How to cure Muscle strain? – Treatment, Exercise
Table of Contents
What is a muscle strain?
- Muscle strain is the injury of a muscle or a tendon. a minor injury may occur due to overstretching of a muscle or tendon and severe injury may include partial or complete tear. they are one of the most common injuries among athletes.
- During sports activity or while performing tasks Muscle damage occur in the form of tearing of the muscle fibers and the tendons attached to the muscle. The tearing of the muscle can also damage blood vessels, causing local bleeding, or bruising, and pain caused by inflammation of the nerve endings in the area.
Factors that can put patients in risk:
- Older age, less flexibility, fatigue, previous muscle injury, and lack of strength in the muscle. Many athletes undergo muscle injuries when they just start a training program.
- That is why these injuries are more common in training camps in the National Football League than in the regular playing season.
What is difference between strain, sprain and pulled muscle?
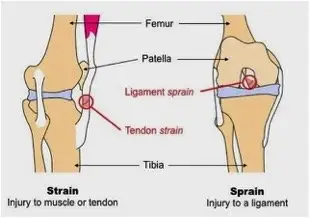
- The difference between a sprain and a strain is that a sprain injures to the muscle that connect with two bones, whereas a strain involves associate injury to a muscle or to the tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. there is no difference between a strained and pulled muscle, solely use the terms interchangeably. People can also treat muscle strains at home and use specific exercises to speed up their recover
- A muscle strain or pulled muscle occurs when your muscle is overstretched or broken. This generally be as a result of fatigue, overuse or indecorous use of a muscle. Strains can be in any muscle, but they ’re most common in your shoulder, neck, hamstring muscle, lower back and hamstring.
- A strain to the muscle or muscle tendon is the exchangeable of a sprain to the ligament. A muscle strain occurs when muscle fibers can not survive the demands placed on them by exercise load and leads to tearing of the fibers. It’s a compression- brought around injury in which muscle fibers tear due to extended mechanical stress. This substantially occurs as a result of a important eccentric compression or over-stretching of the muscle. Thus, it’s typical for non-contact sports with dynamic characteristics similar as sprinting and jumping.
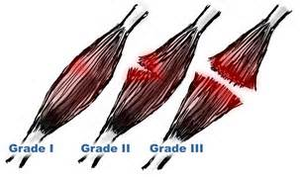
Classification of muscle injury
- Grade 1: partial rupture to individual muscle fibers, that causes minimum loss of strength and movement.
- Grade 2: additional extensive injury with additional muscle fibers involved. Still, the muscle is not highly burst that causes vital loss of strength and stir. these injuries may take two to three months before a whole come to athletics.
- Grade 3: totally damaged of a muscle or connective tissue. These can available with a palpable defect in the muscle or tendon. Still, swelling with in the area may make this tough to understand.These injuries generally need surgery to reattach the broken muscle and connective towel.
Predisposing Factors
Three types of muscle are at possible danger of injury
- Two-joint muscles. Specifically, the movement at one joint increases the tolerant pressure of the muscle associated results in an overstretching injury.
- Muscles contracting eccentrically. Eccentric compression, frequent throughout the swiftness section of activity, could amendment the muscle pressure and induce microfiber overload injury.
- Muscles with a much better proportion of kind II fibers. These areas unit fast- twitch muscles that develop high- speed compression. this suggests the muscle is also susceptible to injury.Most of the muscle exertion in handling and sprinting is eccentric, explaining why similar strains most constantly do in sprinters or‘ speed athletes’. The deltoid muscle, rota-tor cuff, hamstrings, striated muscle, quadriceps, hip flexors, hip adductors, and Erector Spine area unit are most ordinarily burned.
Causes of muscle strains
- An acute muscle strain is when your muscle tears quickly and unexpectedly. muscle tears can occur either from injuries or trauma. This can be due to:
- not warming up properly before physical activity
- poor flexibility
- poor conditioning
- overexertion and fatigue
- weakness
acute muscle strain:
slip your body, jump, run, throw something, lift something heavy, lift something while in you’re in an awkward position.
chronic muscle strain :
sports like rowing, tennis, golf, or baseball, poor posture, holding your back or neck in an awkward position for long periods of time, such as when you work at a desk
Overuse :
Repeating the same movement, whether at work or during an activity like playing sports — can lead to overuse syndrome.
do not stretch or warm-up before exercise: Stretching before exercise gradually increases how much stress you put on your muscles.
A lack of flexibility: If you’re not much flexible, your muscles (and the fibers in them) are tighter, which makes them more susceptible to strains.
Signs and symptoms
Muscle strain symptoms mostly rely on the open severity of the injury.
- In delicate strain muscle could feel slightly stiff, however still versatile enough to be used.
- Sudden onset of pain
- Pain or tenderness
- Redness or bruising
- Limited rang of motion
- Muscle spasms
- Swelling
- Muscle weakness
- Stiffness
- a “knotted-up” feeling
Diagnosing a muscle strain:
- As a part of the opinion, a doctor will commonly designate the injury as a grade 1, 2, or 3 strain Still, they will perform a physical examination and ask a person about their symptom history.
- If a doctor suspects a muscle strain. They may also order imaging studies, a suchlike X-rays, to make sure that the bone has not broken.
Treatment:
FOR immediate
- Nonsurgical, Conservative treatment Most muscle strains do not require surgery if the muscle is totally damage doctors suggest surgery If there is a partial tear then the athlete can return when they are painless and have normal strength and motion. This usually occurs following anywhere from a few weeks to a few months of significant treatment and therapy. When the muscle is totally damage, the athlete may benefit from surgical repair.e self-care of a muscle strain.
- Some doctors suggest avoiding disadvantageous pain medicines that can extend your risk of bleeding — such as over-the-counter(OTC)medicine (naproxen sodium (Aleve) aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), — during the first 48 hours after a muscle strain. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)and others can be helpful for pain relief during this time period. A physiotherapist can help you to improve the stability and strength of the injured joint or limb. Your doctor may suggest that you stabilize the area with a brace or splint. For some injuries, some muscle sprint surgery may be called.
the R.I.C.E approach

- Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling, or discomfort. don’t avoid all physical activity.
- Ice. though you are seeking medical facilities, ice the world right away. Use an associate degree ice pack or slush tub of ice and water for fifteen to twenty minutes every time occasion|anytime} and repeat every 2 to 3 hours. In contrast, you are awake for the primary few days once the injury.
- Compression. to assist stop swelling, compress the world with an associate degree bandage till the swelling stops. do not wrap it too tightly otherwise, you might hinder circulation. Begin wrapping at the top farthest from your heart. Loosen the wrap if the pain increases, space|the world|the realm} becomes numb or swelling is going on below the wrapped area.
- Elevation. Elevate the burned space on top of your heart’s extent, particularly at midnight, that permits gravity to assist scale back swelling.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
goals of Physiotherapy treatment are:
- Relieve pain
- Reduce swelling
- Improve full rang of motion,
- Increases muscle strengths.
following is rehab program for the patients with muscle strain
- Electrotherapy treatment that helps to relive pain and other related symptoms
- Exerciser therapy helps to overall rehabilitation
Electrotherapy program
first few days give electric modality give to relive pain and swelling
- Ultrasound: it has been used is in relation to tissue healing. increases blood circulation and mobility, to reduce swelling.
- Cry o-therapy– Inflammation and swelling can be decreased by applying cry o-therapy in form of ice packs, and cold water baths to the affected area. Continuous application of cold several times a day for 15-30 minutes at a time is recommended.
- TENS-Trans-cutaneous electrical nerve stimulation may be able to heal reduce pain and muscle spasms.
Rehab program:
- phase one– the first week after injury
- rest from painful exercise
- ice use, 3 times par day
- phase two-the alternate and third week after injury
- ice appliance 15-20 min, after exercise
- start active rang of motion exercises
- no stretching exercises
- phase three-3 to 4 weeks after injury
- gentle strengthening exercises
- gental pain free stretching
- phase four– strengthening exercises
- stretching exercises
- progressive resistance exercises
Other treatment:
surgical treatment
most of muscle tear do not require to surgery .A severe tear that requires surgical repair can take months or longer to heal.
How to prevent Muscle strain?
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for your sports, fitness, or work activity, as a part of an overall physical conditioning program, can help to minimize your risk of muscle strains.
- Try to be in a shape to play your sport; do not play your sport to get in shape. If you have a physically demanding occupation, regular conditioning can help to prevent injuries.
- Follow a healthy diet and an exercise program to maintain a healthy weight. The extra weight can put more stress on the muscles, making muscle strains more likely to do.
- Walk at a moderate pace for 3 to 5 minutes before doing any sports or an other physical exercise. Going this will warm up the muscles and prepare them for an increase in the intensity of the exercise.