FRICTION
Table of Contents
DEFINATION :
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other.
Friction is the force that opposes motion between any surfaces that are in contact. There are four types of friction: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction. Static, sliding and rolling friction occur between solid surfaces. Fluid friction occurs in liquids and gases.
TYPE OF FRICTION
DRY FRICTION: this is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into static friction (“stiction”) between non-moving surfaces, and kinetic friction between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features.
FLUID FRICTION: describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other.
LUBRICATED FRICTION: this is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces.
SKIN FRICTION: is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body.
INTERNAL FRICTION: is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a solid material while it undergoes deformation.
Static Friction :

Static friction acts on objects when they are resting on a surface. For example, if you are hiking in the woods, there is static friction between your shoes and the trail each time you put down your foot. Without this static friction, your feet would slip out from under you, making it difficult to walk. In fact, that’s exactly what happens if you try to walk on ice. That’s because ice is very slippery and offers very little friction.
Sliding Friction :
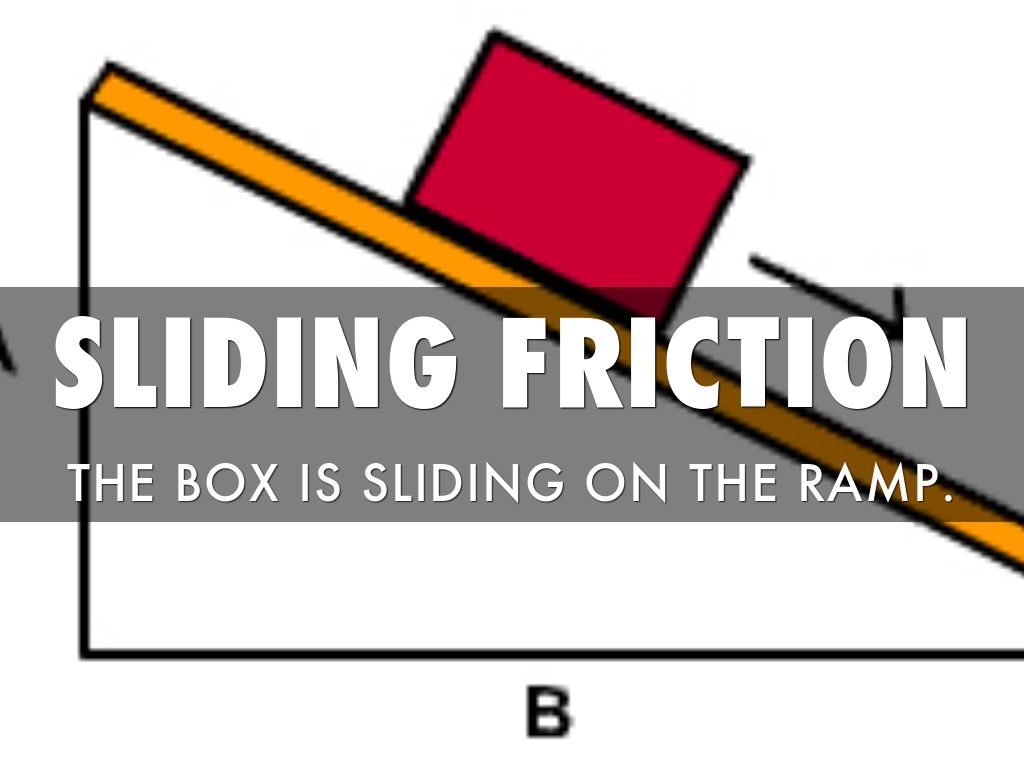
Sliding friction is friction that acts on objects when they are sliding over a surface. Sliding friction is weaker than static friction. That’s why it’s easier to slide a piece of furniture over the floor after you start it moving than it is to get it moving in the first place. Sliding friction can be useful. For example, you use sliding friction when you write with a pencil. The pencil “lead” slides easily over the paper, but there’s just enough friction between the pencil and paper to leave a mark.
Rolling Friction :
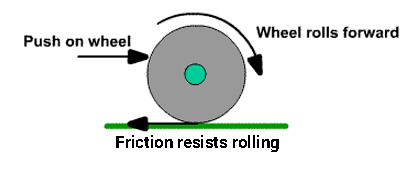
Rolling friction is friction that acts on objects when they are rolling over a surface. Rolling friction is much weaker than sliding friction or static friction. This explains why most forms of ground transportation use wheels, including bicycles, cars, 4-wheelers, roller skates, scooters, and skateboards. Ball bearings are another use of rolling friction.
Fluid Friction :
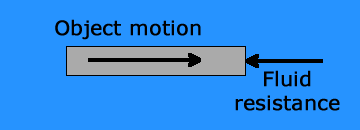
Fluid friction is friction that acts on objects that are moving through a fluid. A fluid is a substance that can flow and take the shape of its container. Fluids include liquids and gases. If you’ve ever tried to push your open hand through the water in a tub or pool, then you’ve experienced fluid friction. You can feel the resistance of the water against your hand.
What are the characteristics of friction?
It is also characterised as the opposition to the motion of one body making contact with the surface of another body. To sum it up, the two main characteristics of friction are: Wear and tear caused at interface of two surfaces. The heat is produced at the point of contact between the two surfaces.
ADVANTAGES OF FRICTION
Friction plays a vital role in our daily life. Without friction we are handicapped.
- It is becomes difficult to walk on a slippery road due to low friction. When we move on ice, it becomes difficult to walk due to low friction of ice.
- We can not fix nail in the wood or wall if there is no friction. It is friction that holds the nail.
- A horse can not pull a cart unless friction furnishes him a secure Foothold.


One Comment