary.
- Certain people who get Wernicke’s aphasia fully recover without treatment. Children under 8 years of age often regain language ability even later severe damage.
- Most people require speech therapy. Recovery commonly happens within 3 months. Yet aphasia may take up to a year to improve. Lots of people do not regain full language ability. This can cause frustration for you & your caregivers.
- Caregivers, friends, and family require to adapt and learn new ways to communicate. A speech therapist can assist your family to learn new methods.
These can involve:
- Using shorter, simple sentences,
- Asking yes or no questions,
- Using natural, adult language and conversation,
- Not correcting speech,
- Using pointing, pictures, drawing, or devices,
- Including people with aphasia in conversations,
- Allowing many of time for people with aphasia to express themselves.
You can practice simple sentences in a silent space on your own if you have aphasia. Try practicing with your speech therapist and then with friends and family as you acquire more comfortable. Communicating and speech practice will assist you to feel connected to others.
FAQs
Wernicke’s aphasia causes you to speak in a jumbled “word salad” that others can not understand. Broca’s aphasia quotes you with limited language. You might only be able to say single words or very small sentences. But others can commonly understand what you mean.
Wernicke’s aphasia patient may speak in long sentences without any meaning, using unnecessary words and even making made-up words. For example, someone with Wernicke’s aphasia may say, “You know that moodle tinkered and that I want to get him round and take care of him as you want previously.”
Symptoms of Wernicke’s Aphasia
Speech is fluent with usual prosody & intonation.
Speech does not create sense; the words do not make a coherent thought.
Speech often involves neologisms or invented words that have no meaning.
Impairment with repeating words/phrases.
The features of Wernicke’s aphasia are Impaired reading & writing. An inability to grab the meaning of spoken words (producing connected speech is not affected). An inability to create sentences that hang together.
The three most usual types of aphasia are:
Broca’s aphasia.
Wernicke’s aphasia.
Global aphasia1.
Damage to Wernicke’s area can conduct to disorders associated with speech and language such as Wernicke’s aphasia. This condition causes hard in understanding language and forming meaningful sentences.
The brain region known as the Wernicke part, shown in blue, supports a critical component of speech production, referred to as phonologic retrieval, in which the phonemes to be articulated, & their temporal order, are represented mentally.
Communication Partner Training (CPT)
Communication partner training is sometimes the first and most effective treatment to establish communication and begin building rapport with a person with Wernicke’s aphasia.
Physiotherapists get to manage patients with neurological conditions that may and often lead to aphasia.
In general, the aims of aphasia treatment as described by ASHA involve: restoring lost language abilities. strengthening intact communication skills. compensating for impairments by teaching strategies & using AAC.
.