Inflammation: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Inflammation Symptoms, Causes & Diagnosis
Inflammation Symptoms, Causes & Diagnosis
Introduction What to do before the investigation? General Inspection Subjective Red Flags Cervical Myelopathy Signs & Symptoms Cervical Instability Definition Sign and symptoms Vertebral Artery Insufficiency Sign & symptom Inflammatory or even Systemic Disease Sign and symptoms Yellow Flags Investigations Radiological Considerations Observation Posture Palpation Supine position Prone position Movement Tests Functional Movement Combined movements…

What is dizziness? When you are dizzy, you may feel: What is the difference between dizziness and vertigo? It feels such as you or objects around you are: How common is dizziness? What are the Symptoms of dizziness? People who are dizzy may experience various sensations, involving: Often, dizziness is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or…
Introduction Signs and symptoms of Hyperekplexia Frequency Genetics Diagnosis Other Names for This Condition Treatment of Hyperekplexia Physiotherapy treatment How Does Hyperekplexia Progress? Symptoms of hyperekplexia generally enhance in infancy, yet some fairly mild symptoms may persist via the majority. Likely long-term results of the disease contain: History FAQs
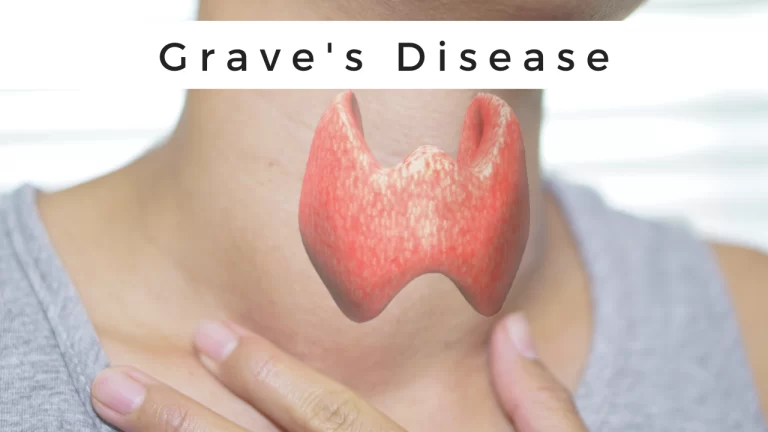
What is Grave’s Disease? Grave’s disease is an immune system disorder(autoimmune disorder). In Grave’s disease, there is an overproduction of thyroid hormones that leads to hyperthyroidism. The thyroid present in the body is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck. Thyroid hormones regulate the way the body uses energy, so they affect…
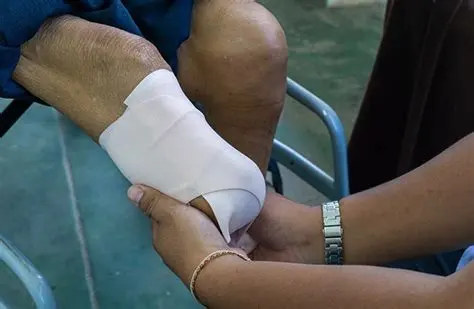
What is phantom limb pain? Phantom limb pain is defined as pain in the limb after an amputation. Some people experience pain in the part of the limb that is no longer present. This type of sensation is phantom limb pain. The pain is real. It is most common in arms and legs, but some…
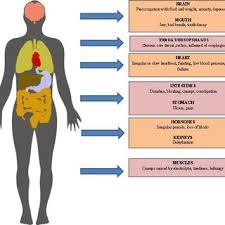
Definition Bulimia nervosa, usually called bulimia, is a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder. individuals with bulimia can secretly binge — eating greater amounts of food with a loss of control over the eating — and then purge, trying to get rid of the extra calories in an unhealthy way. Criteria for Bulimia Nervosa Types of…
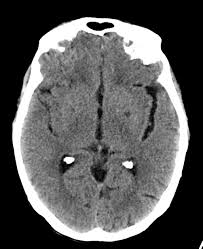
Introduction Cause Epidemiology Pathophysiology What is main Todd’s paralysis disease? Symptoms Evaluation Treatment of Todd’s Paralysis A person with epilepsy may be able to tell when they are about to have a main seizure. This awareness is known as a warning and aura. It may also involve: Differential Diagnosis Non-convulsive status epilepticus: Usually occurs after…
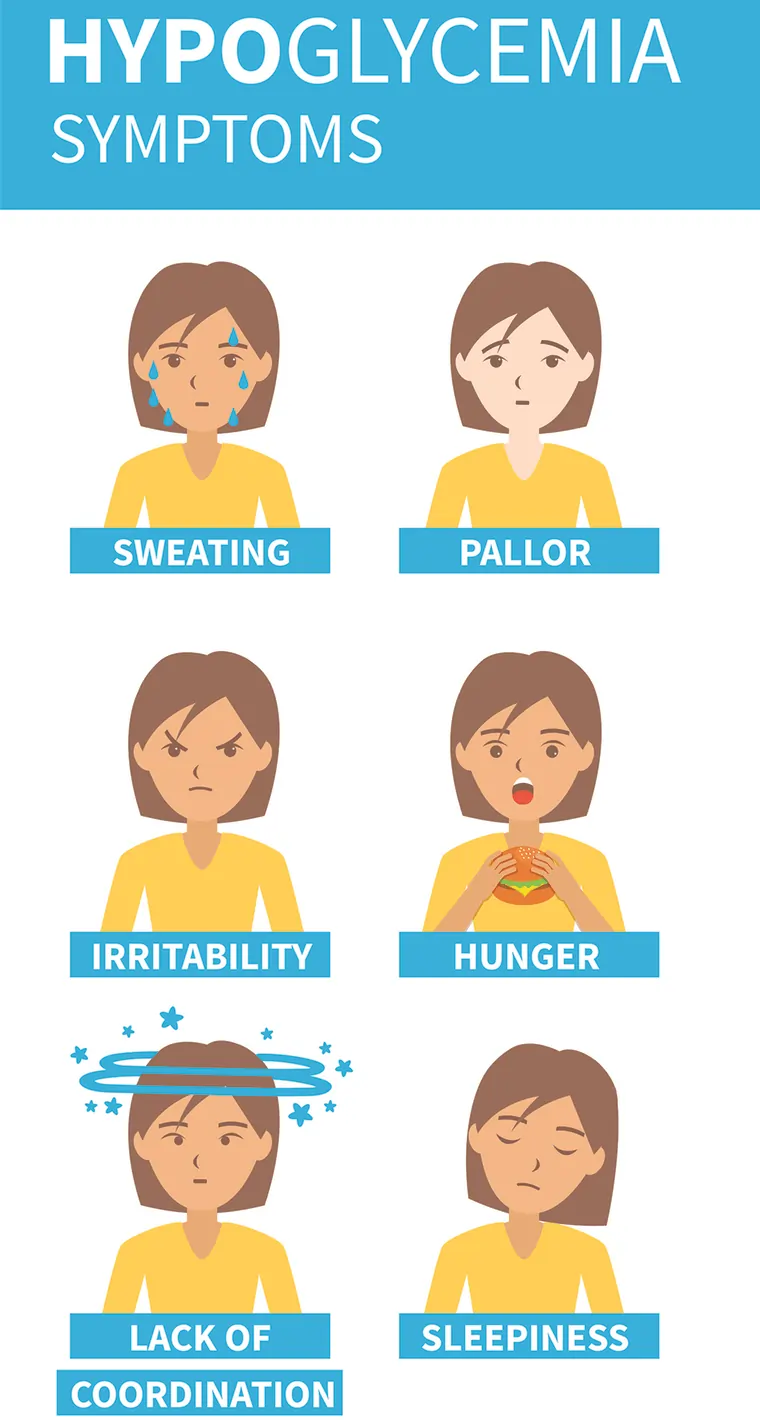
What is hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)? What is blood sugar? How common is hypoglycemia? What are the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia (decrease blood sugar)? The signs involve: Signs of severe hypoglycemia involve: Symptoms may involve: When do hypoglycemia symptoms appear? You may benefit from the following: What are the complications of low blood sugar?…
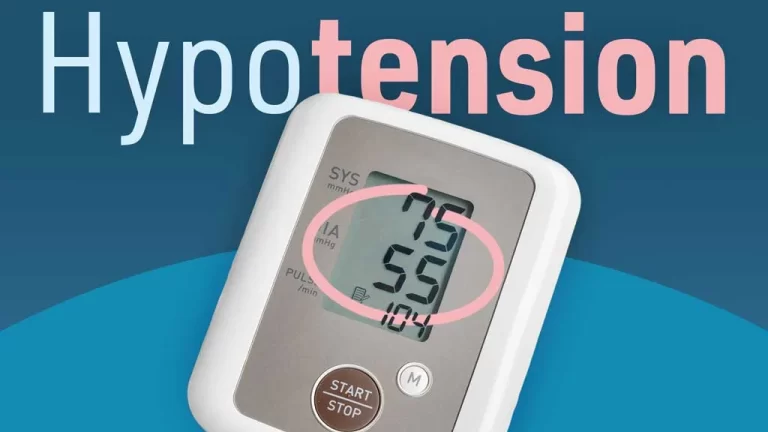
What is low blood pressure? Hypotension has 2 definitions: How does low blood pressure affect my body? Whom does low blood pressure affect? How common is low blood pressure? What are the symptoms of low blood pressure? These involve: What causes low blood pressure? Causes of low blood pressure involve: Is it contagious? How is…