Knee to Wall Test
Table of Contents
Introduction
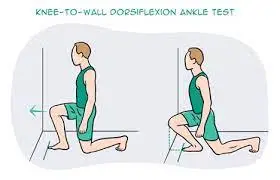
The Knee to Wall Test is a simple and useful way to measure your ankle dorsiflexion range of motion. It is a common test utilized by physical therapists and other healthcare specialists to assess ankle mobility and function.
Purpose
An evaluation of the dorsiflexion range of movement (DROM) at the ankle joint is done and using the weight-bearing lunge test (WBLT) or the dorsiflexion lunge test (DFT).
Dorsiflexion
The movement of elevating the foot upward and towards the shin is known as dorsiflexion. A good range of motion here will enable you to be stable and have weight-bearing over the entire foot, not just on the front section of it, making it a crucial action for weightlifting.
How to Perform the Test
Locate a wall and face it.
Put your right leg’s toes up on the wall and step back half a step with your left leg.
Aim to maintain your hips looking forward as you advance your knee towards the wall.
If you can accomplish this without difficulty, shift your foot 1-2 cm away from the wall and attempt again to touch your knee to the wall.
Continue until your knees can no longer touch the wall.
Keep track of the longest distance you can go.
Repeat the test with the other leg’s knee to the wall.
Results
- ankle mobility is low if less than 5 cm.
- Acceptable ankle movement is up to 10 cm.
- more than 10 cm: good ankle mobility
Keep your pelvis in position, your back and torso straight, and your heel on the ground while taking the measurement.
A measurement that is incorrect might be the consequence of not doing any of these things.
How to Continue If the Results Aren’t Ideal
Did your score go below 5 cm? Or did you notice a difference in your left and right ankles?
If so, it’s critical to develop stronger calf muscles.
Your calf muscles can get stronger and more flexible by performing exercises like box jumps and calf lifts on a step. Your calf muscles’ flexibility can also be increased by foam rolling them.
Evidence
Weight-bearing lunge test inter-rater reliability was R = 0.99 (95% CL: 0.97 – 0.99) for the distance measured. The measurement’s outstanding intra-rater reliability (ICC of 0.98 to 0.99) was also noted. There is also significant evidence that the weight-bearing lunge test’s intra-rater reliability (ICC = 0.65 – 0,99) and inter-rater reliability (ICC = 0.80 – 0.99) are both good.
This was shown in a recent systematic review of the reliability of the weight-bearing lunge test. It was proposed that the weight-bearing lunge test is a valid technique for determining ankle dorsiflexion range of motion since it yields repeatable results and exhibits acceptable responsiveness.
FAQ
What is the knee-to-wall test?
Washington Athletic Club’s “Knee to Wall” test
Kneel with your lead foot two to three inches from the wall in the lunch position. Check to check whether your front knee reaches the wall without your heel rising by pushing it forward. If you can touch your knee to the wall, try reversing your position until you can just about touch your knee to the wall.
What is the normal weight-bearing dorsiflexion?
Ankle joint dorsiflexion is typically within the range of 0 to 16.5 degrees while not bearing any weight and 7.1 to 34.7 degrees when doing so.
What does the lunge test do?
An evaluation of the dorsiflexion range of movement (DROM) at the ankle joint is done using the weight-bearing lunge test (WBLT) or the dorsiflexion lunge test (DFT).
What is the normal knee-to-wall measurement?
Test of Weight Bearing Lunge and Passive Range of Motion of the Ankle
As long as the patient can reach the wall with one knee while maintaining the other foot firmly planted on the ground, the distance can be increased. Normal ROM is defined as a wall distance of at least 5 inches (12.5 cm). As a general guideline, use one-hand breadth.
What is the dorsiflexion lunge test?
Test of Weight Bearing Lunge and Passive Range of Motion of the Ankle
Ankle dorsiflexion may be continuously measured with this technique. In a number of approaches published in the literature, the clinician measured the amount of dorsiflexion in either the front or rear limbs while the patient was lunging. The doctors either employed an inclinometer or a tape measure.
What is the dorsiflexion weight-bearing lunge test?
The weight-bearing lunge test (WBLT), which measures ankle dorsiflexion motion based on the movement of the tibia over the stationary foot towards a wall, was initially introduced by Bennel et al1. The great toe and the center of the calcaneus are measured along a floor-positioned tape.
What is the purpose of the lunge test?
The weight-bearing ankle dorsiflexion range, an essential component of gait, may be accurately measured by the Ankle Lunge Test (ALT) in both healthy ankles and a variety of musculoskeletal disorders.
Reference
- Knee to Wall Test. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Knee_to_Wall_Test
- Carreon, J., & Carreon, J. (2022, January 13). Knee-to-wall test – Washington Athletic Club. Washington Athletic Club. https://www.wac.net/wac-wire/knee-to-wall-test/
- Konor, M. M. (2012, June 1). RELIABILITY OF THREE MEASURES OF ANKLE DORSIFLEXION RANGE OF MOTION. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3362988/
- Easy Knee to Wall Test To Check Flexibility. (2021, June 23). PhysioFit Health. https://physiofithealth.com.au/knee-to-wall-test/
- Knee to Wall Test (Ankle Mobility). (n.d.). https://sportsphysio.ie/test/knee-to-wall-test-ankle-mobility-3650.html