How to treat Disc herniation?
The treatment of disc herniation typically involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, more invasive interventions. Conservative treatment options include rest, pain medication, physical therapy, and exercises to strengthen the core muscles. If conservative measures are ineffective, other treatments such as epidural steroid injections or surgical intervention may be considered. However, the specific treatment approach depends on the severity of the herniation, the location of the affected disc, and individual patient factors.
Here in this article, we discuss What you should take precautions for and which kind of Treatment is the best option and also discuss a Back extension exercise that helps to strengthen your lower back muscles and also related Backcare and Neck care.
You should also consult your Healthcare Doctor and Physical Therapist for proper recovery.
Table of Contents
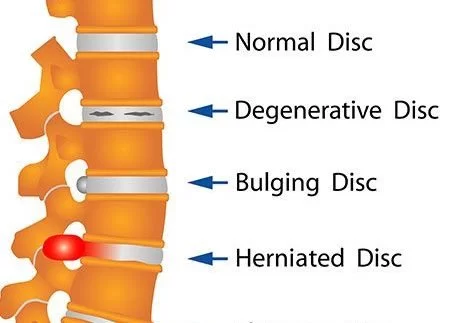
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disk, also known as a slipped disk or a ruptured disk, refers to a condition where the soft inner material of a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the outer layer of the disc. The spinal discs are rubbery cushions that sit between the vertebrae (bones) of the spine, acting as shock absorbers and providing flexibility.
It occurs in any part of the spine and is the most common in the lower lumbar & cervical area. The most common cause of a herniated disk is age-related degeneration, where the discs lose moisture and become less flexible over time. Other factors that can contribute to a herniated disk include injury, trauma, lifting heavy objects with improper technique, or repetitive strain on the spine.
When a disk herniates, the soft gel-like material inside the disc (called the nucleus pulposus) pushes out through the weakened or damaged outer layer (annulus fibrosus). This protrusion can put pressure on nearby spinal nerves, causing pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the area of the body served by those nerves. The symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation.
Causes of Disc herniation
The following are the most common causes of Disc herniation
- Aging
- Excessive weight
- Repetitive motions
- Strain from lifting or twisting.
- Wear and tear called disk generation
- Less flexible
- Injury
- Long-standing trauma
- Stress fractures
- Sudden heavy strain and or increased pressure.
- Congenital abnormalities
Symptoms of Disc herniation
If you have Disc Herniation you may have the following symptoms
- Low backache
- Radiculopathy
- Nerve root compression
- Muscular weakness
- Muscle Spasms
- Numbness( foot, hand, stiff neck)
- Tingling
- Burning
- Sciatic nerve pain
- Slow reflexes
- Poor posture
- Dull ache pain
- Balance issues
- Loss of bowel and bladder control
- Difficulty getting up to the seated position
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
- Loss of coordination
- Trouble balancing in Rare conditions
Diagnosis :
-Most commonly used imaging is MRI.
–X-ray: It is a radiation procedure that can show and structure of vertebrae and joints. and the x-ray is spine to search for other causes such as tumors, infection, fractures, etc.
CT scan: This image is created after a computer reads to X-ray and the shape and size of the spinal canal, etc.
MRI – Magnetic resonance imaging: this is a diagnostic test for 3D images of body structure using a powerful magnet and showing the spinal cord and nerve roots and areas of enlargement, degeneration, and tumors.
Electromyogram and nerve conduction studies: The electrical impulse along nerve roots, peripheral nerves, muscular tissue, etc. is measured by this test.
How to Treat Disc Herniation?
In disc herniation, mostly conservative Medical treatment and Physiotherapy treatment are the preferred choices of treatment.
- Rest and activity modification: Initially, you may need to rest and avoid activities that worsen your symptoms. However, prolonged bed rest is generally not recommended, as it can weaken the muscles and prolong recovery.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications or muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can guide you through exercises and stretches that target the affected area. These exercises can help strengthen the supporting muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate symptoms.
- Heat and cold therapy: Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected area in the early stages can help reduce pain and inflammation. After a few days, heat therapy, such as warm showers or heating pads, may help relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Epidural steroid injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
- Lumbar Traction / Cervical Traction: Axial Traction helps the spine to relieve pressure on the affected disc. Intermittent Manual Traction and Mechanical devices are used to relieve pressure on the affected area. Traction should only be performed under the guidance of a trained professional.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments haven’t provided relief or if there is significant nerve compression, surgery may be considered. Surgical options include discectomy (removal of the herniated portion of the disc) or spinal fusion (joining vertebrae together).
Medical Treatment :
Complete bed rest is the best treatment option for disc herniation for the First 3 weeks (21 days) with the use of Hot Pack and Cold packs are the Best Home remedies for Disc Herniation.
Symptomatic pain relieving Medicine such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) – Mostly Aceclofenac with a combination of Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, muscle relaxants are prescribed by your Doctors. (Never Take Medicine without Prescription)
If Symptoms are not controlled or relieved then Injections of steroids are given by your Doctors, and you will also be referred to Physiotherapy Treatment and exercise.
Physiotherapy Treatment of Disc herniation :
Physiotherapist Treatment options are Pain relieving Modalities such as Short-wave Diathermy(SWD), Interferential Therapy(IFT), and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) with Pain-free Back extension exercise.
Back extension exercises, and cervical/lumbar traction help to relieve pain, and isometric abdominal and lower extremity exercises.
walking within the limits of comfort is also encouraged. Sitting and riding a bike/car is discouraged.
The following are the Best Physical therapy Treatment options are:
1. Bed rest:
-Semifocular position in this position, both the hip and knee of the patient are flexed. this position is very comfortable and relieves
stress on the back.
-Lying on your back with pillows beneath the knees also helps in relieving the pain.
-Side-lying with hip and knee flexed was also found to be effective
2. Cryotherapy:
-During the acute phase are most commonly used to it. it helps to reduce pain, and swelling. it also reduces
the local metabolic activity and delays the nerve condition.
-Cold pack are used during the first 24-48 hours and is found to be very effective.
3. Thermotherapy;
-Hydrocollator packs- used in two towels and placed on the patient’s back for 15-20 minutes.
-Deep heat: There are two common modes of deep heat therapy ultrasound and the SWD.
-TENS and IFT are effective in relieving both acute and chronic pains.
4-Used to intermittent Cervical/Lumbar traction
-Used to mechanical devices, weight is applied and released for short periods of time.it is very effective as produces a massaging
effect over the spine and provides relaxation.
5. Used to the lumbar-sacral belt.
6 Massage Helps fully stimulate the tissues and thus relax the contracted muscles.
7 Back Extension Exercise
Benefits of Exercise of disk herniated:
- It reduces pain.
- To strengthen the weak muscles.To improve posture.
- To improve spinal mobility.
- To stabilize the hypermobile segments.
- To stretch the tight muscles, ligaments, and capsules.
- Helps to relieve the mechanical stress on spinal structures.
Back extension exercises can be beneficial for some individuals with a herniated disc, as they can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine and promote proper alignment. However, it’s important to note that not all back extension exercises are suitable for everyone with a herniated disc, as the appropriateness of these exercises can vary depending on the severity and location of the herniation, as well as individual factors. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist who can assess your condition and provide specific recommendations tailored to your needs.
Prone Press-Up Exercise:

Lie face-down on a mat or a comfortable surface, with your legs extended and your hands positioned under your shoulders.
Keeping your pelvis in contact with the floor, slowly push up with your hands, lifting your upper body off the ground.
Arch your back gently, but do not overextend or push into pain.
Hold the position for 5-10 seconds, then slowly lower your back down to the first position.
Repeat the exercise for several repetitions, gradually increasing the range of motion and the number of repetitions as tolerated.
Remember to start with simple movements and progress slowly. If you experience pain or discomfort during the exercise, stop immediately and consult with a healthcare professional for further guidance.
Hip extension exercises
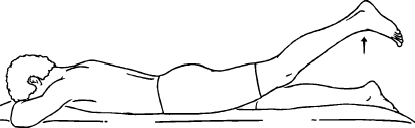
Hip extension exercises in a prone lying position can help strengthen the muscles in your buttocks and lower back, including the glutes and hamstrings.
Lie face down on a mat or a comfortable surface, with your legs extended and your arms resting by your sides.
Contracts your core muscles.
Begin by squeezing your buttocks and lifting one leg off the ground. Keep your leg straight and maintain a slight bend in the knee.
Lift your leg as high as you comfortably can, while maintaining control and without overarching your lower back.
Hold the top position for a few seconds, then lower your leg back down slowly.
Repeat the exercise with the opposite leg.
Perform several repetitions for each leg, gradually increasing the number of repetitions as you get stronger.
It’s important to focus on proper form and control throughout the exercise. Avoid any exercise that causes pain.
Superman Exercise:
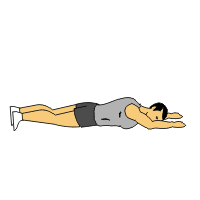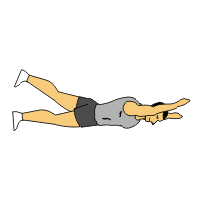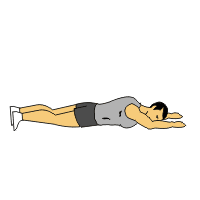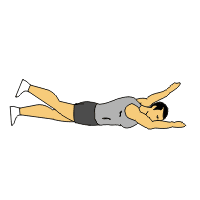
Lie face down on a soft mat while keeping your arms extended overhead and your legs straight.
Simultaneously lift your arms, chest, and legs off the ground, keeping your neck in a neutral position.
Hold the lifted position for a few seconds, then lower back down to the starting position.
Repeat for several repetitions, gradually increasing the duration of the hold and the number of repetitions.
Pelvic Tilt Exercise

The pelvic tilt exercise is a simple yet effective exercise that targets the muscles of the core and helps promote stability in the pelvis and lower back. Here’s how to perform a pelvic tilt exercise:
Lie on your back on a mat or a comfortable surface with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor while Keeping your arms by your sides.
Take a deep breath in.
As you exhale, engage your abdominal muscles and gently press your lower back into the floor or mat. Imagine flattening your spine against the surface.
Hold the contraction for a few seconds while maintaining a relaxed upper body and breathing naturally.
Gradually release the position and return to the starting position.
Repeat the exercise for several repetitions, gradually increasing the duration of the contraction and the number of repetitions as you get more comfortable with the movement.
When performing the pelvic tilt exercise, it’s important to avoid excessive arching or straining the lower back. Focus on engaging the deep abdominal muscles, such as the transverse abdominis, rather than using the larger superficial muscles like the rectus abdominis. Also, try to maintain a relaxed upper body and breathe normally throughout the exercise.
The pelvic tilt exercise can be incorporated into a warm-up routine, as part of a core strengthening program, or used for gentle movement and relief of lower back discomfort.
How to Prevent Disc Herniation?
While it’s not always possible to completely prevent disc herniation, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk and maintain a healthy spine. Here are some tips for preventing disc herniation:
- Practice good posture: Habit your Body for proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking. Avoid slouching or hunching forward, as this can put a strain on the discs in your spine. Keep your shoulders back, chest lifted, and spine aligned in a neutral position.
- Lift properly: Use proper lifting techniques to avoid straining your back. flex your knees while keeping your back straight, and lift with use your legs rather than your back. Avoid twisting movement while lifting and carrying heavy objects.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your core muscles and support your spine. Focus on exercises that target the muscles in your abdomen, back and pelvis. Strengthening your core can help stabilize and protect the discs in your spine.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on your spine and increase the risk of disc herniation. Keep a normal weight through a balanced diet and exercise to reduce the load on your spine.
- Use proper ergonomics: Ensure that your workstation and other environments where you spend significant time are ergonomically designed. Maintain proper alignment of your body while sitting, use supportive chairs with lumbar support, position your computer monitor at eye level, and take regular breaks to stretch and move around.
- Avoid repetitive movements and excessive strain: Be mindful of repetitive movements or activities that put excessive strain on your spine. If your job or hobbies involve repetitive movements or heavy lifting, take regular breaks and use proper body mechanics to minimize the risk of injury.
- Warm-up before physical activity: Before engaging in physical activities or exercise, warm up your muscles with gentle stretching and light aerobic activity. Warming up helps prepare your muscles and joints for movement, reducing the risk of injury.
- Quit smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow and oxygen supply to the spinal discs, which can weaken them and make them more susceptible to injury. Quitting smoking can help improve the health of your discs and reduce the risk of disc herniation.
- Practice proper body mechanics in daily activities: Pay attention to your body mechanics during everyday activities like bending, lifting, and carrying. Use your legs and avoid putting excessive strain on your back. Be mindful of your movements and make adjustments to reduce stress on your spine.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and increase the risk of back pain and disc herniation. Practice stress management techniques such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and seeking support from friends, family, or professionals.
It’s important to remember that while these tips can help reduce the risk of disc herniation, they do not guarantee complete prevention. If you experience persistent or severe back pain, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Summary
Disc herniation is a condition where the soft gel-like material inside a spinal disc protrudes through a weakened area, causing pain and other symptoms. While complete prevention may not be possible, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of disc herniation:
- Habit your Body for proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking and body mechanics during daily activities.
- Lift heavy objects using proper techniques, using your legs and not your back.
- Engage in regular exercise, particularly activities that strengthen the core muscles.
- Maintain a normal weight to relieve stress on the spine.
- Use ergonomic principles in your workstation and other environments to promote proper alignment.
- Avoid repetitive movements or excessive strain on the spine.
- Warm up before physical activities to prepare your muscles and joints.
- Quit smoking to improve the health of your spinal discs.
- Manage stress, as chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and back pain.
Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, personalized advice, and appropriate treatment if you experience persistent or severe back pain or suspect a disc herniation.



2 Comments