Urinary Incontinence
Table of Contents
What is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence, or the inability to control an individual’s bladder, is frequently unpleasant. The intensity might range from sometimes leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having a sudden, intense need to urinate that prevents you from reaching a toilet in time. Urinary incontinence isn’t a natural part of becoming older, even though it happens more frequently as individuals age.
Do not hesitate to visit the doctor if urine incontinence interferes with daily activities. Most people may address their urine incontinence symptoms with easy food, lifestyle adjustments, or medical attention.
Not only is urinary incontinence a medical issue. It can impact social, psychological, and emotional health. Urinary incontinence sufferers frequently experience anxiety when doing routine everyday tasks. People do not want to be too far from a toilet. Urinary incontinence may prevent people from enjoying life.
Many individuals believe that developing urine incontinence is a natural aspect of aging. Yet it isn’t. It can also be controlled or cured. Find out more here. Consult your physician. Find the best course of therapy for a person.
Epidemiology
- The problem of urinary incontinence continues to be prevalent globally, affecting people of all racial and cultural backgrounds.
- As was already said, it is challenging to estimate the prevalence globally because of variations in the criteria used, the population polled, the survey method, response rate, age, gender, the accessibility and effectiveness of health care, and other factors.
Clinically relevant anatomy
Pelvic Floor:
- The muscles, ligaments, and fascial components that make up the pelvic floor work in a manner to support the pelvic organs and apply compressive pressures to the urethra during elevated intra-abdominal pressure.
- The muscular layer of the pelvic floor is referred to as the pelvic floor muscles.
- The levator ani, the split urogenital sphincter, the external anal sphincter, the ischiocavernosus, and the bulbospongiosus are all parts of it.
- The pelvic floor muscles surround the urethra, vagina, and rectum as they travel through it.
- To give support under elevated intra-abdominal pressure, the pelvic floor muscles must contract.
- Urine, anus, and vagina shut with contraction of the pelvic floor muscles.
- To avoid the unintentional loss of urine or rectal contents, contraction is crucial.
- To empty, the pelvic floor muscles must also untense.
What causes Urinary Incontinence?
- There are a wide range of reasons that you could encounter incontinence.
- These causes can change depending on whether you’re a lady or a man.
- Certain causes are temporary medical issues that generally disappear once treated.
- Incontinence can be brought about by long-term (constant) illnesses.
- At the point when you experience incontinence issues due to a persistent condition, it’s typically something you should oversee over a more extended period.
- Indeed, persistent conditions typically don’t go away, even with treatment. Over time, as a result of your ongoing condition, incontinence may need to be monitored.
Transitory or transient reasons for incontinence can include:
Urinary tract infection (UTIs):
A disease inside your urinary tract (urethra, ureters, bladder, and kidneys) can cause pain and increase your need to urine more regularly. When treated, the desire to urine often as a rule disappears.
Pregnancy:
During pregnancy, your uterus puts additional strain on the bladder as it extends. Most ladies who experience incontinence during pregnancy notice that it disappears in the weeks after conveyance.
Medications:
Incontinence can be a result of specific drugs, including diuretics and antidepressants.
Beverages:
There are some beverages — like espresso and liquor — that can make you really want to urine substantially more frequently. On the off chance that you quit drinking these refreshments, your need to urine much of the time commonly goes down.
Constipation:
Chronic constipation (stool that is hard and dry) can cause you to have bladder control issues.
Constant or long-term reasons for incontinence can include:
Pelvic floor problems: When a person’s pelvic floor muscles are weaker, it might affect how your organs—including your bladder—function.
Stroke: A stroke can affect muscles controlling the urinary system.
Diabetes: At the point when you have diabetes, your body creates more urine. Furthermore, fringe neuropathy may affect the bladder’s functionalities.
Menopause: Menopause is another period of rapid physical change in a woman’s body, during which her hormone levels shift and her pelvic floor muscles may become more susceptible to injury.
Multiple sclerosis (MS): In the event that you have MS, you might encounter a deficiency of control of your bladder, prompting spillage issues.
Larger prostate: At the point when the prostate is bigger than typical, it can cause a few bladder control issues. You could likewise hear this condition called harmless prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH.
After prostate malignant growth medical procedure: The sphincter muscle may occasionally be injured during treatment for prostate disease, leading to pressure incontinence.
Side effects
Many individuals experience intermittent, minor holes in urine. Others might lose little to habitually direct measures of urine.
Key Measurements
- A quarter of Americans, or 33%, experience urinary incontinence.
- Around 33 million have overactive bladder (otherwise called OAB) addressing side effects of direness, recurrence, and regardless of urge incontinence.
- Concentrates on showing that numerous things increment risk.
- For example, maturing is connected to urinary incontinence.
- Pregnancy, conveyance, and the number of kids increase the risk in ladies.
- Women who have had a child have more elevated paces of urinary incontinence.
- The risk increases with the number of youngsters.
- This is valid for cesarean segment (c-area) and vaginal conveyance.
- Women who develop urine incontinence during pregnancy are likely to experience it shortly after.
- Women who have had menopause may develop urine incontinence.
- This may be because of the decrease in estrogen (the female sex chemical).
- Taking estrogen, in any case, has not been displayed to help urinary incontinence.
- Gentlemen who have prostate problems are similarly at expanded risk.
- Urinary incontinence has been linked to a few prescription drugs, and some uncommon medications make it worse.
- Proportions show that unfortunate in general well-being additionally increases risk.
- Diabetes, stroke, hypertension, and smoking are likewise connected.
- Urinary incontinence is more likely to occur in stout people. Reducing weight can lessen the negative effects of urine incontinence and help the bladder function better.
Risk factors
Age
The seriousness and prevalence of UI increase with age, but age alone is not a significant risk factor when controlling for co-morbidities.
Weight
This is a serious area of strength for an element of UI. Also, weight decrease is related to progress or goal of side effects, especially with stress urinary incontinence.
Method of conveyance
Ladies who have had a vaginal conveyance have an expanded part of UI, nonetheless, cesarean conveyance doesn’t safeguard ladies from UI.
Family ancestry
This might be a risk factor for UI, especially with ask incontinence and overactive bladder.
Other
Conditions like diabetes, stroke, and sorrow are related to an expanded risk of UI
What happens regularly?
- The cerebrum and the bladder control urinary capability.
- The bladder stores urine until a person is prepared to exhaust it.
- The muscles in the lower portion of the pelvis hold the bladder setup.
- Especially, the smooth muscle of the bladder is loose.
- The bladder holds urine and is closed at one end to prevent leakage.
- The sphincter muscles are closed surrounding the urethra.
- The tube that produces the body’s pee is called the urethra.
- At the point when the sphincter muscles hold the urethra closed, urine doesn’t spill.
- When you are prepared to urinate, the mind conveys a message to the bladder.
- Then the bladder muscles contract. This allows the urine out via the urethra, the cylinder that conveys pee from the body. The sphincters extend up when the bladder contracts.
What are the types of urinary incontinence?
Incontinence of the bladder is not a disease. It is a result of numerous factors. Causes may differ among individuals. It isn’t inherited, though. Furthermore, it isn’t simply a typical piece of maturing.
The 4 categories are as follows:
Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI)
- SUI causes weak pelvic muscles, which allow urine to leak out.
- It is one of the most widely recognized kinds of urinary incontinence. It is normal in more seasoned ladies. It is less normal in men.
- When the pelvic floor muscles are stretched, SUI happens. The bladder has to do the real labor.
- Then the bladder spills.
- Releasing may occur with working out, strolling, bowing, lifting, or in any event, sniffling, and hacking.
- It tends to be a couple of drops of pee to a tablespoon or more. SUI can be gentle, moderate, or extreme.
- There are no FDA-supported medications to treat SUI yet, yet there are things you can do.
- Ways of overseeing SUI incorporate “Kegel” activities to strengthen the pelvic floor. Way of life changes, vaginal and urethral gadgets, cushions, and even a medical procedure are alternate ways of overseeing SUI.
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
- OAB is one more typical kind of urinary incontinence. Another name for it is “desperation” incontinence. In the United States, OAB affects more than 30% of males and 40% of women. It affects people’s lives.
- They might restrict exercise. They might fear they will out of nowhere urine when they aren’t close to a washroom.
- They may not have the option to get a decent night’s rest.
- Specific individuals have both SUI and OAB and this is identified as blended incontinence.
- With OAB, your mind advises your bladder to discharge – in any event, when it isn’t full.
- On the other hand, the bladder muscles are excessively dynamic.
- They contract (crush) to pass urine before your bladder is full.
- This drives the urge (need) to urine.
- The principal side effect of OAB is the unexpected desire to urine.
- You have zero control over or disregard this “must go” feeling.
- Another side effect is peeing commonly during the constant. OAB is almost certain in men with prostate issues and ladies after menopause.
- It is brought about by numerous things. Indeed, even eating routines can influence OAB.
- There are various medicines.
- They include a way of life changes, sedatives that loosen up the bladder muscle, or medical procedures. Certain individuals have both SUI and OAB.
Mixed Incontinence (SUI and OAB)
Certain individuals spill pee with movement (SUI) and frequently want to pee (OAB). This is blended incontinence. The individual has both SUI and OAB.
Overflow Incontinence
- With overflow incontinence, the body makes more pee than the bladder can hold or the bladder is full and can’t void in this manner making it spill pee.
- Furthermore, there might be something impeding the stream or the bladder muscle may not agree (press) as it ought to.
- One side effect is successive urine of a limited quantity. Another side effect is a consistent trickle, called “spilling.”
- This sort of urinary incontinence is uncommon in ladies. It is more considered normal in men who have prostate issues or have had prostate medical procedures.
Side effects of specific kinds
These are the side effects for each:
Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI)
- With SUI, powerless pelvic muscles let pee escape.
- It is one of the most widely recognized kinds of urinary incontinence. It is normal in more seasoned ladies. It is less normal in men.
- SUI occurs when the pelvic floor muscles have extended. Actual work comes down on the bladder.
- Then the bladder spills.
- Releasing may occur with working out, strolling, bowing, lifting, or in any event, sniffling, and hacking.
- It tends to be a couple of drops of pee to a tablespoon or more. SUI can be gentle, moderate, or extreme.
- The critical side effect of SUI is spilling when you are stressed.
- The movement and measure of spilling rely heavily on how extreme the SUI is.
overactive bladder (OAB)
- The fundamental side effect of OAB is an unexpected, compelling impulse to urine that you have zero control over.
- It’s possible that the tendency will cause your bladder to leak.
Mixed incontinence (SUI and OAB)
- The side effects of blended incontinence incorporate releasing an unexpected, compelling impulse to urine.
- Mixed incontinence is the point at which you have more than one sort of incontinence.
- Most frequently, individuals with mixed incontinence have SUI and OAB.
OIverflow Incontinence
- Regular little urine and consistent spilling are the fundamental side effects of overflow incontinence.
- The bladder can’t void. Side effects happen when the bladder is full.
- This type is once in a while in ladies nonetheless, dropped bladders, earlier bladder medical procedures, or diabetes might influence this.
- It is more considered normal in men with a background marked by prostate issues or medical procedures.
Diagnosis and Tests
Often, the decision-making process for incontinence will start with a conversation about your clinical background and problems with bladder control with your healthcare provider. Your provider may ask questions to you such as:
- How frequently do you urine?
- Do you spill urine between excursions to the latrine, how frequently does this occur and how much urine do you release each time?
- How long have you been encountering incontinence?
- These inquiries can assist your supplier with sorting out an example of your spillage, which frequently focuses on a particular kind of incontinence.
- It’s critical to include a complete list of all of your medications when providing your supplier with information about your clinical history, as several medications have the potential to cause incontinence.
- Your physician will likewise get some information about any past pregnancies and the subtleties around every conveyance.
There are additionally a few explicit tests that your supplier could do to analyze incontinence, including:
Physical test:
Your physician will ordinarily do an actual test right off the bat in the finding system. During this test, your physician will search for any actual explanation that could be causing your incontinence. This could incorporate doing a pelvic test if you’re a lady or looking at the size of a man’s prostate.
Urine samples:
Your supplier might take tests of your urine to test for contamination or blood. Testing your urine is likewise called urinalysis.
An ultrasound of your bladder:
An ultrasound is an easy test that uses sound waves to make a picture of your interior organs.
This imaging test will allow your supplier to take a gander at the items in your bladder and survey the ability to purge your bladder painlessly.
Stress test:
Your provider will ask you to hack throughout this test in order to see if any pee leaks from this action. In the unlikely event that you have seen spillage during other exercises, including sprinting or jumping, your provider may ask you to repeat those exercises in order to determine whether you are experiencing spillage.
Cystoscopy:
A cystoscopy is a medical procedure that is commonly used to diagnose, monitor, and treat conditions that affect the bladder and urethra. Your doctor may recommend a cystoscopy when investigating the causes of certain signs and symptoms such as blood in the urine, incontinence, overactive bladder, and painful urination.
Urodynamic testing:
This testing includes a few tests that check how much your bladder can hold and how well your urethral sphincter muscle (the muscle that holds your urethra shut) is working. One piece of this testing might include inserting a cylinder into your bladder that will top the bladder off with liquid. This checks how much your bladder can hold.
Pad test:
Your supplier may give you a pad to wear to absorb any urine leakage during the test. Toward the end of the test, this pad will measure the amount of urine you lost.
While at home, your supplier could suggest you monitor any spillage in a diary for a couple of days. By recording how frequently you experience incontinence issues over the range of a couple of days, your supplier could recognize an example. This can truly assist in the determination of handling. Try to record how frequently you want to urine, the amount you can go each time assuming you spill between outings to the restroom, and any exercises you may be doing when you spill urine. You’ll then, at that point, carry this diary with you to your arrangement and discuss it with your supplier.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Capability and Strength
Altered Oxford reviewing framework:
0 – no compression
1 – glint
2 – frail press, no lift
3 – fair press, unequivocal lift
4 – great press with a lift
5 – solid press with a lift
Palpation
Palpation of the pelvic floor muscles per the vagina in women and per the rectum in male patients.
Wonderful mental helper evaluation:
P – power, may utilize the Changed Oxford reviewing scale
E – perseverance, the time (in a flash) that the greatest withdrawal can be maintained
R – redundancy, the number of redundancies of a greatest willful constriction
F – quick constrictions, the quantity of quick (one second) greatest withdrawals
ECT – each constriction planned, reminds the advisor to persistently over-burden the muscle action to reinforce.
Treatment
Drugs to treat incontinence
There are quite some rare medications that may decrease leakage. Some of these drugs stabilize the muscle squeezes that cause problems with an overactive bladder. Other medications do the contrasting thing — relaxing muscles to permit the bladder to empty fully. Hormone replacement therapies — usually concerning replacing estrogen that’s reduced during menopause — can also help restore normal bladder function.
Generally speaking, medications can support the bladder’s normal functionality quite well. The doctor will carefully select a medication that meets the specific needs. Often, the pharmacist will begin by giving you a small amount of the prescription and then gradually increase it. This is done in an effort to reduce the risk of unintentional effects and to track how effectively the medication is working to treat your incontinence.
Normal prescriptions that can be utilized to treat incontinence include:
Oxybutynin (Ditropan®), oxybutynin XL (Ditropan XL®), oxybutynin TDDS (Oxytrol®).
Tolterodine (Detrol®).
Solifenacin (Vesicare®).
Fesoterodine (Toviaz®).
Darifenacin (Enablex®).
Trospium (Sanctura XR®).
Upper medicine — Imipramine (Norfranil, Tipramine, Trofranil).
Mirabegron (Myrbetriq®).
Vaginal supplement:
There are over-the-counter devices that can pack the urethra and help women with pressure incontinence. These devices can be placed in the vagina.
Devices to contain urinary
There are many devices and products designed to collect and contain urine. They support the management of incontinence and urine retention. Urinary retention refers to a situation where the bladder doesn’t empty. Urinary incontinence (UI) is when urine leakage occurs that you have no control over.
When all is said and done, devices and objects can benefit people. For specific people, they are the best way to oversee bladder issues. These gadgets can likewise give more established and debilitated people more opportunities.
Indwelling Catheters
- A catheter is an adaptable device put in your bladder. An “inhabiting” catheter stays in your bladder the entire constantly.
- There are two kinds of inhabiting catheters. Inhabiting “Foley” catheters are put in your urethra.
- Inhabiting “suprapubic” catheters go over your pubic bone through a little careful cut in the gut. With the two kinds, an inflatable holds the cylinder in your bladder.
- The two of them likewise channel urine into a pack outside the body.
- A physician will put the Foley catheter in your urethra. When used for an extended period, the catheter can be monitored by home care personnel.
- A urologist puts the suprapubic catheter with a minor medical procedure.
- A Foley catheter ought to be utilized for under 2 years.
- On the off chance that you want an inhabiting catheter for a more extended timeframe, you ought to consider a suprapubic catheter.
- Since the suprapubic catheter is just in the bladder, there is less form of microbes developing (since it is away from the vagina and rectum).
- That implies less gamble of urinary lot diseases, particularly in ladies.
- Both Foley and suprapubic catheters should be supplanted with another catheter something like once consistently.
- This additionally brings down the risk of disease.
- The two catheters can cause difficulties whenever utilized for quite a while. Bladder, gonad (guys), kidney contaminations, bladder stones, and bladder disease can happen.
- Foley catheters can cause long-lasting harm to the urethra.
- Foley and suprapubic catheters ought to be taped or tied to the upper thigh or lower gut.
- This brings down the opportunity of injury assuming that the catheter is pulled incidentally.
- Catheters are produced using plastic with Teflon covering or silicone.
- The decision relies upon an individual’s sensitivities and the medical care supplier’s inclination.
- A few catheters are covered with anti-toxins to forestall disease.
- There is banter about whether this works.
- Inhabiting catheters differ in shape, tube size, and tip.
- They are measured utilizing the French (Fr) scale. Size 14 Fr is the most widely recognized size.
- After the catheter is embedded, an inflatable swells.
- This holds the catheter back from dropping out.
- The inflatable is typically loaded up with around 2 teaspoons of sterile water.
External Collecting Systems
- For men, there are outer gathering frameworks called condoms or Texas catheters.
- These unique condoms are turned over the penis. They are kept set up by glue or lashes.
- The condoms have openings at the tip. A cylinder goes from the opening to a waste sack.
- Urine from incontinence gathers in the waste pack. More up-to-date condoms are normally silicone.
- They come in sizes, with an estimating guide.
- This gadget might be difficult to utilize on the off chance that you generally disapprove of finger skill.
- A parental figure or relative would have to apply the condom catheter.
- Cement pockets might be better for men whose penis has withdrawn (stepped back).
- An outside assortment gadget for ladies channels pees from a pocket through a cylinder to a gathering gadget. These should be adhered to beyond the labia.
- They are seldom utilized as the labia don’t frame a decent water-tight seal, so pee spills.
Urine Drainage Bags
- Both inhabiting and outer gathering devices are associated with waste packs.
- They collect urine that comes out of the bladder.
- Drainage bags come in various sizes.
- Short-term packs hold 1500 to 2000 milliliters (1.5 to 2.0 liters) of pee.
- These are enormous and can’t be covered up.
- A leg pack is a more modest waste sack. It holds 500 to 800 milliliters.
- It permits more development opportunities. Usually, it’s hidden beneath clothing.
- It very well may be tied to the thigh or calf.
- Another sort called the Midsection Pack, is tied to the stomach. Waste sacks work by gravity.
- So they ought to be lashed someplace underneath the bladder.
- While picking a pack, ensure the tie isn’t excessively prohibitive or tight.
- The valve that channels urine from the pack ought to be not difficult to open.
- Drainage bags can be cleaned and freshened up.
- Absorb for 20 minutes an answer of two sections vinegar and three sections water.
Catheters for Intermittent Catheterization (IC)
- Irregular catheterization is likewise called “in and out” catheterization. It is additionally called “clean discontinuous catheterization” (CIC). Since it is perfect you don’t require gloves and sterile readiness.
- The urethra is punctured three to five times a day with a catheter.
- After you emptied your bladder, you remove the catheter and dispose of it.
- You or a guardian can implant the catheter.
- You don’t need to wear it constantly. This brings down the opportunity of contamination.
- What’s more, these devices don’t have an inflatable like the inhabiting catheter.
- More seasoned people can perform CIC and ought to be on a normal timetable.
- How much pee in the bladder ought to be 15 ounces or less.
- Catheterization might be required four to five times each day.
- Most medical care protections and Federal medical insurance will pay for 4 catheters per day (120 every month).
- Most IC catheters are straight. Some (called Coudé catheters) have a bent tip.
- It could be simpler for a man to propel a bent tip past the prostate organ.
- The length of a catheter is six creeps for women and twelve crawls for men.
- You can get catheters and different supplies, like grease, bundled together.
- These bundles are useful assuming you want to utilize the catheter at work. Catheter supply organizations convey catheters and different supplies via mail.
Absorbent Products
- Absorbent items, for example, cushions and grown-up diapers are accessible for incontinence.
- There are many plans. A few cushions or undies liners have cement strips that join to clothing.
- There are likewise underpants, grown-up briefs, and defensive clothing.
- There are monitors and dribble assortment pockets for men.
- These items all retain pee spillage and they assist with shielding the skin from pee likewise, they hold pee back from wetting clothing.
- Absorbent products can be expendable or reusable.
- Absorbent incontinence items are intended to assimilate and hold urine.
- The purpose of ladylike cleaning cushions is to absorb blood, not pee.
- The benefit of utilizing incontinence items is that the surface region is nearest to the urethral opening, which is over the vaginal opening.
- The absorbent are retentive and they cause less skin bothering and less rashes.
- Reusable cushions are made of material with a rayon or polyester center and assist pee with retaining.
- While picking an item, think about convenience.
- Consider whether you want to take off external attire to change the devices.
- Consider the materials, the liner, and the permeability as well.
- For instance, outside covers made of plastic might disturb the skin.
- Cost is likewise a worry for some individuals.
Toilet Substitutes
- Convenient gadgets can be extremely useful on the off chance that you can’t get to an ordinary latrine. These devices incorporate cabinet seats or bedside chests. There are additional chamber pots and urinals.
- A bedside cabinet is put near the bed. It is not difficult to use around evening time or on the house floor with no washroom. While picking a chest you are urged to consider its level and weight, that it is natural to purge, seat type, and cost. A delicate surface might be more agreeable.
- There are likewise raised seats (latrine raisers) that can help you get all over from a customary latrine all alone.
- Chamber pots are generally not extremely compelling or agreeable. If you are recovering from medical treatment and are unable to move, an exceptional break container may be of assistance.
- Urinals (plastic container-type gadgets) are valuable if you can’t move without any problem. You pee into these gadgets straightforwardly.
- They can help when bathrooms are not available.
- They are additionally valuable while driving.
- Furthermore, they are a choice if you are bound to a bed or seat.
- Most urinals, for example, the more current spill-confirmation ones, are simpler for men to utilize.
- Urinals for ladies are not as simple to utilize.
External management
Skin health management Items
Assuming you are utilizing incontinence gadgets or items, you might require healthy skin. Over the long run, urine leakage can cause skin breakdown, rash, and redness. Pee on your skin can prompt microorganism development and disease.
Cleansers, skin items, effective antimicrobials, chemicals, and skin hindrance items can all assistance whenever utilized appropriately. Regular washing with cleanser and water can dry out your skin. Flushes or cleaning agents made to eliminate pee might be better for washing the skin around the urethra.
Expendable wipes or wash garments as opposed to toilet paper might assist with keeping your skin sound. Saturating creams, salves, or glues keep the skin clammy. They seal in or add dampness. Boundary items safeguard the skin from contact with dampness. They lower grinding from retentive incontinence items.
Way of life changes to oversee incontinence
- Now and again, there are changes to your daily existence that can help your incontinence.
- These progressions frequently incorporate activities you can do to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, changes to your ordinary propensities, and a better eating routine.
- Certain individuals notice enhancements by rolling out these improvements at home and needn’t bother with extra treatment.
- Converse with your medical services supplier about these home therapy choices for incontinence before beginning any of them.
- You probably won’t have the option to treat a wide range of incontinence with these way of life changes.
- Your supplier could likewise make definite ideas to you about the best way of life changes to attempt given your incontinence analysis.
Way of life changes to assist with further developing incontinence can include:
- Completing your bladder’s course on a regular schedule This practice of using the restroom on a regular schedule rather than relying on the need to pass is also known as planned voidings.
- Discharging your bladder before proactive tasks On the off chance that you want to practice or do actual work, plan to exhaust your bladder before the movement begins to keep away from spillage.
- Trying not to lift weighty items On the off chance that you want to move something huge, get an extra individual to help you.
- Doing normal Kegel activities to assist with reinforcing your pelvic floor muscles.
- Trying not to drink caffeine or a lot of liquids before gazing at an action. If you experience continuous pee and spillage around evening time, you could likewise need to try not to drink refreshments just before bed.
- Wearing cushions and items that are intended to get any spilled pee can likewise be a helpful method for overseeing incontinence.
- These items can as a rule be worn under your garments without anybody seeing and they give consolation that you won’t encounter urine spilling through your garments.
- Rehearsing bladder preparation to help with loosening up how much time between each excursion to the washroom.
- The objective in bladder preparation is to attempt to stand by somewhat longer between urine each opportunity to develop fortitude.
- Keeping a sound body weight. Having an abundance of body weight can be one reason for incontinence. By eating a sound eating routine and working out, you can decrease the gamble of incontinence.
- There are likewise gadgets that you can use at home to assist with incontinence. One over-the-counter gadget that you can utilize is a:
Methods and medical procedures to treat incontinence-
Assuming other harmless treatment choices have neglected to treat your incontinence, there are a few techniques that your supplier could propose. These methods include simple infusions as well as more complex medical treatments. Your provider will assess which procedure is ideal for you based on the type of incontinence you have and any side effects.
Methods to treat incontinence can include:
Bulking agents: This treatment choice is an infusion that is commonly utilized in ladies with stress incontinence. A long-lasting substance is infused into the coating of your urethra to assist with expanding the size of the urethra’s covering.
Botulinum poison infusions (Botox®): You could consider Botox® a restorative treatment, yet it can likewise be utilized to loosen up muscles in your body. Your supplier could infuse Botox® into your bladder to assist with loosening up the muscles — assisting with ask incontinence. This treatment isn’t super durable and should be rehashed over the long run.
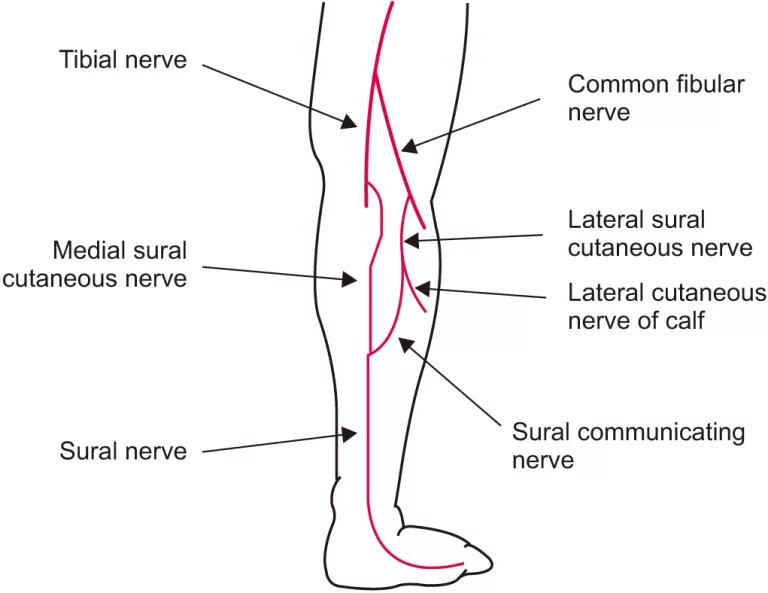
Neuromodulation gadgets: Pacemakers that invigorate the nerves to the bladder to further develop control can be embedded. Moreover, a nerve close to your lower leg can be invigorated to accomplish better bladder control.
Sling techniques: There are sling methods to treat incontinence for all kinds of people. In ladies, either a manufactured material or your very own segment tissue is normally used to help the urethral channel.
Counterfeit urethral sphincter: This is a gadget that is utilized in men with stress incontinence and is put to close the urethra while not peeing. It’s ordinarily utilized for spillage after a prostate malignant growth medical procedure.
Who gets incontinence?
Incontinence can happen to anybody. Be that as it may, it’s more considered normal in specific gatherings and at specific times in your day-to-day existence. Incontinence is significantly more typical in ladies than in men. This is much of the time connected with pregnancy, labor, and menopause.
Over time, all of these interactions may weaken a woman’s pelvic support muscles.
As you age, you will also undoubtedly have incontinence. Over time, the muscles that support your pelvic organs may become more susceptible, which may lead to spilling problems.
Physiotherapy treatment
Pelvic Floor Muscle Preparation (PFMT)
Kegel
The Kegel practice is presumably the most well-realized pelvic floor workout. It comprises an isometric constriction of the pelvic floor muscles.
To do a Kegel workout, follow these means:
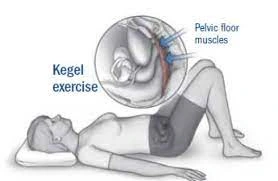
- Begin by holding your pelvic floor muscles in for 5 seconds. Keeping breathing during this contraction is significant.
- In the wake of holding for 5 seconds, gradually and totally loosen up your muscles for 5 seconds.
- Rehash this cycle multiple times, no less than multiple times consistently.
- The pelvic floor muscles might get exhausted during this activity.
- On the off chance that this occurs, pause and do the activity sometime in the future.
- Try not to select the stomach, adductors, or butt cheek muscles while doing this activity.
- Activities can be advanced by expanding the time you hold and rest your pelvic floor muscles.
- Begin with 5 seconds, and gradually develop the time every week until you’re holding in and resting for 10 seconds.
Backward Kegel
Exhausted pelvic floor muscles and imbalanced intra-stomach tensions can prompt hypertonic pelvic floor muscles.
The Opposite Kegel is a method to carefully loosen up pelvic floor muscles. The patient concentrates on the pelvic floor muscles and afterward deliberately attempts to loosen up them. The sensation of dropping the pelvic floor is like the snapshot of alleviation when you have arrived at the washroom; at the point when you pee or have defecation, You release the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) by first lowering your pelvic floor.
To play out a reverse Kegel, follow these means:
- Begin by tenderly getting the pelvic floor to feel what fixing the muscles feels like.
- Unwind, and discharge the strain to feel the distinction between pressure and unwinding.
- Then, attempt to picture that the muscles between the pubic bone and tailbone stretch by delicately moving the pubic bone towards the roof (assuming you are lying on your back), and tenderly moving your tailbone towards the surface you are lying on.
- Envision the pelvic floor muscles lengthening, creating more space.
- During the above activity, make certain to typically relax.
- As you play out a reverse Kegel, be certain you keep your pelvis spine still.
- These can be acted in sitting and remaining too.
Cross over Abdominis Initiation
- It has been demonstrated that activating the transversus abdominis (TrA) can affect the pelvic floor muscles and vice versa. Without explicitly preparing the pelvic floor muscular structure, TrA enactment also stimulates increased pelvic floor muscle activity.
- Cross-over abdominis initiation can be advanced because of body position, expanding hold times, and expanding sets. Enactment can initially start in low-load body positions, including prostrate, quadruped, sitting, or standing.
- TrA initiation can be tested by adding arm or potentially leg developments and developments like strolling or adjusting on a slant board. The board is an incredible activity for TrA.
Biofeedback
- Biofeedback is an instrument-helped mediation that permits patients to notice constant pelvic floor muscle movement.
- Biofeedback can be utilized to reinforce powerless pelvic floor muscles and to loosen up hypertonic pelvic floor muscles.
- Similar to the Kegel exercise, biofeedback techniques involve switching up periods of rest and withdrawal.
- Biofeedback mediations might further develop responsiveness and neuromuscular control of the pelvic floor muscles.
- While utilizing biofeedback with a patient, be certain you measure standard pelvic floor muscle movement before starting the activity.
Hypopressive exercises

- The stomach hypopressive approach can help women who have recently given birth heal from pelvic floor disruption and prevent confusion like UI and prolapse.
- The strategy includes breathing, given stomach termination, apnoea, and height of the stomach, combined with postural and dynamic muscle-extending practices.
- Hypopressive activities (HE) have been utilized in the treatment of PFM dysfunctions, like urinary incontinence.
- Hypopressive activities are postural activities that loosen up the stomach, decrease intra-stomach pressure, and initiate stomach and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) without intentional enactment.
- They can be acted in various positions like prostrate, sitting or standing, stooping, quadruped, and with differing places of arms and legs.
- This presentation is mixed with apnea (breath hold at end-lapse) while attracting their mid-region and opening their rib confine.
- The postural muscles, such as the deep abdominal and pelvic floor muscles, have been illustrated as being enacted by the ensuing tension changes.
- In every one of the hypopressive stances, patients play out the “hypopressive move,” as follows.
- Patients are asked to: Take full breaths; Breathe out breath totally (that activity hoists the stomach); Close their glottis; and afterward be approached to extend their rib enclosure to such an extent that, hypothetically, intra-stomach pressure drops.
- An 8-week of moderate activities showed a decline in pelvic floor problems related to side effects and further developed pelvic floor muscle contractility.
- Another review shows that PFMs, and stomach, gluteal, and adductor muscles are actuated during the HE move.
- As a result, it suggests HE only targets the deeper muscles. However, real advisors and other specialists involved in HE should be aware that the shallower stomach wall muscles—the rectus abdominis and outside angled—did not seem to alter during HE and would be addressed with appropriate exercises.
Pelvic Clock Exercise
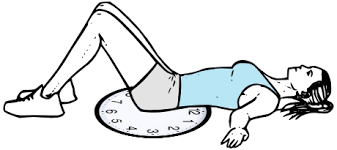
- Pelvic clock practices assist in creating proprioceptive mindfulness and pelvic development with controlling.
- Start with the bridging position and move your pelvis in the clockwise direction.
- Initially do it 10 times after that increase the count.
Bridge

- Lie on the floor with your back level against the ground and your knees bowed at a 90-degree point.
- Pushing through your heels, raise your hips off the ground by crushing your glutes, pelvic floor, and hamstrings.
- Stop for a couple of moments and return to the principal position.
Bird dog activity
This is the way to make it take place:
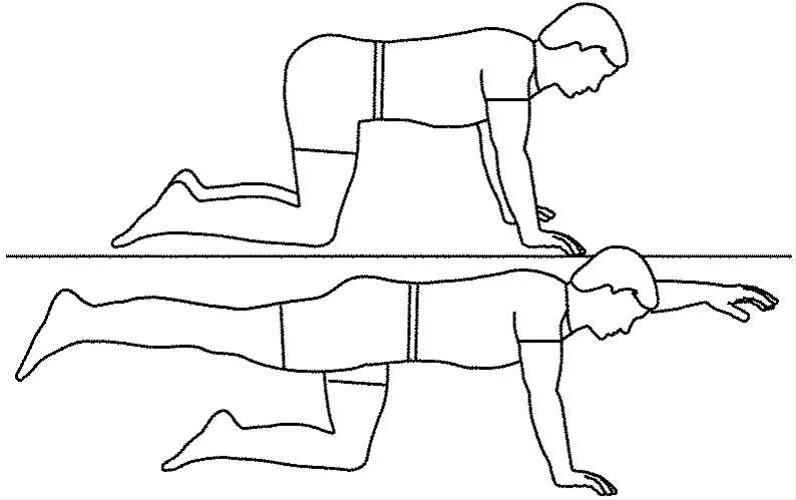
- Begin down on the ground in the tabletop position.
- Put the knees under the hips and your hands under the shoulders.
- Keep an unbiased spine by connecting with your stomach muscles.
- Draw your shoulder bones together.
- Raise your right arm and left leg, keeping your shoulders and hips lined up with the floor.
- Extend your neck and tuck your chin to look down.
- Stand firm on this footing for a couple of moments, then lower down to the beginning position.
- Raise your left arm and right leg, standing firm on this footing for a couple of moments.
- Get back to the beginning position. This is 1 round.
- Do 2 to 3 arrangements of 8 to 12 reiterations.
Side lunge
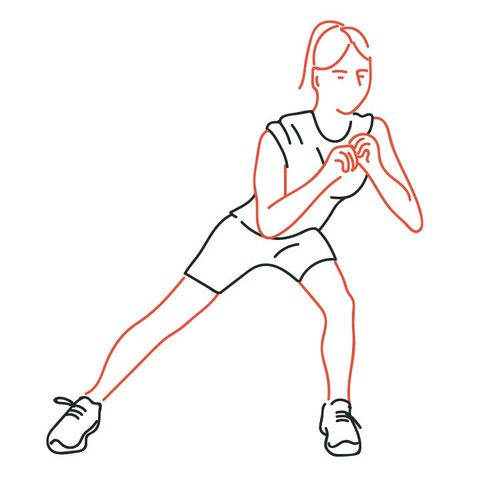
- Stand in great stance with your feet together, and your toes pointed forward.
- Make one major move to the side with your left leg.
- Drive once more into your left hip while keeping your right leg straight with your toes pointed forward.
- You urge to feel a stretch in your right crotch muscle.
- Push your passed by walking through the floor and return to the feet together position.
- Either substitute sides or do every one of the reps on one side and rehash on the other.
Deep squat

- A legitimate profound squat starts with your help base — your feet, which are ordinarily shoulder-width separated and level on the floor.
- In the meantime, your toes are either straight ahead or at a little, 7-degree toe-out position, your knees are straight, and your trunk is erect.
- Start by crouching as though you’re sitting in a seat. Your lower legs, knees, and hips will twist as one while your spine remains straight.
- As you lower, your knees will go ahead over your toes, and your hips will go in reverse to keep your focal point of gravity over your feet.
- Your feet urge to stay level on the ground during the whole development.
- Your trunk and pelvis will remain nonpartisan and adjusted as you twist at your hips.
- At the most reduced profundity, your pelvis will be in relative arrangement with your shins.
- Preferably, your pelvis will stay in an unbiased position, without tucking under or shifting in reverse.
- Your knees will remain in arrangement with your feet when seen from the front.
- At last, push through your feet with your weight focused simply before your lower legs and return to the beginning position.
Sitting hamstring
Mix to the front of your seat
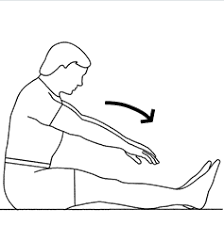
- Keeping your hands on the opposite leg, place one leg out before you
- Presently keep your leg straight and arch your foot towards the roof
- Guarantee you stay upstanding with a straight back and incline forward at the hips
- Maintain for the set time and change legs.
Hypopressive
Hypopressive breathing can be finished as follows:
- Take in regularly and discharge the air totally, until the midsection starts to contract all alone;
- ‘Contract’ your midsection by sucking the stomach muscles inwards towards the spine;
- Save this withdrawal for 10 to 20 seconds at first and, over the long run, continuously increment the compression time.
- Hold this as far as might be feasible without relaxing.
- Fill your lungs with air and unwind totally, getting back to your typical relaxing.
Hip flexor stretch
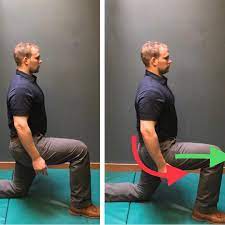
- Lie level on your back on a table or level seat, with your knees and lower legs draping off the edge of the table.
- Snatch your great leg at the knee, and pull that knee back toward your chest. …
- Maintain the stretch for no less than 10 to 20 seconds.
- Repeat 2 to multiple times.
Dead bug

- Allow your shoulders and lower back to fall weighty to the floor.
- Draw the shoulders down away from your ears.
- To get into the beginning position, lift your hands so your elbows are over your shoulders with your clenched hands pointing toward one another.
- Lift the legs so the knees are straight over the hips.
- On a breath out, gradually bring down your right arm and left leg until they’re simply over the floor.
- On a breathe in, take them back to the beginning position.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
- This is 1 rep.
Wall squat
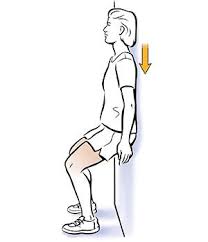
You can play out this exercise place you approach a level wall.
- Begin with your back against a wall with your feet shoulder width and around 2 feet from the wall.
- Draw in your stomach muscles and gradually slide your back down the wall until your thighs are lined up with the ground.
- Change your feet so your knees are straight over your lower legs (instead of over your toes).
- Keep your back level against the wall.
- Stand firm on the foothold for 20 to 60 seconds.
- Slide gradually back up the wall to a standing position.
- Rest for 30 seconds and rehash the activity multiple times. Increment your hold time in five-second additions as you increment your solidarity.
Stomach propping
Stage 1: Full breath in
Take a full breath in, growing your rib confine.
- Standing or resting, calmly inhale utilizing your stomach, ideally breathing through the nose, growing your rib confine.
- The volume of breath that you breathe in is reliant upon the movement you’re preparing for.
- For instance, while playing out an extreme focus development like a weighty deadlift, you’ll need to breathe in around 70% of your all-out lung limit.
- Be that as it may, if you’re doing a less extreme move, for example, twisting around to get your knapsack, you just have to breathe in a modest quantity of air, around 5 to 10 percent of your all-out lung limit.
- Additionally calls attention to that you commonly don’t need to intentionally contemplate propping your center to perform low-power developments as your body will do it consequently.
Step 2: Support the stomach muscles
Make an unbending nature by getting all your center muscles.
- To make an unbending nature in every one of the muscles that encompass your waist, pull your rib confine down. Consider it making a solid strong girdle, which safeguards your back and sensory system.
- Fix your waist by pulling your paunch button towards the spine.
- Make sure to inhale while doing this.
- Very much like the initial step, you’ll differ the power of your center withdrawal to the movement you’re doing.
- For instance, while playing out a weighty deadlift, you’ll need to get the center muscles maximally.
- However, if you’re getting a rucksack, you can do a low-level constriction like 5% of the compression power.
Adductor stretches
Side Leg Swings

- This stretch empowers more prominent dynamic development and extension of the hips than would ordinarily be conceivable. Dynamic stretches, like this one, require an elevated degree of equilibrium and coordination.
- Since it is a unique activity, it is brilliant for preparing the body to embrace activities or partake in athletic exercises.
- To start, track down a nearby wall or other tantamount help and stand tall and adjusted, upheld by the hands. Kick one leg as far to the side as you are capable, and subsequently, draw that equivalent leg across the midline of the body quite far.
- Continue stealing and adducting the leg in a melodic manner until ten repetitions are completed.
- Rehash on the opposite side.
Maintaining a taut center requires pulling in the abs and keeping the middle straight. Gently and deliberately move your legs by tensing and relaxing your muscles. Increasing the pace and allowing the leg to extend beyond its range of motion can result in a deeper stretch (however long simply a stretch feeling is felt in the agony free-roaming).
Malasana
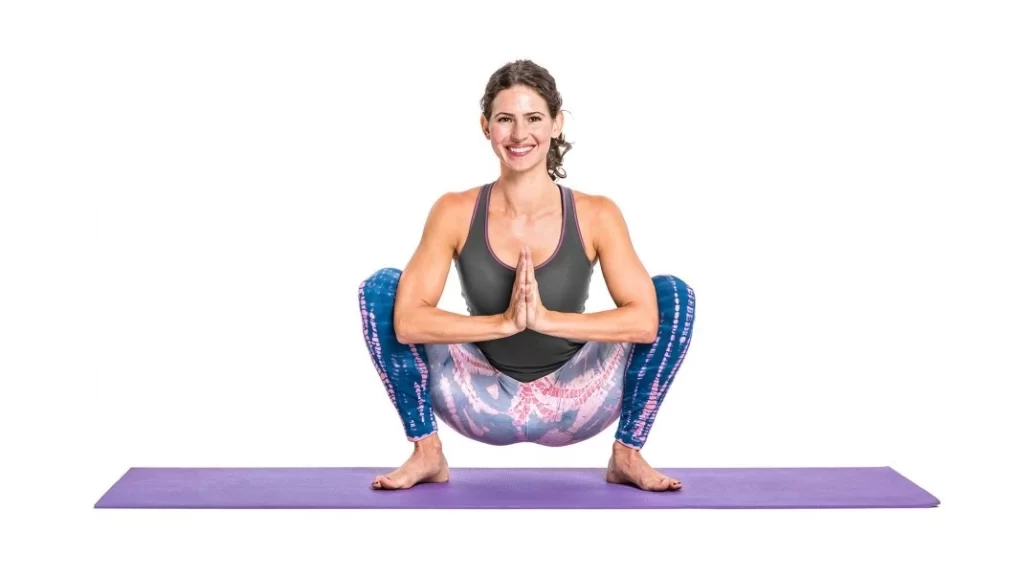

- Malasana proceeds as follows:
- Sit down on the mat or the ground with your feet marginally more extensive than your hips.
- Then, at that point, as displayed in the image, twist your knees into a squat position.
- Then, unite your hands and join your palms in the ‘Namaskar’ position.
- Tenderly press your elbows toward your internal thighs.
- Then, at that point, attempt to carry your hips nearer to the ground.
- Keep a straight spine all through the activity.
- Then, at that point, gradually come to the first position.
warrior 2

- Face the long side of your mat with your arms extended directly from your shoulders and your feet lined up with one another in a wide position.
- You need your lower legs roughly underneath your wrists.
- Turn your right foot and knee to confront the front of the mat.
- Point your left toes somewhat toward the upper left corner of the mat.
- Twist your right knee and stack it over your right lower leg.
- Appropriate your weight equally between the two legs.
- Push down through the external edge of your back foot.
- Hold the crown of the head stacked over the pelvis and the shoulders over the hips.
- Arrive at firmly through the two arms toward the front and back of the mat and turn your head to look past your right fingertips.
- Remain here for 5-10 breaths.
- To emerge from the posture, breathe out as you push down through your feet, then, at that point, breathe in and fix your legs. Return your feet to resemble confronting the left lengthy side of the mat.
- Rehash on the opposite side.
Utkatasana
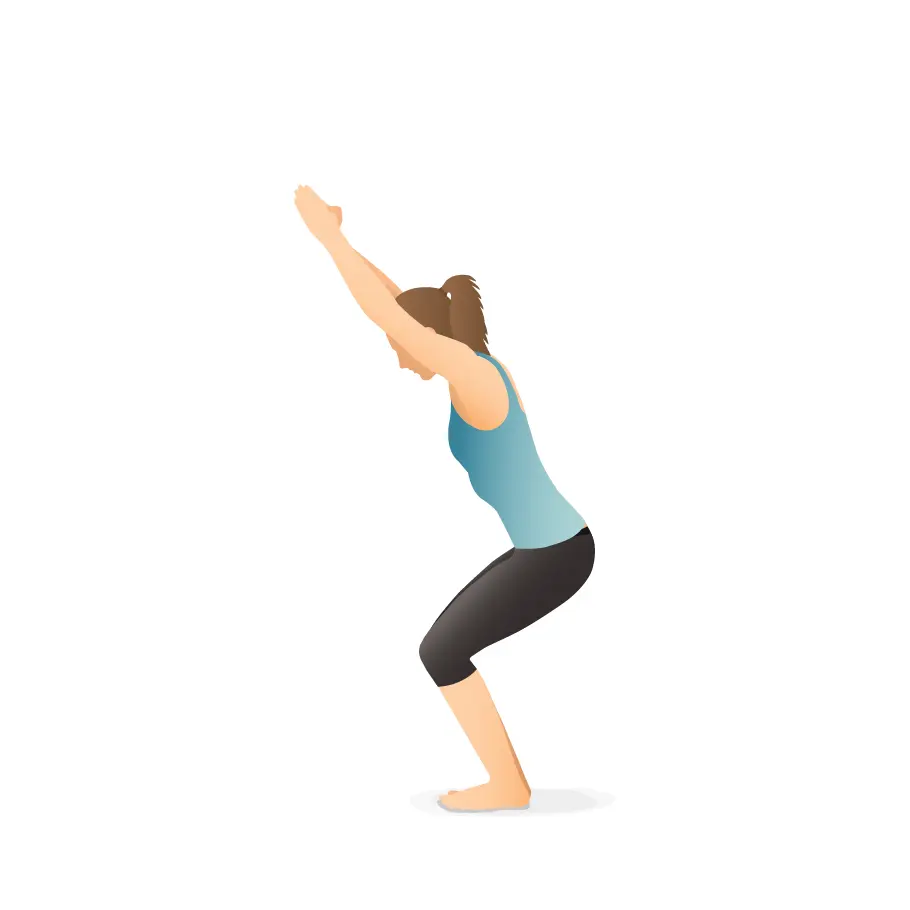

- Stand in Tadasana. Breathe in and raise your arms above so your biceps are only somewhat before your ears. Either keep the arms equal, palms confronting internally, or join the palms.
- Breathe out and twist your knees so your thighs are as lined up with the floor as could be expected. Until your front midsection structures roughly a right point with the highest points of your thighs, your knees will project out over your feet and your trunk will curve somewhat forward over your thighs.
- Maintain your internal thighs lined up with one another and press the tops of the thigh bones down toward your heels.
- Put pressure on the bones in your shoulders and back. To hold your lower back for a longer period of time, tilt your tailbone downward toward the floor and your pubis.
- Remain for 30 seconds to a moment. Fix your knees with an inward breath to emerge from this posture, lifting firmly through your arms. Breathe out and deliver your arms to your sides into Tadasana.
Bound Point Posture
- Take a staff posture to begin. Instead of sitting behind your sitting bones, sit directly on top of them.
- Your knees should be open to the sides as you twist them.
- The pelvic floor muscles are known as the levator ani, comprised of the pubococcygeus – puborectalis complex.
- Those muscles structure a sling around the anorectal intersection.
- They are comprised of both Kind I (slow-jerk) and Type II (quick-jerk) filaments.
- The larger part is Type I (around 70%) which offer supported help and are exhaustion safe.
- The leftover Kind II filaments give the speedy compressive powers important to go against spillage during expanded stomach pressure.
- A withdrawal of the pelvic floor muscles likewise causes a reflex restraint of the detrusor muscle.
- Patient-explicit preparation is important to guarantee a legitimate withdrawal of the pelvic floor muscle bunch.
- It is likewise vital for training both the quick and slow-jerk muscle strands.
- Similarly, when getting ready, keep in mind the guidelines for voluntary compressions both before and during an action that could result in incontinence, such as lifting, wheezing, and hacking.
- Patients are commonly prescribed to perform practices four to multiple times day to day.
- A non-controlled preliminary concentrating on the impacts of locally established pelvic floor muscle preparation and bladder preparation in ladies with urinary incontinence showed that joined pelvic floor muscle preparation and bladder preparation diminished the side effects and worked on personal satisfaction.
Social Treatment
- The focal point of social treatment is on the way of life changes, for example, liquid or diet the executives, weight control, and entrail guideline. Instruction about bladder aggravations, similar to caffeine, is a significant thought.
- Additionally, examining inside propensities to decide whether stoppage is an issue it is critical to teach the patient about abstaining from stressing.
- Training and clarification about ordinary lower urinary plot capability are additionally included.
- Patients are advised to understand the function of the pelvic floor muscles and the bladder.
- A randomized clinical preliminary inspected the impacts of a gathering controlled conduct treatment for urinary incontinence in more established ladies and viewed it as an unobtrusively successful treatment for lessening the side effects of urinary incontinence.
- The gathering conduct treatment incorporated a one-time, two-hour bladder wellbeing class, including composed material and a sound Disc.
Bladder Preparing
- The information gathered from the bladder diary is used to guide decision-making for bladder re-preparation, which includes avoiding a strategy that is crucial to increase the bladder’s capacity for people with recurrent problems.
- By having patients void on a schedule rather than out of sincerity, bladder preparation aims to interrupt the cycle. Promote the use of informed concealing techniques like unwinding and interruption.
- It means quite a bit to help the patient to get the pelvic floor to cause detrusor hindrance.
- Intentionally compressing the pelvic floor muscles helps to limit detrusor constrictions, aids in urethral constriction, and manages urine leakage.
FAQ
What is the primary driver of urinary incontinence?
Ask incontinence might be brought about by a minor condition, like contamination, or a more serious condition like a neurological issue or diabetes. Flood incontinence. You experience incessant or steady spilling of pee because of a bladder that doesn’t void totally.
Is there a method for fixing urinary incontinence?
Liquid and diet the executives, to recapture control of your bladder. a person may have to scale back or keep away from liquor, caffeine, or acidic food sources. Lessening fluid utilization, getting fitter, or expanding active work can facilitate the issue.
What is the best item for urinary incontinence?
The 7 Best Incontinence Stack of 2023, Tried and Investigated
Balance Most extreme Incontinence Cushions are our top pick since they’re amazingly permeable, have maximum inclusion, extraordinary smell control, and are HSA/FSA qualified. Michael Menna, DO, is as of now a going to crisis medication doctor at White Fields Emergency clinic in White Fields, New York, with almost 10 years of involvement.
What is the best treatment for incontinence?
The pelvic floor muscle works out. Your supplier or actual specialist can assist you with figuring out how to do Kegel activities to reinforce your pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. …
Liquid utilization. …
A solid way of life changes. …
Bladder preparing.
Might incontinence at any point be restored for all time?
Urinary incontinence can happen to anybody and the seriousness differs depending upon the age, cause, and kind of urinary incontinence. Most instances of urinary incontinence can be restored or controlled with fitting treatment.
References
- Urinary incontinence – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2023, February 9). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/symptoms-causes/syc-20352808
- Incontinence: Symptoms & Treatment – Urology Care Foundation. (n.d.). https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/u/urinary-incontinence
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Urinary Incontinence. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17596-urinary-incontinence
- Urinary Incontinence. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Urinary_Incontinence
- Pelvic Floor Exercises. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Pelvic_Floor_Exercises


7 Comments