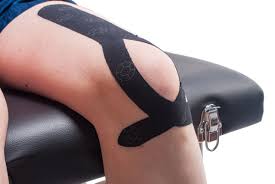
Kinesio taping vs Rigid taping
Kinesio taping vs Rigid taping is totally different technique from each other. Kinesio taping works totally different from rigid or athletic tape. The Kinesio tape is quite stretchy and is applied in a stretched position. Because it is stretchable.
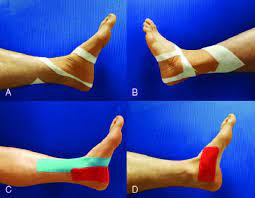
Rigid tapping is the most common method and has been used for a veritably long time in the sport. It’s used primarily on joints similar to ankles, knees, wrists, elbows, and shoulders. The function of the tape recording is to physically support the joint by limiting movement.
Table of Contents
Kinesio taping introduction:

Kinesio Taping Method is a therapeutic tool utilized by the rehabilitation specialists in all programs (paediatric,geriatric,orthopaedic,neurological, oncology and others) and levels of care (acute care, inpatient rehabilitation, outpatient, home care, and Day Rehab).
Dr. Kenzo Kase first presented the idea of using elastic tape to mimic the therapist’s hands in the1970s.
Since then it has become the modality used in pain management, soft tissue injury, tissue and joints malalignment, edema, and more.
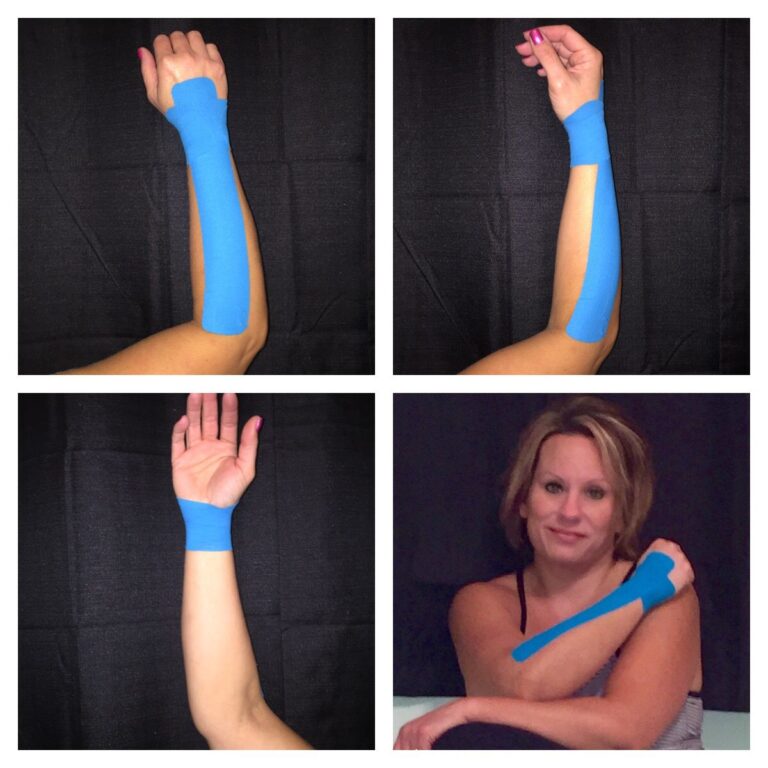
Kinesiological taping is a rehabilitative cum protective use of stretchable kinesiological tapes to reduce pain, enhance performance, prevent injuries, support the joint, reposition the structure as well as for fascial and ligamentous correction.
It facilitates the healing process while providing the full range of motion with support to the joint’s supportive structures and the mobilization effect.
Rigid taping introduction:
Rigid tapping has also known as athletic taping. Rigid tapping or Athletic taping is a temporary technique or an adjunct mechanism adopted as a measure of post-injury rehabilitation. Athletes mainly use it as a preventive measure to protect an existing injury.
The goals of the taping in sports are to restrict the motion of an injured joint, compress soft tissues to prevent swelling, support the anatomical structure involved in the injury, serve as a splint or to secure a splint, and secure the dressing and/or bandages, protect the injured part from re-injury and to protect the injured part while the healing process is under progress.
Rigid tapping or Athletic Taping has been at the forefront for a long time. It plays an important role in coping with an athlete’s post-injury conditions and performing in the field even before completing the rehabilitative recovery from injury.

Principle of kinesio taping:
- Protection of the skin-Check the skin sensitivity of the person to be taped that he is not allergic to the adhesive tape. Make sure there are no existing rash or broken skin in the area to b taped.
- Hair removal in the area to be taped-It is better if the hair is removed 12 hours prior to the tape application to reduce skin irritation.
- Clean and prepare the skin.
- The padding of the sensitive areas with adhesive tape.
Principles of rigid taping:
- Athletic taping is based on certain criteria or set rules, regulations, and guidelines which form the major “principles” based on which the experts carry out the process of taping on the injured part of the sports person.
- The general principle also includes a few criteria that practitioners should consider – skin preparation, the functional position of the body part to be taped, body mechanics of the practitioner, tape application, and removal of the tape post activity.
- Skin preparations that should be carried out before taping includes removal of hair, cleaning of skin, addressing of any lesions with necessary consultation, using adherents and lubricants, and erwraps, underpads, etc.
- We are placing the athlete in an appropriate position.
- A comfortable table height and position that is appropriate for the health care provider to minimize strain and fatigue.
- Type and width of the tape.
- To a dry and clean area and at body temperature.
- Immediately after cryotherapy or hydrotherapy is to be prevented.
- Areas subjected to friction blisters should be covered with protective pads or under-wraps.
- The tape is to be broken or torn in an extended or stretched fashion to avoid folded edges.
- Removal of tape should be done following the proper methods by using tape cutters and specially designed scissors.
- The skin has to be cleaned adequately of the tape residue.
- Any blisters or skin abrasions, if noted, should be taken care of immediately.
Aims of kinesio or rigid taping:
- Stabilize or support.
- Relieve pain by de-loading vulnerable or painful structures.
- Facilitate normal movement, muscle action, or postural patterns.
What are the Benefits of Kinesiology Taping?
- In kinesiology taping a thin, elasticized tape is used for many musculoskeletal injuries and physical dysfunctions that frequently present in a women’s health physiotherapy practice.
- The elastic properties of the tape on the skin promote a bunching-up action on the soft tissues immediately beneath the skin.
- This microscopic tissue lifting action can stimulate both lymphatic flow and blood flow, thereby reducing swelling, bruising, and pain.
- Kinesiology taping still provides support to injured tissues, but a certain amount of joint or muscle movement is allowed.
- The amount of tension and direction of pull on the tissues is determined by the Physiotherapist.
- A common presentation that benefits from kinesiology taping are correction of poor shoulder and shoulder blade posture, which is often seen with shoulder rotator cuff injury.
- The taping stimulates awareness by improving shoulder and shoulder blade movement in functional or sporting activities.
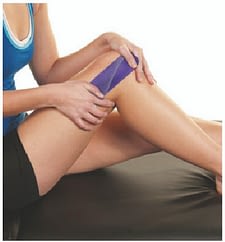
- Knee pain when walking can often be helped with a directional tape that enhances patellar/knee cap tracking and supports knee structures.
- Kinesiology tape can become wet in a shower or when swimming. This tape can be left on for 3 to 5 days.
What are the Benefits of Rigid Taping?
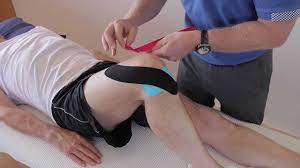
- The type of tape required for rigid tapping is non-elastic tape. The rigid tapping technique is used to restrict movement by providing very firm support.
- In the acute stage of healing, support of ligament sprains, muscle strains, joint instability, and inflammation is beneficial with this form of taping.
- The firm taping allows for very controlled movement of the joints, soft tissue, trunk, pelvis, or limb. When muscles are overworked, in pain and very tight, rigid taping can assist the muscles to rest and become less painful.
- One example of joint instability and painful muscles in pregnancy that is commonly seen in Physiotherapy for Women is pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain.
- A specific rigid taping approach to the pelvis and sacroiliac joints can enable pregnant women to improve their walking by decreasing limping and pain.
- Acute low back pain presenting with inflammation and trigger point tight spinal muscles will often benefit from rigid taping for 2-3 days.
- A pre-taping under wrap can be beneficial when skin is hypersensitive to the adhesive on the rigid tape.
Indications of Kinesio taping:
- Muscle injury
- Muscle tension
- Joint complaints
- General and non-specific musculoskeletal pain
- Irritations of tendon insertions
- Ligament injuries
- Arthrosis
- Sports injuries
- Back pain
- Poor/incorrect posture
- Lymphedema
- Bruising
- Stabilization of joints
- Injury prevention
- Fascia corrections
- Scar treatment
- Blister prevention
Indications of rigid taping:
- Rigid tape can be best used by Physiotherapists to Relieve your pain
- Improve joint stability
- Enhance athlete confidence
- Reduce injury recurrence
- Prevent injury
- Reduce strain on injured or vulnerable tissues
- Correct faulty biomechanics
- Inhibit muscle action
- Facilitate muscle action
- Compress in the presence of edema or lymphatic drainage
Rigid Taping Vs Kinesio Taping
| No | Kinesio Taping | Rigid Taping | |
| 1 | Kinesio taping is also called elastic taping. | Rigid taping is also called athletic taping. | |
| 2 | it’s stretchable. | not stretchable. | |
| 3 | Pre-injury rehabilitation. | post-injury rehabilitation. | |
| 3 | It allows joint movement. | Restrict the joint’s movement. | |
| 4 | This tape can be left on 3 to 5 days. | This tape can be left on 2 to 3 days. | |
| 5 | Provides support to injured tissues. | Support of ligament sprains, muscle strains | |
| 6 | Kinesio Tape is used for muscles and joints. | rigid taping is used for joints such as ankles and shoulders to provide added support. | |
| 7 | Kinesio tape comes in a wide variety of colors. | Rigid tape comes in only one color. | |
| 8 | Reduce inflammation. | It does not reduce inflammation. | |
| 9 | You can wear kinesiology tape during intense exercise. | You can not wear rigid taping during intense exercise. | |
| 10 | cheaper | more expensive |
Contraindication of Kinesio or rigid taping:
Severe Antipathetic responses to the tape recording kinesiology or rigid tape recording adhere to your skin. However, you should avoid victimization the tape recording, If you have a history of severe acuity to bonds. Typically, kinesiology or rigid tape recording is worn throughout the athletic activity, but it can also be worn for many days, and placing your skin in contact with adhesives for an extended period of time can lead to serious antipathetic responses.
Open injuries If you have an open wound or incision that is not absolutely for numerous, do not use physiology tape recording. The tape recording may manufacture a state of affairs wherever microorganism is introduced into the crack.
Presence of deep tone occlusion( DVT) A DVT could be blood in one of the deep modes of the arm or leg. victimization physiology tape recording close to the DVT will increase quality and blood inflow. this might cause the clot to become dislodged and will place you in peril of an embolism, which can be fatal.
Infection If you’re showing signs of infection, kinesiology tape recording shouldn’t be used, as it might worsen your condition.
Altered sensation If you’ve got an uncontrolled polygenic disease, you will suffer from peripheral pathology, a condition wherever you will have altered sensation in your legs or arms. physiology tape recording shouldn’t be used if you have the polygenic disease, since you may not know if the tape recording is inflicting a response or a problem with your skin. other conditions that cause sensation loss, like strokes, may also be contraindicated for an equivalent reason.
Active cancer If you’re currently undergoing treatment for cancer, you should avoid using kinesiology tape recording, since it’s allowed the tape recording to increase rotation, and increasing blood inflow and nutrition to a cancerous lesion may be dangerous.
Functions of kinesiology tape:
kinesiology tape to provide outstanding therapeutic benefits in the areas of recovery and rehabilitation. Because it increases both blood flow and lymphatic drainage, a kinesiology tape application can rapidly relieve swelling and inflammation, as well as accelerate the healing process.
Functions of rigid tape:
The main function of regular sports tape is to provide support and stability to an injured joint or muscle group by immobilizing it.
This would be the taping method of choice in cases of severe injury, where any movement of the injured area could result in additional damage.
The elastic properties of kinesiology tape make it unsuitable in situations where extreme support and stabilization are required.
Benefits of Kinesio taping:
The goals of kinesiology taping are to improve circulation, support muscles, foster healing, and help prevent injury or further injury.
Kinesio tape was originally developed to speed up the recovery time for athletes with injured or overused muscles.
Muscles lose their elasticity when they are injured or overused, and this is what can result in such long recovery times for seemingly small issues.
Many treatments for injuries focus on returning the muscle to its natural shape and position, but this can restrict the movement of the injured body part, which leads to stiffness and slows down recovery time.
By mimicking our muscles’ elasticity, taping can have the opposite effect and actually encourage our muscles to heal faster.
It does this in a number of ways:
- Support: Taping can be used to give support to muscles that have been injured or overused, not only relieving some of the immediate pain but also taking stress off that muscle and allowing for faster recovery.
- Adhesive: The adhesive for these tapes is far more complicated than the kind you would find on an everyday plaster.
- In order for these tapes to work as effectively as possible, it is crucial that they stay in one place.
- The glue used on these tapes will ensure that they do not move, stay completely firmly on the body for days, and lift up the skin underneath for breathability.
- Healing: Other than taking stress off and relieving the pain of an injured muscle, taping is designed to encourage lymphatic flow.
- The lymph system is the system through which a clear liquid (lymph) flows around the body.
- Lymph carries white blood cells, which fight infection, but also take care of any waste, dead cells, etc that may be found in the body.
- By encouraging lymphatic flow, recovery time is greatly reduced.
- Encouraging better movement: The way we use our bodies is not always the best way to use them. For example, poor sleeping posture can lead to chronic pain.
- Similarly, if we learn or train to use certain body parts in certain ways, this can become constricting.
- Taping our bodies in a certain way can retrain them to move in ways that are more natural, easier, or safer.
- Training/Prevention: With the popularity of taping on the rise, many athletes have realized the potential of using tape to train.
- All the above benefits remain applicable, only in a way that prevents an injury rather than treating it.
Benefits of rigid taping :
- Injury prevention: Taping is mainly used to provide assistance to the athlete for the return to activity after a minor injury. Proper application of the tape is generally able to provide stability and support to the injured structure, thus helping the athlete to return to the sport before the area has returned to pre-injury status.
- Taping has been familiarized as one of the major procedure of prevention strategies to reduce injury in collision sports by a reduction in the possibility of extrinsic factors like contact with equipment or another participant Overuse injury of the wrists and ankles, especially in gymnastics can also be prevented.
- The severity of many injuries can be reduced to some extent by taping. Taping may prove to be superior to rigid and semi-rigid bracing in injury prevention. Community amateur and most professional athletic events most frequently use prophylactic taping.
- It has also been proposed that taping reduces the occurrence of injury and its intensity in most sporting.
- Conservative management: Appropriate application of tape has been found to reduce the symptoms of medial tibial stress syndrome or shin splint.
- In most patients, non-operative treatments including patella-femoral taping and bracing have been considered effective. Taping has been found to be effective in combating turf-toe injuries.
- Taping has been referred for a condition “sand toe”, a condition similar to turf-toe along with certain other precautions. Non-operative management in certain wrist injuries in cases of alpine skiing includes taping.
- Biomechanical effects of taping: Taping has significant advantages in assisting the patient in maintaining normal biomechanics during participation.
- Ankle taping has been found to decelerate inversion velocity significantly and facilitate a protective neuromuscular response.
- Taping improves force attenuation in the lower extremity during running by shifting peak force to the forefoot and hence acting synergistically in weight bearing.
- Role in Pain Management: Taping plays a significant role in the reduction of pain from physical activity. Irritated inflamed neural tissue can be mechanically uploaded by taping along the nerve tract, thus shortening the inflamed region and reducing the pain.
- Taping has been found to improve resting scapular position. Often before considering surgical alternatives as in the case of patella-femoral pain syndrome, taping is considered to be a better method.
- Taping has been found to enhance proprioception and position sense at the ankle. Taping is a preventive strategy during lower extremity rehabilitation by minimizing foot and ankle injuries, especially during functional return activities.
Basics of Application of kinesio or rigid taping :
- Complete patient assessment to identify the most appropriate application. Kinesio Taping Method-specific assessment tools should be included in this process.
- Follow contraindications and precautions when choosing Kinesio Taping Method
- Apply the tape on dry skin, free of oils and lotion
- Remove body hair if possible by trimming or shaving the area
- Follow the tension guidelines
- Round all the edges of the tape to prevent premature peeling
- Avoid touching the adhesive side of the tape after removing the backing as this may decrease the adhesive strength on the skin
- Once the tape is applied, activate the heat-sensitive adhesive by rubbing the surface of the tape for a few seconds
- Reassess to determine post-application results
- Inform the patient to defer activities that cause perspiration for 30 minutes if possible
- Inform the patient to remove the tape if an itching or burning sensation occurs or if the pain increases
- Teach the patient and caregiver how to remove the tape if needed
- sign and symptoms of skin irritation and skin allergy
- instruction on tape removal
- information on how long to wear the tape
- physiotherapist contact information
How to remove kinesiology and rigid tape :
- When removing the tape, it’s important to ensure you don’t just tear it off as you could damage your skin and cause irritation.
- To begin, ensure you are removing the product in the direction of your hair growth, to lessen any discomfort experienced. Ease it off carefully, folding the edge of the tape back slowly.
- Make sure to check that you’re peeling the removed tape back against the still applied tape at an angle, as opposed to just ripping it off.
- With your other hand, pull your skin taut and tug gently but firmly in the opposite direction of the applied tape, to assist in the separation of skin and tape and to ensure minimal discomfort.
- If you have not shaved before applying the tape and the area of the body you have treated has a lot of hair growth, it’s a good idea to press down firmly on the tape as you are peeling it back, in order to reduce pain.
- Alternatively, you can apply an adhesive dissolving agent like baby oil, rubbing it in and leaving for approximately 5 minutes, before attempting to remove the tape slowly.
- This will lessen the stickiness and ensure a smooth removal, with no pain. Always use a product like baby or olive oil to remove Kinesio or rigid tape if you have sensi0ve skin or are prone to irritation.
- When you need to remove Kinesio or rigid tape, take care to pull it gently and at a slight angle, in the direction of any hair growth, pulling your skin taut with your other hand.
- Doing it this way will minimize any discomfort or pain and will ensure your skin is not lined as the tape is removed. You can encourage easier removal by stretching the skin behind the tape with a fingertip.
- When you need to remove Kinesio or rigid tape, take care to pull it gently and at a slight angle, in the direction of any hair growth, pulling your skin taut with your other hand.
- Doing it this way will minimize any discomfort or pain and will ensure your skin is not lined as the tape is removed. You can encourage easier removal by stretching the skin behind the tape with a fingertip.
- If you have sensitive skin or want an even gentler removal, cover the tape with a dissolving agent like olive oil or baby oil, leave for a few minutes, then ease the product off carefully.