Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle of Hand
Table of Contents
Description
Flexor digiti minimi brevis is a short intrinsic hand muscle. It corresponds to the group of muscles classified as the hypothenar muscles, together with the abductor and opponens digiti minimi.
The hypothenar prominence is an extension that they developed over the tiny finger’s base. The flexor digiti minimi brevis goes from the flexor retinaculum and hook of the hamate bone to the base of the small finger. , a proximal phalanx of a finger. This muscle’s primary function is to flex the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
Origin of Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle
The flexor retinaculum sometimes called the transverse carpal ligament, and the hamate hook is the origins of the muscle. This muscle links the abductor’s lateral digiti minimi.
Insertion
- The muscle originates in the hook of the hamate bone, located near the bone to the wrist.
- From there, the muscle runs across the palm of the hand and connects the little finger’s proximal phalanx, which is the bone nearest to the palm, at its origin.
- In other words, the Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle originates at the base of the little finger’s proximal phalanx.
Relations
- The flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle forms the hypothenar eminence jointly with the abductor digiti minimi and opponens digiti minimi muscles.
- It is situated on the ulnar side of the palm.
- The muscle is superior and medial, and it is located between the adductor digiti minimi and the opponens digiti minimi muscles.
Innervation
Nerve Supply to Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle is a deep branch of the ulnar nerve that has C8 and T1 root values.
Blood supply
The ulnar artery’s deep palmar branch provides blood to the flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle.
Function of Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle
- The primary function of the flexor digiti minimi brevis is to flex the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
- Additionally, this muscle plays a role in the lateral rotation and opposition of the little finger innervated by the ulnar nerve’s deep branch (root).
Clinical relevance
- Cyclists, for example, may harm the ulnar nerve as it passes via the hamate’s hook and the pisiform bone, putting direct pressure on the Guyon Canal.
- Atrophy, numbness, tingling, and discomfort in the hypothenar eminence as well as the fourth and fifth digits may result from ulnar nerve damage.
- This condition impacts the ulnar nerve, which is similar to “carpal tunnel syndrome.
- “If collateral blood supply is insufficient and the ulnar artery becomes weaker, the hypothenar eminence could have been injured.
- This is sometimes referred to as “hypothenar hammer syndrome.”
- Individuals who use equipment that demand precise grasping and repetitive smashing are more inclined to develop this condition.
- The hypothenar eminence’s vascular blood supply will sense a rebound impact as an outcome of the strong grip and pounding of tools.
Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle stretching
Finger flexion MCP
Flex the entire finger joint with the other hand by putting the thumb and finger above the injured finger’s bottom joint.
Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle strengthening exercise
Isometric finger flexion MCP
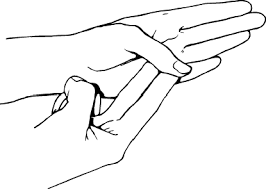
- Put one finger from the other hand above the involved finger’s bottom joint and try to maintain the injured finger straight while giving downward pressure with the other finger.
FAQ
Flexor digiti minimi are injuries caused by repetitive activities such as typing on a computer or playing the piano for extended periods of time. This muscle strain usually shows up as pain in the sensitive pad of the hand near the little finger.
The flexor digitorum brevis is in charge of the toe flexion at the metatarsophalangeal joints of the lateral four digits. It also helps the longitudinal arch of the foot during propelling the body forward during gait.
Finger flexion MCP
Put the thumb and finger above the bottom joint of the injured finger and with the other hand slowly and normally flex the whole finger joint.
Functions. Flexion of the fifth metatarsophalangeal joint is triggered by the flexor digiti minimi brevis. By doing so, the muscle supplies structural support for the lateral longitudinal arch of the foot, which is essential for weight-bearing during long durations of standing.
The abductor digiti minimi’s primary function is to abduct and flex the fifth finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint, therefore pushing it away from the fourth finger. Because of its relationship to the extensor expansion, this muscle additionally plays a role in the flexion of the fifth finger at the interphalangeal joint.

2 Comments