Costello syndrome
Table of Contents
What is Costello syndrome?
- Costello syndrome is a very infrequent genetic condition.
- It occurs when there is a mutation in a gene called the HRAS gene.
- This occurs in a child’s DNA before birth.
- Costello syndrome causes problems that impact the heart, muscles, bones, skin, brain, and spinal cord.
- costello syndrome is also called Faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome & FCS syndrome.
What are the signs and symptoms of Costello syndrome?
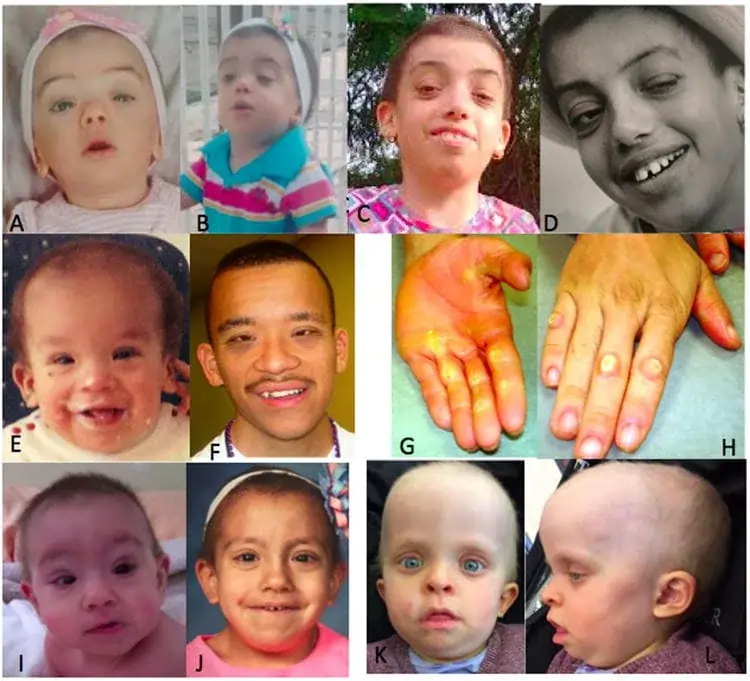
- Parents of a baby with Costello syndrome (SIN-drome) normally notice that the baby is having trouble feeding.
- The baby frequently has several of these features, which are noticed at birth or soon after:
- a large head,
- thick lips,
- wide nostrils,
- slow weight gain,
- loose skin on the neck, fingers, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet,
- very flexible joints,
- wrists angled toward the lateral side.


- As the child grows, other signs usually appear, like as:
- smiling, walking, talking, and doing other things later than other children,
- skin dry lump on the face and around the anus,
- tightly curled/very fine hair,
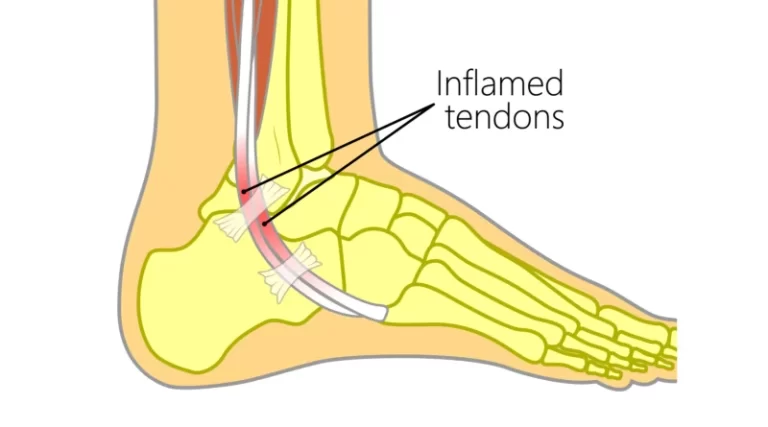
- tight Achilles tendons that cause toe walking,
- heart rhythm problems,
- dry and hard skin on the hands and feet,
- scoliosis,
- kyphosis,
- slow growth,
- short height.
- Other changes caused by Costello syndrome can be seen only on blood tests or imaging tests. These include:
- low levels of growth hormone
- high insulin levels, leading to low blood sugar levels
- thickened heart muscle and other heart problems
- brain and spinal cord changes
- Children who have Costello syndrome also have a higher risk for some types of tumors, which can be benign or malignant.
What is the frequency of Costello syndrome?
- This condition is very frequent, it probably affects 200-300 people worldwide.
- Reported approximate of Costello syndrome common range from 1 in 300,000 to 1 in 1.25 million people.
What are the causes of this syndrome?
- Alteration in the HRAS gene causes Costello syndrome.
- This gene supplies instructions for making a protein called H-Ras, which is part of a pathway that assists in controlling cell growth and division.
- The alteration that causes Costello syndrome leads to the manufacture of an H-Ras protein that is abnormally active.
- The hyperactive protein directs cells to grow and divide constantly, which can lead to the development of benign and malignant tumors.
- It is unclear how alteration in the HRAS gene causes the other features of Costello syndrome, yet many of the signs and symptoms probably result from cell overgrowth and abnormal cell division.
How is Costello syndrome diagnosed?
- To catch out if a child has Costello syndrome, doctors will:
- inquire about the child’s symptoms and medical history
- do an examination
- order genetic testing to look for an alteration in the HRAS gene in the child’s DNA.
- Tell the parents for the child to see specialists, who might order these imaging tests:
- magnetic resonance imaging
- ultrasound scan
- echo-cardiogram.
How is Costello syndrome treated?
- There is no heal for Costello syndrome.
- yet medical care can help nearly every symptom.
- For example:
- A child can get liquid food through a tube in the nose that goes down the throat to the stomach (a nasogastric) or one that goes through the belly wall through the stomach (also known as a G-tube).
- Medicines and surgery can help with heart problems.
- Occupational therapy and physical therapy can help better hand strength & use of the fingers.
- Surgery to lengthen short Achilles tendons can help a child walk, run, and play better.
- Dermatologists can harden skin tags with dry ice or a freezing spray.
- A team of medical specialists safe keeps children with Costello syndrome.
- The team may include:
- a pediatrician: for the routine care
- a cardiologist and cardiothoracic surgeon: for the heart problems
- an orthopedic surgeon: for the treatment of bone, muscle, and tendon problems
- a neurosurgeon: for the treatment of brain and spinal cord problems
- a dermatologist: for skin problems
- a speech therapist: for speech problems
- a dietitian: for help with nutrition
- a social worker: for the help with social services.
- Reaching to the genetic counselor can help families learn what to expect and understand how Costello syndrome can run in families.
- Physiotherapists treat scoliosis, and kyphosis through exercise and also suggest orthosis.
- also treat to toe walking, in this to give Achilles tendon stretching, practice to dorsiflexion and gait training must important and also give orthosis for support.
- Physiotherapists treat muscle pain, inflammation, and walking-related difficulties.